
The combined equation of three sides of a triangle is $\left( {{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}} \right)\left( 2x+3y-6 \right)=0$. If $\left( \sec \theta ,1 \right)$ is an interior point of the triangle then find the value of $\theta $.
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: We will factorize the given equation to find the three sides of the triangle. Then we will look at the range of the x-coordinate for the interior points of the triangle. The value of $\sec \theta $ will have to lie inside this range. We will use the inverse trigonometric function ${{\sec }^{-1}}\theta $ to find the value of $\theta $.
Complete step by step answer:
The given equation is $\left( {{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}} \right)\left( 2x+3y-6 \right)=0$. We can further factorize this equation using the identity $\left( {{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}} \right)=\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)$ in the following manner,
$\left( x+y \right)\left( x-y \right)\left( 2x+3y-6 \right)=0$.
This implies that we have the following three equations,
$x+y=0$....(i)
$x-y=0$....(ii)
$2x+3y-6=0$....(iii)
We can see that the point of intersection of equation (i) and equation (ii) is $\left( 0,0 \right)$.
We will substitute $x=-y$ from equation (i) in equation (iii), as follows,
$2\left( -y \right)+3y-6=0$
Solving the above equation for $y$, we get
$\begin{align}
& y-6=0 \\
& \therefore y=6 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we get $x=-6$. Hence, the point of intersection of equation (i) and equation (iii) is $\left( -6,6 \right)$.
Similarly, we will substitute $x=y$ from equation (ii) in equation (iii), as follows,
$2y+3y-6=0$
Solving the above equation for $y$, we get
$\begin{align}
& 5y-6=0 \\
& \therefore y=\dfrac{6}{5}=1.2 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we get $x=\dfrac{6}{5}=1.2$. Hence, the point of intersection of equation (ii) and equation (iii) is $\left( \dfrac{6}{5},\dfrac{6}{5} \right)=\left( 1.2,1.2 \right)$.
Now, we know that the range of the secant function is $\left( -\infty ,-1 \right]\cup \left[ 1,\infty \right)$. The intersection of the range of the secant function and the triangle is $\left[ -6,-1 \right]\cup \left[ 1,1.2 \right]$. Therefore, $\sec \theta \in \left[ -6,-1 \right]\cup \left[ 1,1.2 \right]$. Hence, $\theta \in \left[ {{\sec }^{-1}}\left( -6 \right),{{\sec }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right) \right]\cup \left[ {{\sec }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right),{{\sec }^{-1}}\left( 1.2 \right) \right]$, that is $\theta \in \left[ {{\sec }^{-1}}\left( -6 \right),\pi \right]\cup \left[ 0,{{\sec }^{-1}}\left( 1.2 \right) \right]$.
Note: We can plot the graph of the three equations and look at the triangle formed as shown in the figure below,
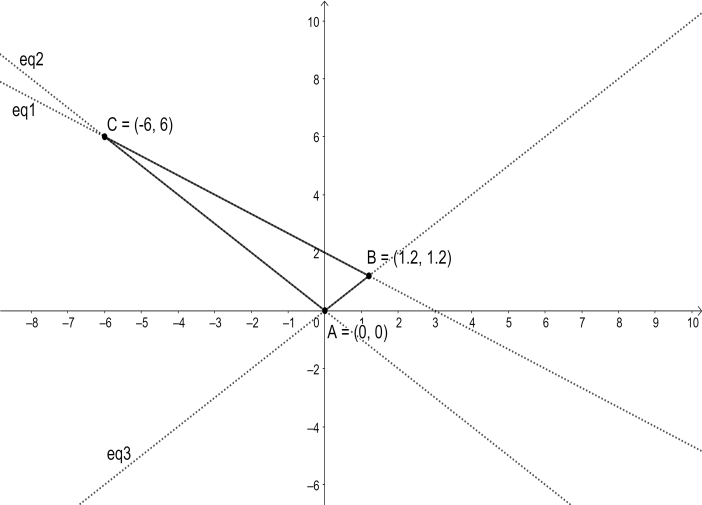
The specific values for arcsec functions are a bit difficult to calculate. We should be familiar with the principle values for inverse trigonometric functions.
Complete step by step answer:
The given equation is $\left( {{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}} \right)\left( 2x+3y-6 \right)=0$. We can further factorize this equation using the identity $\left( {{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}} \right)=\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)$ in the following manner,
$\left( x+y \right)\left( x-y \right)\left( 2x+3y-6 \right)=0$.
This implies that we have the following three equations,
$x+y=0$....(i)
$x-y=0$....(ii)
$2x+3y-6=0$....(iii)
We can see that the point of intersection of equation (i) and equation (ii) is $\left( 0,0 \right)$.
We will substitute $x=-y$ from equation (i) in equation (iii), as follows,
$2\left( -y \right)+3y-6=0$
Solving the above equation for $y$, we get
$\begin{align}
& y-6=0 \\
& \therefore y=6 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we get $x=-6$. Hence, the point of intersection of equation (i) and equation (iii) is $\left( -6,6 \right)$.
Similarly, we will substitute $x=y$ from equation (ii) in equation (iii), as follows,
$2y+3y-6=0$
Solving the above equation for $y$, we get
$\begin{align}
& 5y-6=0 \\
& \therefore y=\dfrac{6}{5}=1.2 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we get $x=\dfrac{6}{5}=1.2$. Hence, the point of intersection of equation (ii) and equation (iii) is $\left( \dfrac{6}{5},\dfrac{6}{5} \right)=\left( 1.2,1.2 \right)$.
Now, we know that the range of the secant function is $\left( -\infty ,-1 \right]\cup \left[ 1,\infty \right)$. The intersection of the range of the secant function and the triangle is $\left[ -6,-1 \right]\cup \left[ 1,1.2 \right]$. Therefore, $\sec \theta \in \left[ -6,-1 \right]\cup \left[ 1,1.2 \right]$. Hence, $\theta \in \left[ {{\sec }^{-1}}\left( -6 \right),{{\sec }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right) \right]\cup \left[ {{\sec }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right),{{\sec }^{-1}}\left( 1.2 \right) \right]$, that is $\theta \in \left[ {{\sec }^{-1}}\left( -6 \right),\pi \right]\cup \left[ 0,{{\sec }^{-1}}\left( 1.2 \right) \right]$.
Note: We can plot the graph of the three equations and look at the triangle formed as shown in the figure below,

The specific values for arcsec functions are a bit difficult to calculate. We should be familiar with the principle values for inverse trigonometric functions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




