
The intermediate between glycolysis and TCA cycle is
(a)Pyruvic acid
(b)Glucose-1,6-diphosphate
(c)Oxaloacetate
(d)Acetyl-CoA
Answer
603.9k+ views
Hint: Aerobic respiration is an enzyme-catalyzed reaction which can be grouped into begins with glycolysis in the cytosol. This intermediate is formed only when the cell has decided to be committed to aerobic respiration.
Complete answer:
After the formation of pyruvate from glucose via glycolysis in cytosol, a cell can take two different cycles depending upon the availability of oxygen. In the presence of oxygen, further oxidation of pyruvate occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Pyruvate is transported from the cytosol to the mitochondrial matrix with the help of a transport protein, where it is oxidized to acetyl-CoA. This conversion of acetyl CoA is catalyzed by a highly organized multienzyme complex called pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
Additional Information:
In the overall reaction, carbon dioxide is removed from the carboxyl group of pyruvate and the two carbons remain reacts with CoA( Coenzyme A) to form acetyl CoA. This reaction is collectively known as oxidative decarboxylation of Acetyl-CoA. Also, the highly exergonic nature of the reaction makes it highly irreversible that is once Acetyl-CoA is formed, the cell is committed to entering the next step in respiration which is Kreb’s cycle or TCA cycle( Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle). It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
In the Krebs cycle, Acetyl-CoA is accepted by ‘oxaloacetate’ a 4-carbon molecule to produce the first product citrate, a 6-Carbon molecule. The net result of the Kreb cycle is that for each acetyl group entering the cycle as acetyl CoA, two molecules of carbon dioxide are released along with energy. All three steps - glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and Krebs cycle, releases energy from the glucose molecule in the form of ATP, NADH, and ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$.
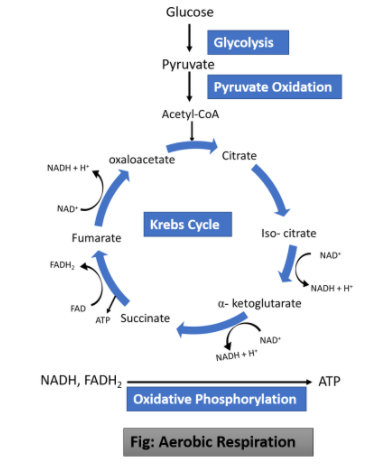
So, the correct answer is ‘Acetyl-CoA’.
Note: The free energy released in the form of NADH and ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ needs to be converted to usable forms of energy i.e ATP, which can be used by the cell. Electrons are transferred from NADH and ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ through a series of electron carriers present on the inner mitochondrial membrane. This is described as oxidative phosphorylation or in common terms electron transport chain(ETC).
Complete answer:
After the formation of pyruvate from glucose via glycolysis in cytosol, a cell can take two different cycles depending upon the availability of oxygen. In the presence of oxygen, further oxidation of pyruvate occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Pyruvate is transported from the cytosol to the mitochondrial matrix with the help of a transport protein, where it is oxidized to acetyl-CoA. This conversion of acetyl CoA is catalyzed by a highly organized multienzyme complex called pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
Additional Information:
In the overall reaction, carbon dioxide is removed from the carboxyl group of pyruvate and the two carbons remain reacts with CoA( Coenzyme A) to form acetyl CoA. This reaction is collectively known as oxidative decarboxylation of Acetyl-CoA. Also, the highly exergonic nature of the reaction makes it highly irreversible that is once Acetyl-CoA is formed, the cell is committed to entering the next step in respiration which is Kreb’s cycle or TCA cycle( Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle). It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
In the Krebs cycle, Acetyl-CoA is accepted by ‘oxaloacetate’ a 4-carbon molecule to produce the first product citrate, a 6-Carbon molecule. The net result of the Kreb cycle is that for each acetyl group entering the cycle as acetyl CoA, two molecules of carbon dioxide are released along with energy. All three steps - glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and Krebs cycle, releases energy from the glucose molecule in the form of ATP, NADH, and ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$.

So, the correct answer is ‘Acetyl-CoA’.
Note: The free energy released in the form of NADH and ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ needs to be converted to usable forms of energy i.e ATP, which can be used by the cell. Electrons are transferred from NADH and ${ FADH }_{ 2 }$ through a series of electron carriers present on the inner mitochondrial membrane. This is described as oxidative phosphorylation or in common terms electron transport chain(ETC).
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




