
The area (in sq. units) of the region bounded by the curves \[y = {2^x}\] and \[y = |x + 1|\], in the first quadrant is :
A. \[\dfrac{3}{2} - \dfrac{1}{{{{\log }_e}2}}\]
B. \[\dfrac{1}{2}\]
C. \[{\log _e}2 + \dfrac{3}{2}\]
D. \[\dfrac{3}{2}\]
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: We will first construct the figure as the area of the region bounded by the given curves. We have to find the area of the region in the first quadrant only. As the curve \[y = |x + 1|\] lies above and the other curve \[y = {2^x}\] lies below so we will subtract the upper from the lower curve and find the limits to determine the area of the bounded region.
Complete step by step answer:
We will first construct both the given curves in the first quadrant and find the limits under which the area needs to be found.
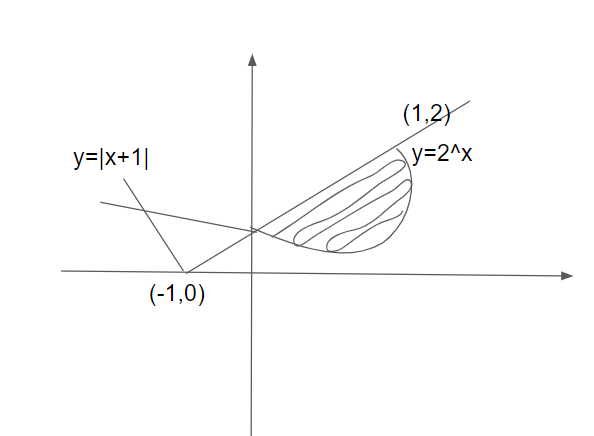
From the figure, we can see that the curve \[y = {2^x}\] lies below and the curve \[y = |x + 1|\] lies above the shaded region.
We have to find the area of the shaded region which is lying between the interval \[\left[ {0,1} \right]\] and we will subtract the curve bounded below from the curve bounded above.
Thus, we get the integral as:
\[
\Rightarrow I = \int\limits_0^1 {\left( {\left( {x + 1} \right) - {2^x}} \right)} dx \\
\Rightarrow I = \left[ {\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2} + x - \dfrac{{{2^x}}}{{{{\log }_e}2}}} \right]_0^1 \\
\]
Since, we have used the basic integration to integrate \[\int {xdx = \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2}} \] and \[\int {{2^x} = \dfrac{{{2^x}}}{{{{\log }_e}2}}} \].
Now, we will apply the limits on the obtained integral value by substituting 1 in place of \[x\] and then 0 in place of \[x\],
Thus, we get,
\[
\Rightarrow I = \left[ {\dfrac{{{1^2}}}{2} + 1 - \dfrac{{{2^1}}}{{{{\log }_e}2}}} \right] - \left[ {0 + 0 - \dfrac{1}{{{{\log }_e}2}}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{3}{2} - \dfrac{1}{{{{\log }_e}2}} \\
\]
Thus, we get the area of the bounded region as \[I = \dfrac{3}{2} - \dfrac{1}{{{{\log }_e}2}}\].
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: We have integrated the term \[{2^x} = \dfrac{{{2^x}}}{{{{\log }_e}2}}\] using the basic knowledge of integration. Constructing the figure in such questions will make the solution easier as the area of the bounded region will be easily determined by subtracting the upper region from the lower region. Also, the limit can also be found from the figure. Basic integration formulas or methods should be in mind to solve such questions. While solving the integration, do it correctly and apply the limits after finding the integration of the functions.
Complete step by step answer:
We will first construct both the given curves in the first quadrant and find the limits under which the area needs to be found.

From the figure, we can see that the curve \[y = {2^x}\] lies below and the curve \[y = |x + 1|\] lies above the shaded region.
We have to find the area of the shaded region which is lying between the interval \[\left[ {0,1} \right]\] and we will subtract the curve bounded below from the curve bounded above.
Thus, we get the integral as:
\[
\Rightarrow I = \int\limits_0^1 {\left( {\left( {x + 1} \right) - {2^x}} \right)} dx \\
\Rightarrow I = \left[ {\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2} + x - \dfrac{{{2^x}}}{{{{\log }_e}2}}} \right]_0^1 \\
\]
Since, we have used the basic integration to integrate \[\int {xdx = \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2}} \] and \[\int {{2^x} = \dfrac{{{2^x}}}{{{{\log }_e}2}}} \].
Now, we will apply the limits on the obtained integral value by substituting 1 in place of \[x\] and then 0 in place of \[x\],
Thus, we get,
\[
\Rightarrow I = \left[ {\dfrac{{{1^2}}}{2} + 1 - \dfrac{{{2^1}}}{{{{\log }_e}2}}} \right] - \left[ {0 + 0 - \dfrac{1}{{{{\log }_e}2}}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{3}{2} - \dfrac{1}{{{{\log }_e}2}} \\
\]
Thus, we get the area of the bounded region as \[I = \dfrac{3}{2} - \dfrac{1}{{{{\log }_e}2}}\].
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: We have integrated the term \[{2^x} = \dfrac{{{2^x}}}{{{{\log }_e}2}}\] using the basic knowledge of integration. Constructing the figure in such questions will make the solution easier as the area of the bounded region will be easily determined by subtracting the upper region from the lower region. Also, the limit can also be found from the figure. Basic integration formulas or methods should be in mind to solve such questions. While solving the integration, do it correctly and apply the limits after finding the integration of the functions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




