
The equivalent capacitance between A and B is
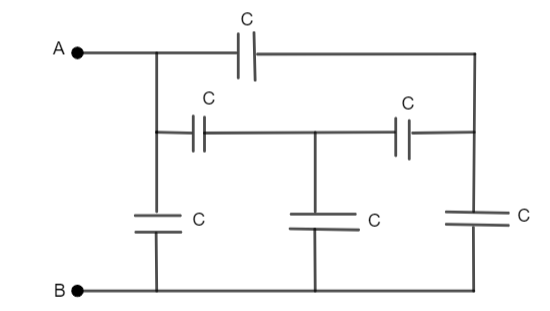
(a) 6C
(b) 4C
(c) 2C
(d) None of the above

Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: We have been provided a circuit which has capacitors connected to it. Make two portions of the circuit. If you will look, the lower portion shows the Wheatstone bridge network. Applying the balancing condition, calculate the equivalent capacitance of the lower portion. Then take the parallel combination and calculate the equivalent capacitance between A and B.
Complete step by step answer:
We have been provided a circuit which has capacitors connected to it. Now, we need to find the equivalent capacitance between A and B. To make the solving portion easy, let’s name each capacitor shown in the figure.
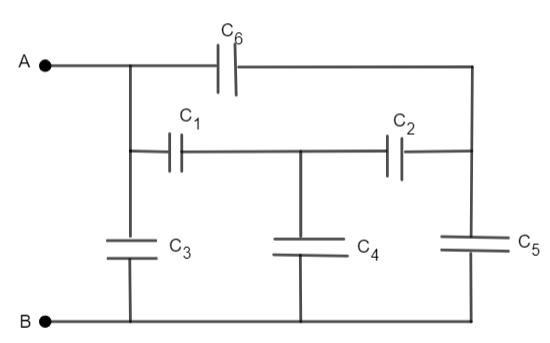
In the circuit, \[{{C}_{4}}\] is in parallel to the rest of the combined capacitors. Thus, we can draw a simplified circuit as,
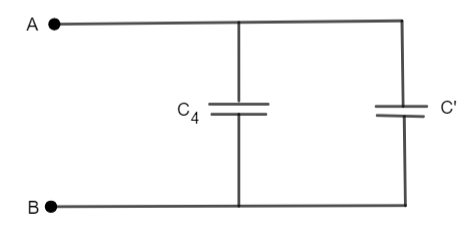
Where C’ is the combined capacitance of the capacitors except \[{{C}_{4}}.\]
Now, look at the rest of the circuit, i.e. C’ then the circuit will look like
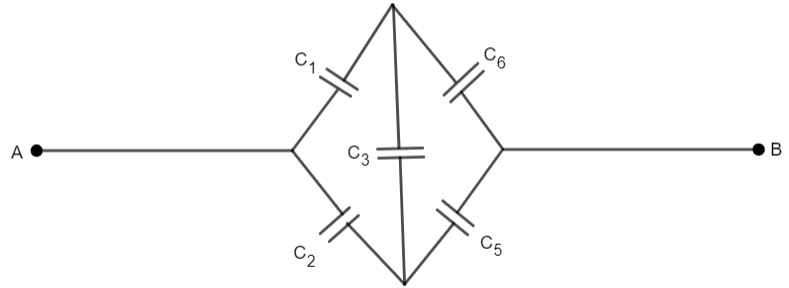
The above circuit is equivalent to Wheatstone’s Bridge Network. So, if we apply the balance condition to the Wheatstone network, then \[{{C}_{3}}\] can be neglected and can be removed. Then the circuit will look like,
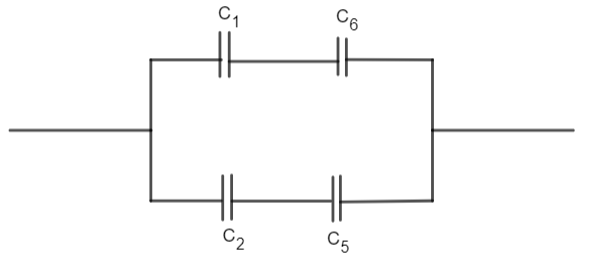
Find the equivalent capacitance, using the series combination in the upper portion.
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C}^{''}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{6}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C}^{''}}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{6}}}{{{C}_{1}}\times {{C}_{6}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{C}^{''}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{1}}\times {{C}_{6}}}{{{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{6}}}\]
Again using the series combination on the lower side of the circuit, we get,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C}^{'''}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{5}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C}^{'''}}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{2}}+{{C}_{5}}}{{{C}_{2}}\times {{C}_{5}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{C}^{'''}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{2}}\times {{C}_{5}}}{{{C}_{2}}+{{C}_{5}}}\]
Hence, the equivalent capacitor can be calculated using the parallel combination of C’’ and C’’’.
Since, C’’ and C’’’ are in series,
\[\therefore {{C}^{'}}={{C}^{''}}+{{C}^{'''}}\]
\[\therefore {{C}^{'}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{6}}}{{{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{6}}}+\dfrac{{{C}_{2}}{{C}_{5}}}{{{C}_{2}}+{{C}_{5}}}\]
We know that, \[{{C}_{1}}={{C}_{6}}={{C}_{2}}={{C}_{5}}=C.\]
\[\therefore {{C}^{'}}=\dfrac{C.C}{C+C}+\dfrac{C.C}{C+C}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{C}^{'}}=\dfrac{{{C}^{2}}}{2C}+\dfrac{{{C}^{2}}}{2C}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{C}^{'}}=\dfrac{C}{2}+\dfrac{C}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{C}^{'}}=C\]
So, the final circuit will look like,
Therefore, the equivalent capacitance between A and B is
\[{{C}_{eg}}={{C}_{4}}+C=C+C=2C\]
[Since \[{{C}_{4}}\] and C are in series]
Here, the equivalent capacitance between A and B is 2C.
Hence, the option (c) is the right answer.
Additional Information:
The capacitor is an electric component that connects the circuit. It stores the charges and it accumulates the charges. The capacitor is a system that consists of two conductors. The electric field between the two conductors is proportional to the magnitude of the electric charge in the region. Besides, the potential difference between the two conductors is proportional to the magnitude of change.
Note:
Students should know that when several numbers of capacitors are connected in series then the current flowing through each of the electrical components will be the same. The equivalent capacitance in series is given as
\[\dfrac{1}{{{\left( {{C}_{eq}} \right)}_{S}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{3}}}+......\]
And when several numbers of the capacitors are connected in parallel, the potential difference across each of the electrical components is the same. The equivalent capacitance in parallel combination is given as
\[{{\left( {{C}_{eq}} \right)}_{P}}={{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}}+{{C}_{3}}......\]
The concept of the capacitor in the series and in the parallel combination is opposite, in the case of the resistor, so do not get confused.
Complete step by step answer:
We have been provided a circuit which has capacitors connected to it. Now, we need to find the equivalent capacitance between A and B. To make the solving portion easy, let’s name each capacitor shown in the figure.

