
The coconut water and the edible part of coconut are equivalent to ____.
(a) Endosperm
(b) Endocarp
(c) Mesocarp
(d) Embryo.
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: The layer matures into their cellular phase and deposits into the rind of the coconut meat.
Complete answer:To answer this question, at first, we have to know the endosperm part of coconut. Coconut water is the endosperm a part of the coconut plant. Endosperm is the most usual nutritive tissue for the development of embryos in Angiosperms and develops as post-fertilization shape from the primary endosperm nucleus. The coconut endosperm is a nuclear type.
Now lets us find the solution from given options –
Coconut fruit is a drupe. It has a membranous epicarp, fibrous mesocarp and stony endocarp.
The endocarp encloses a single seed with brown testa that consists of a small embryo and a white oily endosperm (suitable for eating part) with watery fluid referred to as coconut water.
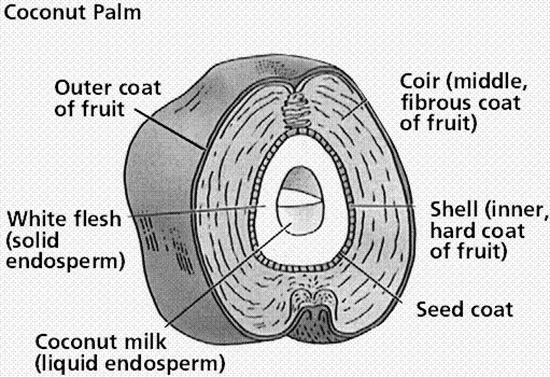
Coconut is surrounded by means of the hard woody layer referred to as the endocarp. The endocarp surrounds the seed.
The outermost layer of coconut, that's typically soft with a greenish color, is referred to as the exocarp. After that the next layer is the fibrous husk, or referred to as a mesocarp.
In a few mature coconuts, we can see the soft, spongy part inside the center when we crack or open the coconut. This is simply a coconut cotyledon, which is also recognized as coconut embryo or coconut apple.
Thus, the correct solution is, ’Endosperm’.
Note:The coconut water represents free-nuclear endosperm and the surrounding kernel represents the cellular endosperm.
Complete answer:To answer this question, at first, we have to know the endosperm part of coconut. Coconut water is the endosperm a part of the coconut plant. Endosperm is the most usual nutritive tissue for the development of embryos in Angiosperms and develops as post-fertilization shape from the primary endosperm nucleus. The coconut endosperm is a nuclear type.
Now lets us find the solution from given options –
Coconut fruit is a drupe. It has a membranous epicarp, fibrous mesocarp and stony endocarp.
The endocarp encloses a single seed with brown testa that consists of a small embryo and a white oily endosperm (suitable for eating part) with watery fluid referred to as coconut water.

Coconut is surrounded by means of the hard woody layer referred to as the endocarp. The endocarp surrounds the seed.
The outermost layer of coconut, that's typically soft with a greenish color, is referred to as the exocarp. After that the next layer is the fibrous husk, or referred to as a mesocarp.
In a few mature coconuts, we can see the soft, spongy part inside the center when we crack or open the coconut. This is simply a coconut cotyledon, which is also recognized as coconut embryo or coconut apple.
Thus, the correct solution is, ’Endosperm’.
Note:The coconut water represents free-nuclear endosperm and the surrounding kernel represents the cellular endosperm.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




