
The hybridisation of $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $ with geometry is
A) $s{p^3}{d^2}$ with linear
B) $s{p^3}$ with pyramidal
C) $s{p^3}d$ with see-saw structure
D) $ds{p^2}$ with square pyramidal
Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint: Refer to the main postulates of Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory. This theory helps us to predict the geometry of the covalent molecules. Generally, the least electronegative atom occupies the central position in the structure. The shape of the molecule depends on the number of valence shell electron pairs (bonded or non-bonded) around the central atom.
Complete answer:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory is used to predict the shapes of many molecules and polyatomic ions in which the central atom is a nonmetal or the least electronegative atom. One of the main postulates of VSEPR theory says that the electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible and hence there is minimum repulsion.
Now let us draw the geometry of a given molecule i.e., $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $ using the VSEPR procedure.
1.) Lewis electron structure of the molecule: In a polyatomic molecule, $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $, the central atom would be the I (iodine). I contribute 7 valence electrons, each fluorine atom contributes 7 valence electrons and each oxygen atom contributes 6 valence electrons and the additional one negative charge is equal to one electron. Thus, total valence electrons are: $7 + 2(7) + 2(6) + 1 = 34$ . The Lewis structure is:
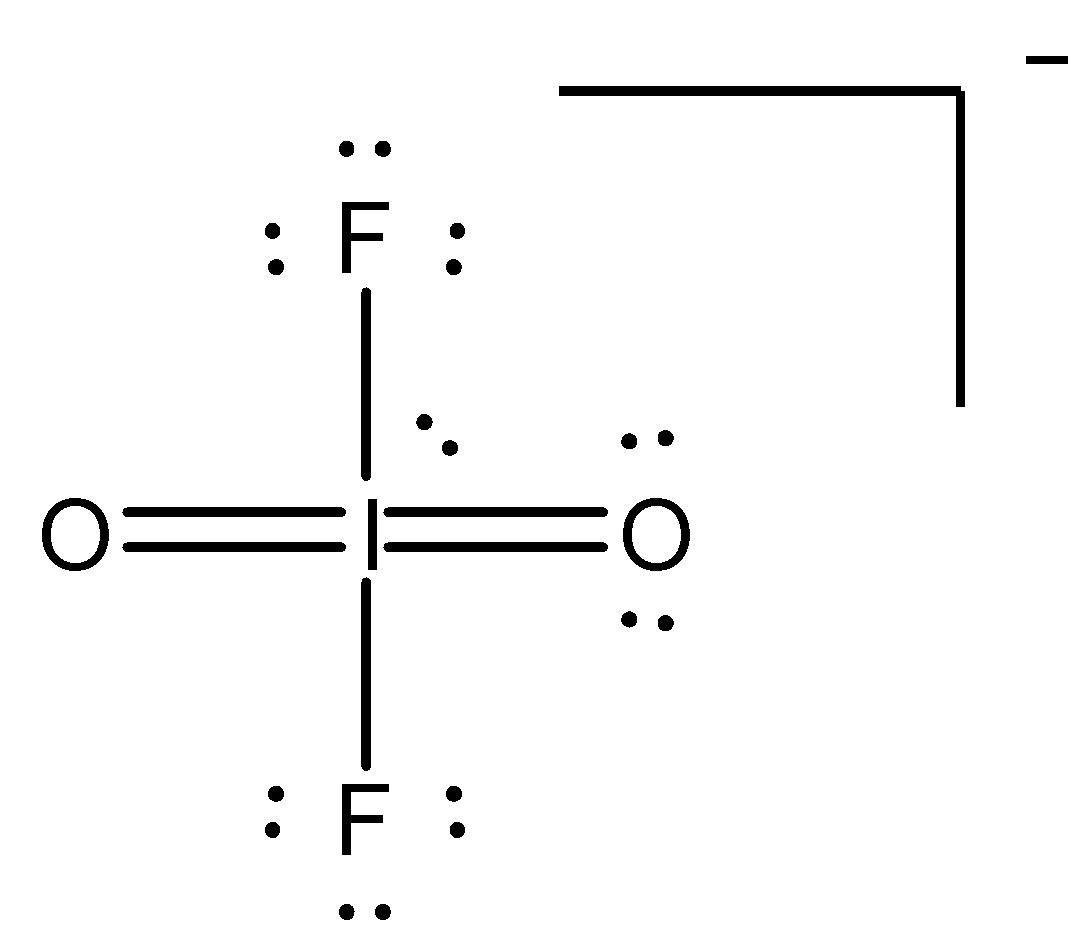
There must be a double bond between each pair of I and O atoms. Each fluorine atom is bonded to iodine atom by a single bond. The remaining valence electrons on oxygen, iodine and fluorine constitute lone pairs (unshared pairs of electrons or non-bonded electron pairs).
2.) Hybridisation of $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $: Outer electronic configuration of I: $4{d^{10}}5{s^2}5{p^5}$. In the structure of $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $¸ five atomic orbitals (i.e., one $s$, three $p$, and one $d$ orbital) are including in hybridisation, hence the hybridisation of $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $ is $s{p^3}d$.
3.) Geometry for $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $: Since, there is one lone pair present on the central atom i.e., I, and there are four bond pairs. Hence, the type of the molecule for the given molecule $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $ is $A{B_4}E$ where A is the central atom having one lone pair (E) and 4 bond pairs (B). The most stable shape for this type of molecule is see-saw.