In the circuit, \[{{C}_{4}}\] is in parallel to the rest of the combined capacitors. Thus, we can draw a simplified circuit as,

Where C’ is the combined capacitance of the capacitors except \[{{C}_{4}}.\]
Now, look at the rest of the circuit, i.e. C’ then the circuit will look like

The above circuit is equivalent to Wheatstone’s Bridge Network. So, if we apply the balance condition to the Wheatstone network, then \[{{C}_{3}}\] can be neglected and can be removed. Then the circuit will look like,

Find the equivalent capacitance, using the series combination in the upper portion.
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C}^{''}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{6}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C}^{''}}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{6}}}{{{C}_{1}}\times {{C}_{6}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{C}^{''}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{1}}\times {{C}_{6}}}{{{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{6}}}\]
Again using the series combination on the lower side of the circuit, we get,
\[\dfrac{1}{{{C}^{'''}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{5}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{C}^{'''}}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{2}}+{{C}_{5}}}{{{C}_{2}}\times {{C}_{5}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{C}^{'''}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{2}}\times {{C}_{5}}}{{{C}_{2}}+{{C}_{5}}}\]
Hence, the equivalent capacitor can be calculated using the parallel combination of C’’ and C’’’.
Since, C’’ and C’’’ are in series,
\[\therefore {{C}^{'}}={{C}^{''}}+{{C}^{'''}}\]
\[\therefore {{C}^{'}}=\dfrac{{{C}_{1}}{{C}_{6}}}{{{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{6}}}+\dfrac{{{C}_{2}}{{C}_{5}}}{{{C}_{2}}+{{C}_{5}}}\]
We know that, \[{{C}_{1}}={{C}_{6}}={{C}_{2}}={{C}_{5}}=C.\]
\[\therefore {{C}^{'}}=\dfrac{C.C}{C+C}+\dfrac{C.C}{C+C}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{C}^{'}}=\dfrac{{{C}^{2}}}{2C}+\dfrac{{{C}^{2}}}{2C}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{C}^{'}}=\dfrac{C}{2}+\dfrac{C}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{C}^{'}}=C\]
So, the final circuit will look like,
Therefore, the equivalent capacitance between A and B is
\[{{C}_{eg}}={{C}_{4}}+C=C+C=2C\]
[Since \[{{C}_{4}}\] and C are in series]
Here, the equivalent capacitance between A and B is 2C.
Hence, the option (c) is the right answer.
Additional Information:
The capacitor is an electric component that connects the circuit. It stores the charges and it accumulates the charges. The capacitor is a system that consists of two conductors. The electric field between the two conductors is proportional to the magnitude of the electric charge in the region. Besides, the potential difference between the two conductors is proportional to the magnitude of change.
Note:
Students should know that when several numbers of capacitors are connected in series then the current flowing through each of the electrical components will be the same. The equivalent capacitance in series is given as
\[\dfrac{1}{{{\left( {{C}_{eq}} \right)}_{S}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{C}_{3}}}+......\]
And when several numbers of the capacitors are connected in parallel, the potential difference across each of the electrical components is the same. The equivalent capacitance in parallel combination is given as
\[{{\left( {{C}_{eq}} \right)}_{P}}={{C}_{1}}+{{C}_{2}}+{{C}_{3}}......\]
The concept of the capacitor in the series and in the parallel combination is opposite, in the case of the resistor, so do not get confused.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




