
The corrosive action of ${H_2}S{O_4}$ on skin is due to its dehydrating action.
A. True
B. False
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Sulphuric acid is a mineral acid that is odorless, colorless and viscous liquid soluble in water. corrosive substances damage the other substances with which they come into contact. Dehydration means removal of water. Some substances have this corrosive property.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of sulphuric acid is as follows-
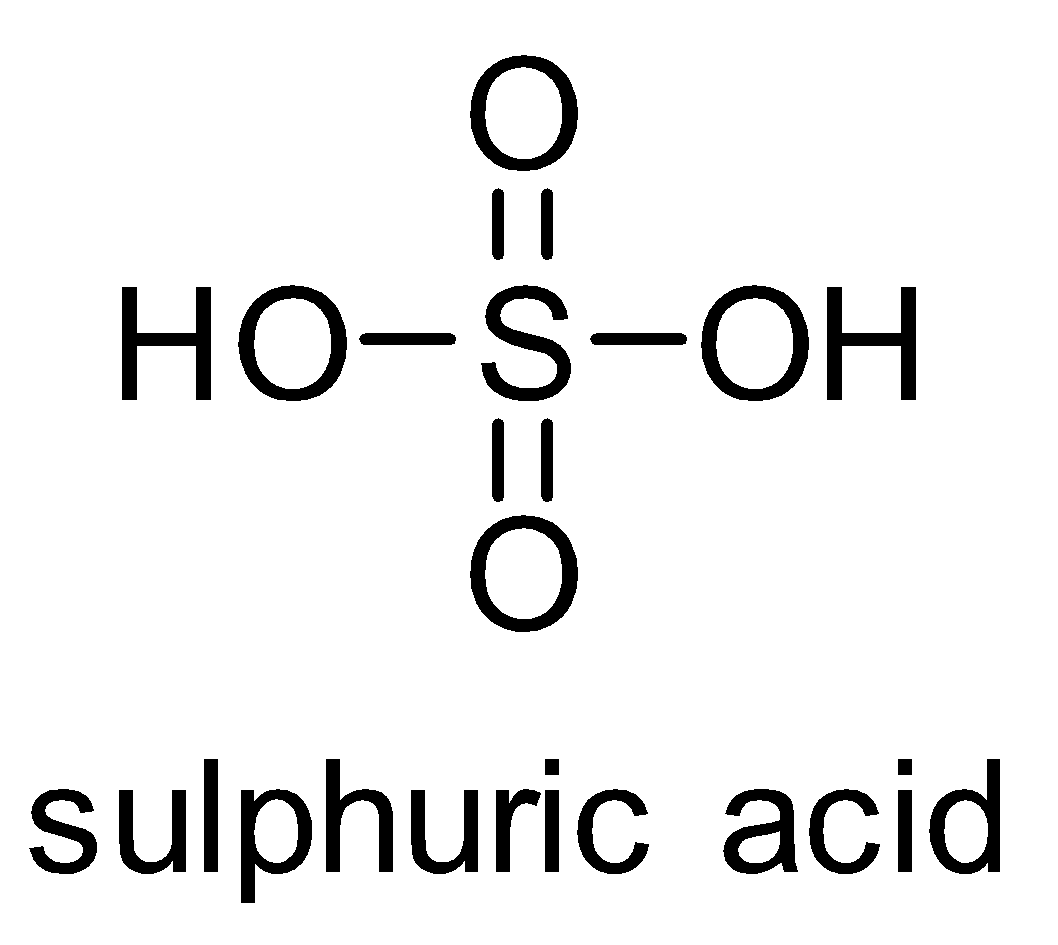
It is a dibasic acid. Concentrated sulphuric acid is known as king of acids because it is a strong acid and more reactive than other acids. It is also called as oil of vitriol because in ancient days it was prepared by distillation of green vitriol. Sulfuric acid is prepared industrially by the reaction of water with sulphur trioxide. Sulphur trioxide is made from sulphur dioxide and oxygen by the contact process.
Sulphuric acid is prepared industrially by the contact process. The catalyst used in this process is vanadium oxide. Sulphuric acid is used widely in the manufacture of fertilizers, chemicals such as acids, synthetic dyes, detergents, pigments, explosives and drugs.
A dehydrating agent is a substance or chemical which can remove water molecules from a given compound. OR Any substance that can readily absorb moisture from its surroundings is called a dehydrating agent.
Sulphuric acid is used as a dehydrating agent since it readily protonated the water molecule and forms hydronium ions.
On reaction with skin it absorbs the moisture from the skin causing damage to the cells leading to skin burns.
So ,the statement is true. The corrosive nature of ${H_2}S{O_4}$ is due to its dehydrating action. .
Note: Such skin burns can be treated with alkali since it can neutralize the acid.
Some other examples of dehydrating agents are concentrated phosphoric acid, hot aluminium oxide. Sulphuric acid is highly viscous in nature because its molecules are associated with hydrogen bonding. It is a highly corrosive chemical. It is also used as a sulphonating agent in organic reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of sulphuric acid is as follows-

It is a dibasic acid. Concentrated sulphuric acid is known as king of acids because it is a strong acid and more reactive than other acids. It is also called as oil of vitriol because in ancient days it was prepared by distillation of green vitriol. Sulfuric acid is prepared industrially by the reaction of water with sulphur trioxide. Sulphur trioxide is made from sulphur dioxide and oxygen by the contact process.
Sulphuric acid is prepared industrially by the contact process. The catalyst used in this process is vanadium oxide. Sulphuric acid is used widely in the manufacture of fertilizers, chemicals such as acids, synthetic dyes, detergents, pigments, explosives and drugs.
A dehydrating agent is a substance or chemical which can remove water molecules from a given compound. OR Any substance that can readily absorb moisture from its surroundings is called a dehydrating agent.
Sulphuric acid is used as a dehydrating agent since it readily protonated the water molecule and forms hydronium ions.
On reaction with skin it absorbs the moisture from the skin causing damage to the cells leading to skin burns.
So ,the statement is true. The corrosive nature of ${H_2}S{O_4}$ is due to its dehydrating action. .
Note: Such skin burns can be treated with alkali since it can neutralize the acid.
Some other examples of dehydrating agents are concentrated phosphoric acid, hot aluminium oxide. Sulphuric acid is highly viscous in nature because its molecules are associated with hydrogen bonding. It is a highly corrosive chemical. It is also used as a sulphonating agent in organic reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




