
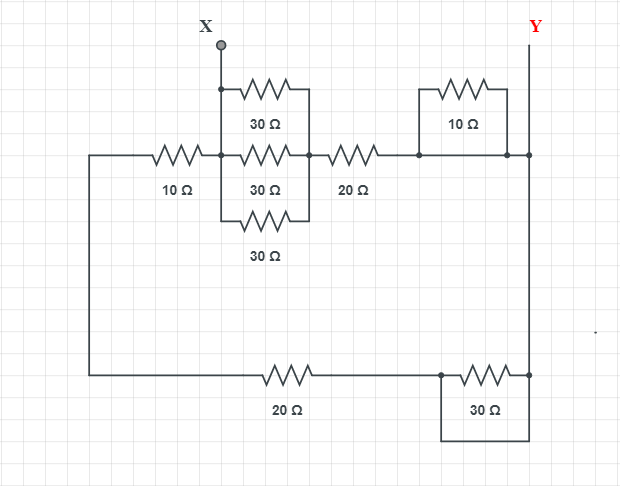
The equivalent resistance between point X and Y:

Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: We have to reduce the circuit to find the equivalent resistance. We must keep in mind that current always travels through the least resistance path. So at the junction of part three and two, current flows through the path with no resistance. Thus only part three and two of the circuit contributes to the equivalent resistance.
Formula used:
${{R}_{eq}}={{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}+.......$
$\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}+..........$
Complete answer:
Part I is short circuited because current flows through the path of smallest resistance. Same happens for part II as well.
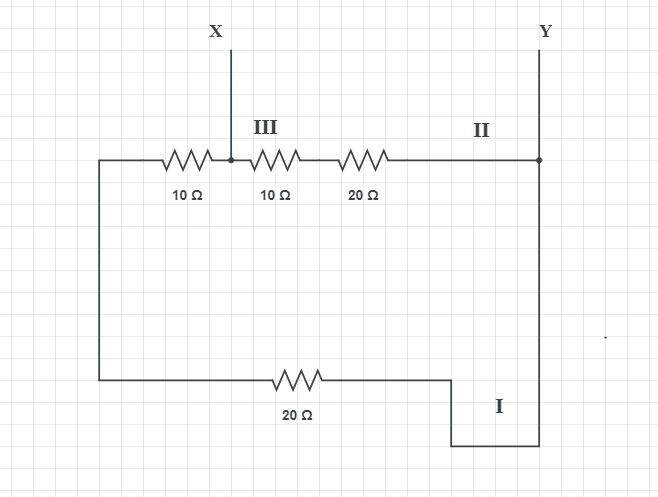
In a parallel type of circuit, different parts of the circuit are connected across different branches. Hence, electron flow occurs in several parts. If in one path a circuit break occurs, electric current still flows in other paths. Household wiring of appliances are based on parallel circuits, so if one light bulb goes down, the other will still flow.
As far as part III is concerned, the resistors are in parallel so
$\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}+..........$
${{R}_{eq}}=\dfrac{(\dfrac{30\times 30}{30+30}\times 30)}{(\dfrac{30\times 30}{30+30}+30)}=10\Omega $
Resistance between X and Y is
R=$\dfrac{30\times 30}{30+30}=15\Omega $
Note:
The possibility of making a mistake in this question is by reducing the entire circuit and considering all the resistors to find the equivalent resistance. The ohm's law used here states that the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the amount of current flowing through it. Current flowing through all the resistors connected in series is the same while the voltage is different. Voltage across each resistor connected in parallel is the same while current is different.
Formula used:
${{R}_{eq}}={{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}+.......$
$\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}+..........$
Complete answer:
Part I is short circuited because current flows through the path of smallest resistance. Same happens for part II as well.

In a parallel type of circuit, different parts of the circuit are connected across different branches. Hence, electron flow occurs in several parts. If in one path a circuit break occurs, electric current still flows in other paths. Household wiring of appliances are based on parallel circuits, so if one light bulb goes down, the other will still flow.
As far as part III is concerned, the resistors are in parallel so
$\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}+..........$
${{R}_{eq}}=\dfrac{(\dfrac{30\times 30}{30+30}\times 30)}{(\dfrac{30\times 30}{30+30}+30)}=10\Omega $
Resistance between X and Y is
R=$\dfrac{30\times 30}{30+30}=15\Omega $
Note:
The possibility of making a mistake in this question is by reducing the entire circuit and considering all the resistors to find the equivalent resistance. The ohm's law used here states that the voltage across a resistor is directly proportional to the amount of current flowing through it. Current flowing through all the resistors connected in series is the same while the voltage is different. Voltage across each resistor connected in parallel is the same while current is different.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