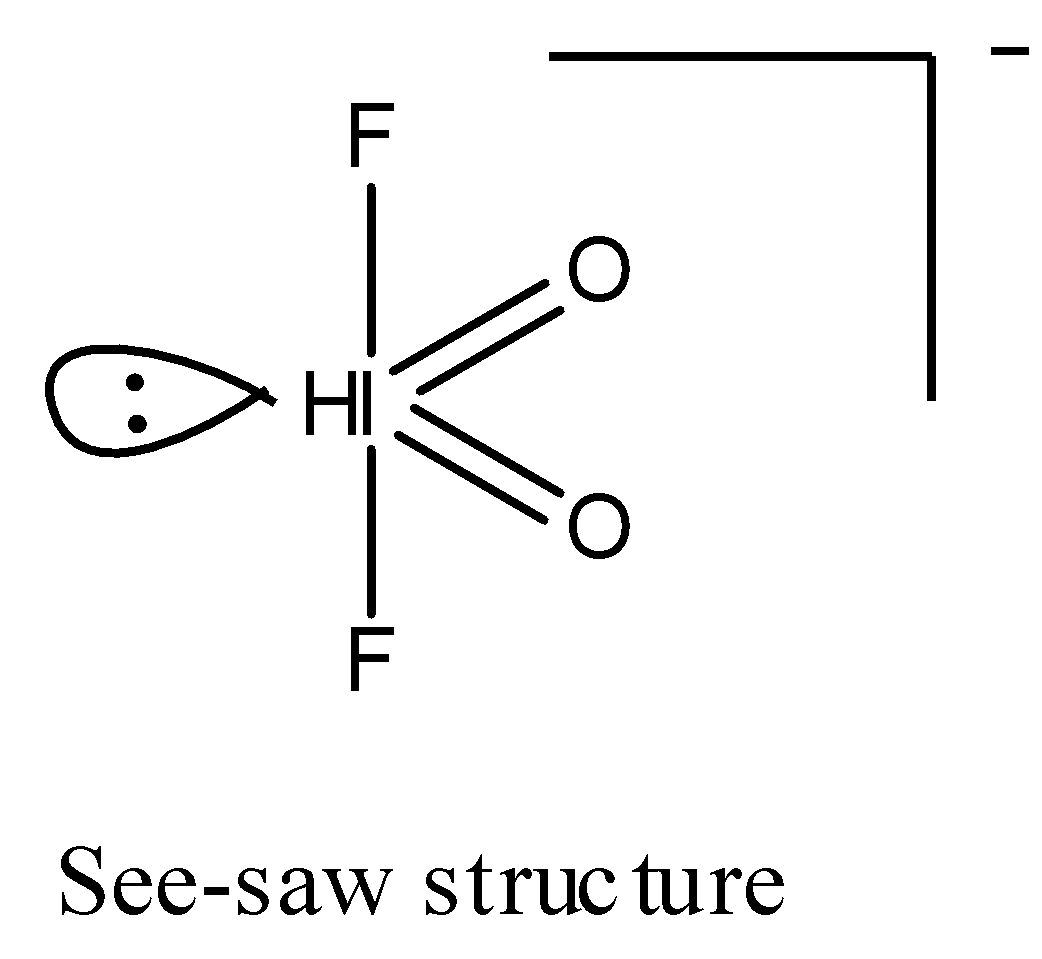
Hence, the hybridisation of $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $ is $s{p^3}d$ with see-saw structure.
Thus, option C is correct.
Note:
In the see-saw structure, lone pair is in an equatorial position and there are only two lone pair –bond pair repulsions. Hence, this conclusion made the see-saw structure most stable for the molecule type $A{B_4}E$.
Complete answer:
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory is used to predict the shapes of many molecules and polyatomic ions in which the central atom is a nonmetal or the least electronegative atom. One of the main postulates of VSEPR theory says that the electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible and hence there is minimum repulsion.
Now let us draw the geometry of a given molecule i.e., $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $ using the VSEPR procedure.
1.) Lewis electron structure of the molecule: In a polyatomic molecule, $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $, the central atom would be the I (iodine). I contribute 7 valence electrons, each fluorine atom contributes 7 valence electrons and each oxygen atom contributes 6 valence electrons and the additional one negative charge is equal to one electron. Thus, total valence electrons are: $7 + 2(7) + 2(6) + 1 = 34$ . The Lewis structure is:

There must be a double bond between each pair of I and O atoms. Each fluorine atom is bonded to iodine atom by a single bond. The remaining valence electrons on oxygen, iodine and fluorine constitute lone pairs (unshared pairs of electrons or non-bonded electron pairs).
2.) Hybridisation of $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $: Outer electronic configuration of I: $4{d^{10}}5{s^2}5{p^5}$. In the structure of $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $¸ five atomic orbitals (i.e., one $s$, three $p$, and one $d$ orbital) are including in hybridisation, hence the hybridisation of $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $ is $s{p^3}d$.
3.) Geometry for $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $: Since, there is one lone pair present on the central atom i.e., I, and there are four bond pairs. Hence, the type of the molecule for the given molecule $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $ is $A{B_4}E$ where A is the central atom having one lone pair (E) and 4 bond pairs (B). The most stable shape for this type of molecule is see-saw.

Hence, the hybridisation of $I{O_2}{F_2}^ - $ is $s{p^3}d$ with see-saw structure.
Thus, option C is correct.
Note:
In the see-saw structure, lone pair is in an equatorial position and there are only two lone pair –bond pair repulsions. Hence, this conclusion made the see-saw structure most stable for the molecule type $A{B_4}E$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




