
The length of a string between a kite and a point on the ground is 90 metres. If the string makes an angle $\theta $ with the ground level such that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{15}{8}$, how high is the kite? Assume that there is no slack in the string.
Answer
527k+ views
Hint:Assume that the point on the ground is A and the kite is at point C and B is the point vertically below the kite on the ground. Observe that $\Delta ABC$ is a right-angled triangle, right-angled at B. As $\tan \theta =\dfrac{15}{8}$, assume that $BC=15x,AB=8x$. Use Pythagoras Theorem to calculate the length of all sides of the triangle and thus, the length of side BC.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that the length of string between a kite and a point on the ground is 90m and the string makes an angle $\theta $ with the ground such that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{15}{8}$. We have to find the height of the kite.
Let’s assume that the point on the ground is A and the kite is at point C and B is the point vertically below the kite on the ground. We observe that $\Delta ABC$ is a right-angled triangle, right-angled at B.
As $\tan \theta =\dfrac{15}{8}$assume that $BC=15x,AB=8x$, as shown in the figure.
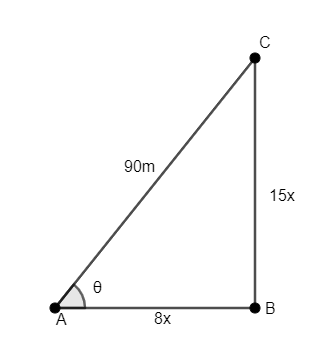
We know that Pythagoras Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the sum of the square of two perpendicular sides is equal to the square of the third side. So, we have $A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$.
Substituting $AB=8x,BC=15x,AC=90$ in the above formula, we have ${{\left( 8x \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 15x \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 90 \right)}^{2}}$.
Simplifying the above equation, we have $64{{x}^{2}}+225{{x}^{2}}=8100\Rightarrow 289{{x}^{2}}=8100$.
Rearranging the terms of the above equation and taking the square root, we have ${{x}^{2}}=\dfrac{8100}{289}\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{\dfrac{8100}{289}}=\dfrac{90}{17}$.
So, the height of the kite is $BC=15\left( \dfrac{90}{17} \right)=79.41m$.
Hence, the height of the kite is 79.41 metres.
Note: We have to use Pythagoras Theorem to calculate the length of the sides of the triangle. One must know that tangent of any angle is the ratio of the length of the perpendicular and the base. We can also find the value of the angle $\theta $ as $\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{15}{8} \right)$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that the length of string between a kite and a point on the ground is 90m and the string makes an angle $\theta $ with the ground such that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{15}{8}$. We have to find the height of the kite.
Let’s assume that the point on the ground is A and the kite is at point C and B is the point vertically below the kite on the ground. We observe that $\Delta ABC$ is a right-angled triangle, right-angled at B.
As $\tan \theta =\dfrac{15}{8}$assume that $BC=15x,AB=8x$, as shown in the figure.

We know that Pythagoras Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the sum of the square of two perpendicular sides is equal to the square of the third side. So, we have $A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$.
Substituting $AB=8x,BC=15x,AC=90$ in the above formula, we have ${{\left( 8x \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 15x \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 90 \right)}^{2}}$.
Simplifying the above equation, we have $64{{x}^{2}}+225{{x}^{2}}=8100\Rightarrow 289{{x}^{2}}=8100$.
Rearranging the terms of the above equation and taking the square root, we have ${{x}^{2}}=\dfrac{8100}{289}\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{\dfrac{8100}{289}}=\dfrac{90}{17}$.
So, the height of the kite is $BC=15\left( \dfrac{90}{17} \right)=79.41m$.
Hence, the height of the kite is 79.41 metres.
Note: We have to use Pythagoras Theorem to calculate the length of the sides of the triangle. One must know that tangent of any angle is the ratio of the length of the perpendicular and the base. We can also find the value of the angle $\theta $ as $\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{15}{8} \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




