
The area of the figure bounded by \[\left| y \right| = 1 - {x^2}\] is in square units,
\[\left( {\mathbf{1}} \right)\] : \[4/3\]
\[\left( {\mathbf{2}} \right)\] : \[8/3\]
\[\left( {\mathbf{3}} \right)\] : \[16/3\]
\[\left( {\mathbf{4}} \right)\] : \[1\]
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: A parabola is the set of all the points in a plane, equidistant from a fixed point and a fixed line in that plane. The fixed point is called the focus and the fixed line is called the Directrix. The line through the focus and perpendicular to the directrix is called the axis of the Parabola. The point where the parabola intersects the axis is called the Vertex. The focal chord (cord passing through the focus) perpendicular to the axis of the parabola is called the latus rectum of the parabola.
The standard form of upward parabola is:
\[ = \int\limits_{ - a}^a {f(x)dx = \left\{ {2\int\limits_{ - a}^a {f(x)dx} } \right\}} \]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given curve: \[|y| = 1 - {x^2}\]
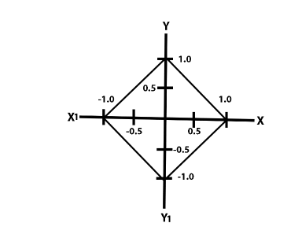
Step1:
Above is the graph of given curve:
The area bounded by a given curve is equal to the area bounded by the downward parabola: and the upward parabola (as shown in figure).
Step2:
Consider a differential vertical rectangular lab of area \[\left( {Y_1 - Y_2} \right)\] dx and integrate it with proper limits as follow:
\[\int\limits_{ - a}^a {(Y_1 - Y_2)dx} \]
where a is lower limit and a is upper limit.
\[\int\limits_{ - a}^a {(( - {x^2} + 1) - ({x^2} - 1))dx} \]
\[ = \int\limits_{ - 1}^1 {( - 2{x^2} + 2)dx} \]
Now, we are using the property.
\[ = \int\limits_{ - a}^a {f(x)dx = \left\{ {2\int\limits_{ - a}^a {f(x)dx} } \right\}} \] if f is an even function.
\[= 0\] if ‘f’ is an odd function.
Here the above function is even.
therefore,
\[ = 2\int\limits_0^1 {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 2{x^3}}}{3} + 2x} \right)_0^1} \]
\[ = 2\int\limits_{}^{} {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 2{{( - 1)}^3}}}{3} + 2(1)} \right)} - \left( {\dfrac{{ - 2{{(0)}^3}}}{3} + 2(0)} \right)\]
\[ = 2\left( {\dfrac{2}{3} + 2(1)} \right)\]
\[ = 2\left( {\dfrac{{ + 2 + 6}}{3}} \right)\]
\[ = 2\left( {\dfrac{8}{3}} \right)\]
\[ = \dfrac{16}{3}\]
so, \[\dfrac{16}{3}\] square unit is bounded area of given curve,
Hence, option \[\left( 3 \right)\] is the right answer.
So, the correct answer is “Option 3”.
Note: Parabola has been found to be of great use in several fields. For example, the path of a projectile is a parabola if we know the equation of the path, thus we can find many important results like greatest height attained, horizontal range reached and velocity at any instant, etc. Near Parabolic Areas are used in suspension cable bridge construction, when the roadway of a suspension bridge is uniformly loaded per horizontal metre, which are almost parabolic arcs. Parabolic reflections follow the property that “light rays are sound waves coming parallel to the axis of the parabola converge at its focus and then it reflects them parallel to the axis”.
The standard form of upward parabola is:
\[ = \int\limits_{ - a}^a {f(x)dx = \left\{ {2\int\limits_{ - a}^a {f(x)dx} } \right\}} \]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given curve: \[|y| = 1 - {x^2}\]

Step1:
Above is the graph of given curve:
The area bounded by a given curve is equal to the area bounded by the downward parabola: and the upward parabola (as shown in figure).
Step2:
Consider a differential vertical rectangular lab of area \[\left( {Y_1 - Y_2} \right)\] dx and integrate it with proper limits as follow:
\[\int\limits_{ - a}^a {(Y_1 - Y_2)dx} \]
where a is lower limit and a is upper limit.
\[\int\limits_{ - a}^a {(( - {x^2} + 1) - ({x^2} - 1))dx} \]
\[ = \int\limits_{ - 1}^1 {( - 2{x^2} + 2)dx} \]
Now, we are using the property.
\[ = \int\limits_{ - a}^a {f(x)dx = \left\{ {2\int\limits_{ - a}^a {f(x)dx} } \right\}} \] if f is an even function.
\[= 0\] if ‘f’ is an odd function.
Here the above function is even.
therefore,
\[ = 2\int\limits_0^1 {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 2{x^3}}}{3} + 2x} \right)_0^1} \]
\[ = 2\int\limits_{}^{} {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 2{{( - 1)}^3}}}{3} + 2(1)} \right)} - \left( {\dfrac{{ - 2{{(0)}^3}}}{3} + 2(0)} \right)\]
\[ = 2\left( {\dfrac{2}{3} + 2(1)} \right)\]
\[ = 2\left( {\dfrac{{ + 2 + 6}}{3}} \right)\]
\[ = 2\left( {\dfrac{8}{3}} \right)\]
\[ = \dfrac{16}{3}\]
so, \[\dfrac{16}{3}\] square unit is bounded area of given curve,
Hence, option \[\left( 3 \right)\] is the right answer.
So, the correct answer is “Option 3”.
Note: Parabola has been found to be of great use in several fields. For example, the path of a projectile is a parabola if we know the equation of the path, thus we can find many important results like greatest height attained, horizontal range reached and velocity at any instant, etc. Near Parabolic Areas are used in suspension cable bridge construction, when the roadway of a suspension bridge is uniformly loaded per horizontal metre, which are almost parabolic arcs. Parabolic reflections follow the property that “light rays are sound waves coming parallel to the axis of the parabola converge at its focus and then it reflects them parallel to the axis”.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




