
The hybridization of Xe in $Xe{{O}_{2}}{{F}_{2}}$ and it’s shape are:
A.$s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$, T shaped
B.$s{{p}^{3}}d$, see saw
C.$s{{p}^{3}}$, tetrahedral
D.$s{{p}^{3}}d$, V shaped
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: The shape of $A{{B}_{5}}$ molecule with zero lone pair is trigonal bipyramidal and with 4 bond pairs and one lone pair is T- shape and with 3 bond pair and 2 lone pairs is T- shape .We need to know about VSEPR theory for more details.
Complete step by step answer:
- VSEPR theory is defined as the electron pairs surrounding the atom present in the centre that must be arranged in space in such a distance so as to minimize the electrostatic repulsion experienced between them.
- The most important rule of the VSEPR theory states that the bond angles about a central atom are those that minimize the overall repulsion which is experienced between the Electron pairs in the valence shell of the atom.
- As the interior angle increases, the repulsion forces decrease sharply. As the value of electronegativity of an atom forming a molecule gets increased, the influence of a bonding electron pair decreases.
- Multiple bonds behave similar to a single electron pair for the sake of VSEPR bond theory.
- Hybridization of an atom can be found out by calculating the summation of lone pairs and sigma bonds.
If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 2, we have sp hybridization
If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 3 , we have $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization
If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 4 , we have $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization
If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 5, we have $s{{p}^{3}}d$ hybridization
If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 6, we have $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization.
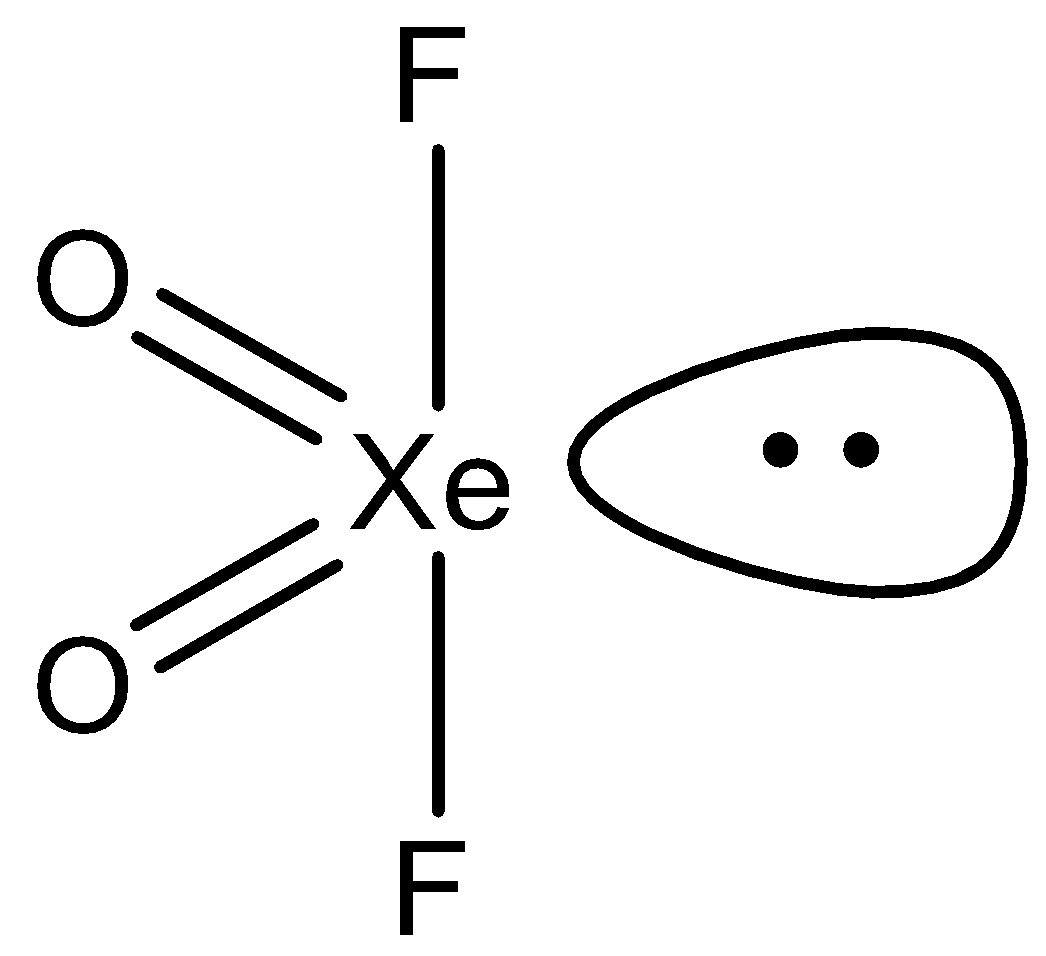
So the given molecule has 4 sigma bonds 1 lone pair that the sum is 5. So its hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}d$ and therefore the shape is see saw.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
As a result of the distortions created different types of shapes can be drawn :
Complete step by step answer:
- VSEPR theory is defined as the electron pairs surrounding the atom present in the centre that must be arranged in space in such a distance so as to minimize the electrostatic repulsion experienced between them.
- The most important rule of the VSEPR theory states that the bond angles about a central atom are those that minimize the overall repulsion which is experienced between the Electron pairs in the valence shell of the atom.
- As the interior angle increases, the repulsion forces decrease sharply. As the value of electronegativity of an atom forming a molecule gets increased, the influence of a bonding electron pair decreases.
- Multiple bonds behave similar to a single electron pair for the sake of VSEPR bond theory.
- Hybridization of an atom can be found out by calculating the summation of lone pairs and sigma bonds.
If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 2, we have sp hybridization
If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 3 , we have $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization
If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 4 , we have $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization
If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 5, we have $s{{p}^{3}}d$ hybridization
If a sum of sigma bonds and lone pairs is 6, we have $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization.

So the given molecule has 4 sigma bonds 1 lone pair that the sum is 5. So its hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}d$ and therefore the shape is see saw.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
As a result of the distortions created different types of shapes can be drawn :
| Bond pair | Lone pair | Shape |
| 5 | 0 | Trigonal bipyramidal |
| 4 | 1 | See saw |
| 3 | 2 | T shape |
| 2 | 3 | Linear. |
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




