
The given figure represents one of the steps in the process of transcription in bacteria. Identify the step and label A, B & C marked in the figure.
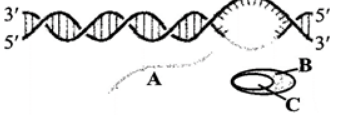
A. Initiation; A - DNA, B - RNA, C - Promoter
B. Termination; A - RNA, B - RNA polymerase, C - Rho factor
C. Elongation; A - RNA, B - RNA polymerase, C - Sigma factor
D. Elongation; A-DNA, B - DNA polymerase, C - RNA

Answer
371.7k+ views
Hint: Transcription refers to the formation of a strand of messenger RNA complementary to DNA. Bacterial transcription undergoes three phases: Initiation, Elongation, Termination. Factors like RNA polymerase enzyme, the genetic code on DNA guide the whole process.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Initiation is done when the sigma factor binds to RNA polymerase enzymes,thus, making a holoenzyme. This further recognizes and attaches to the ‘promoter’ region of DNA. These constitute part of the DNA strand between 10 and 35 nucleotides before the initiation site. This opens up the DNA strand which is now ready to be transcribed.
Elongation starts right after initiation. IN this process, more nucleotides complementary to the DNA strand get converted into RNA. The sigma factor is removed after moving on 10 nucleotides. The RNA polymerase enzyme keeps moving on the template strand of DNA in 3’ to 5’ direction.
This process occurs until a ‘rho factor’ joins with RNA polymerase enzyme and detaches the mRNA and template DNA. Thereby, terminating the process. This process is accelerated by a sequence on the DNA strand which favours stopping of the process. This is called Rho-dependent termination.
The process can also be stopped by another method called Rho-independent termination. RNA polymerase while transcription comes across a region rich in nucleotides: Guanine and Cytidine. This causes the RNA strand to mould in a hairpin shaped structure. This results in termination of the process.
In the figure given, A represents mRNA
B represents RNA polymerase
C represents the rho factor.
Since the RNA strand has been formed and detached, it demonstrates termination of the reaction.
Therefore, the correct option is B: Termination; A - RNA, B - RNA polymerase, C - Rho factor
Note: When DNA is converted into messenger RNA, the nucleotide Thymine is replaced by Uracil.
The mRNA thus formed is complementary to the template strand of DNA. The other strand of DNA is called the coding strand although it does not code for RNA. Thus, it is almost similar to the RNA formed except at places where Thymine is present.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Initiation is done when the sigma factor binds to RNA polymerase enzymes,thus, making a holoenzyme. This further recognizes and attaches to the ‘promoter’ region of DNA. These constitute part of the DNA strand between 10 and 35 nucleotides before the initiation site. This opens up the DNA strand which is now ready to be transcribed.
Elongation starts right after initiation. IN this process, more nucleotides complementary to the DNA strand get converted into RNA. The sigma factor is removed after moving on 10 nucleotides. The RNA polymerase enzyme keeps moving on the template strand of DNA in 3’ to 5’ direction.
This process occurs until a ‘rho factor’ joins with RNA polymerase enzyme and detaches the mRNA and template DNA. Thereby, terminating the process. This process is accelerated by a sequence on the DNA strand which favours stopping of the process. This is called Rho-dependent termination.
The process can also be stopped by another method called Rho-independent termination. RNA polymerase while transcription comes across a region rich in nucleotides: Guanine and Cytidine. This causes the RNA strand to mould in a hairpin shaped structure. This results in termination of the process.
In the figure given, A represents mRNA
B represents RNA polymerase
C represents the rho factor.
Since the RNA strand has been formed and detached, it demonstrates termination of the reaction.
Therefore, the correct option is B: Termination; A - RNA, B - RNA polymerase, C - Rho factor
Note: When DNA is converted into messenger RNA, the nucleotide Thymine is replaced by Uracil.
The mRNA thus formed is complementary to the template strand of DNA. The other strand of DNA is called the coding strand although it does not code for RNA. Thus, it is almost similar to the RNA formed except at places where Thymine is present.
Recently Updated Pages
Choose the incorrect statement regarding the HardyWeinberg class 12 biology NEET_UG

Explain in brief the separation and isolation of DNA class 12 biology NEET_UG

Number of testicular lobules in testes is A 250 B 500 class 12 biology NEET_UG

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




