
State the bond angle and polar character of the carbon atom present in carboxylic acid.
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: An organic acid is an organic compound which contains carboxylic groups. Their general formula is $R - COOH$. Where R represents an alkyl or phenyl group. Polarity means when a high electronegative atom pulls the electron density of a lesser electronegative atom.
Complete step by step answer:
In the structure of formic acid and formaldehyde, it is to be found that apart from formic acid’s acidic hydrogen, both have a planar structure that may be accounted for by carbonyl carbon $s{p^2}$ hybridization. The strong carbon-oxygen double bond is shortened. Its length amounts to ${1.23^0}A$
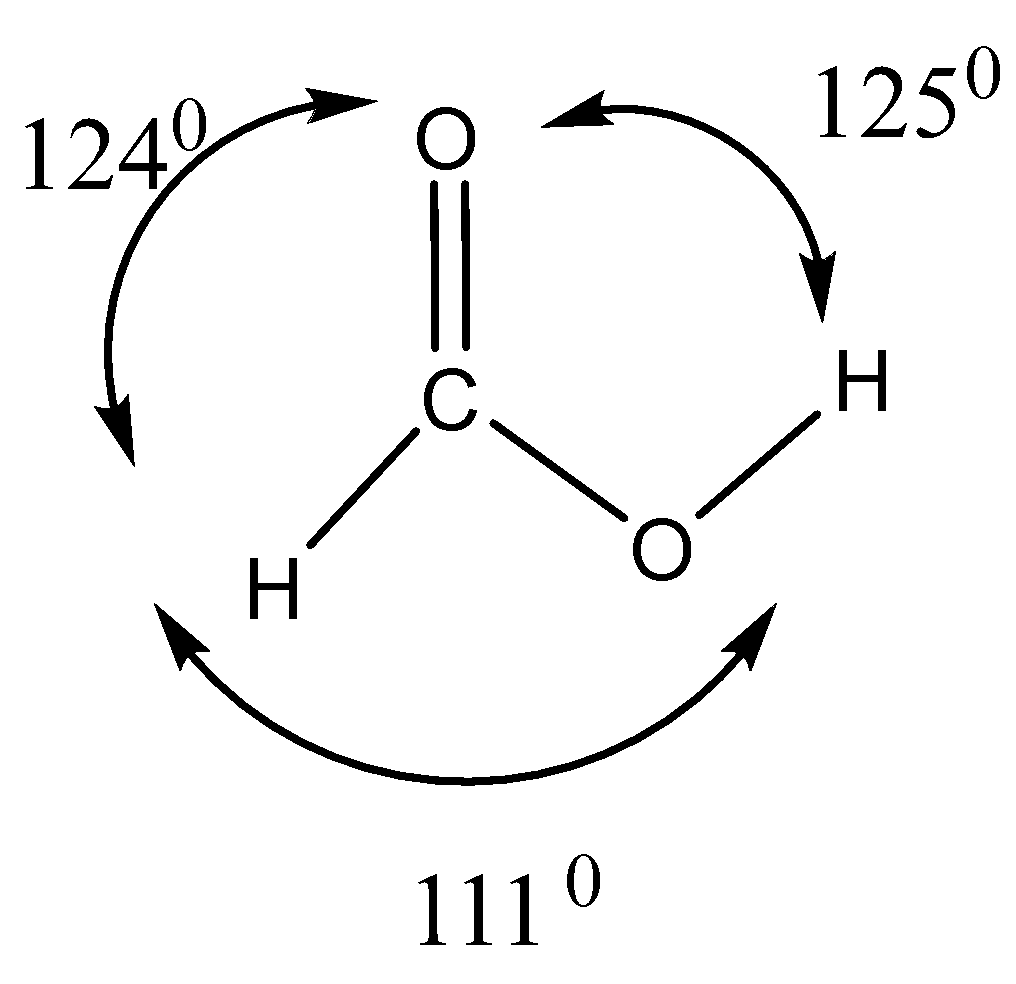
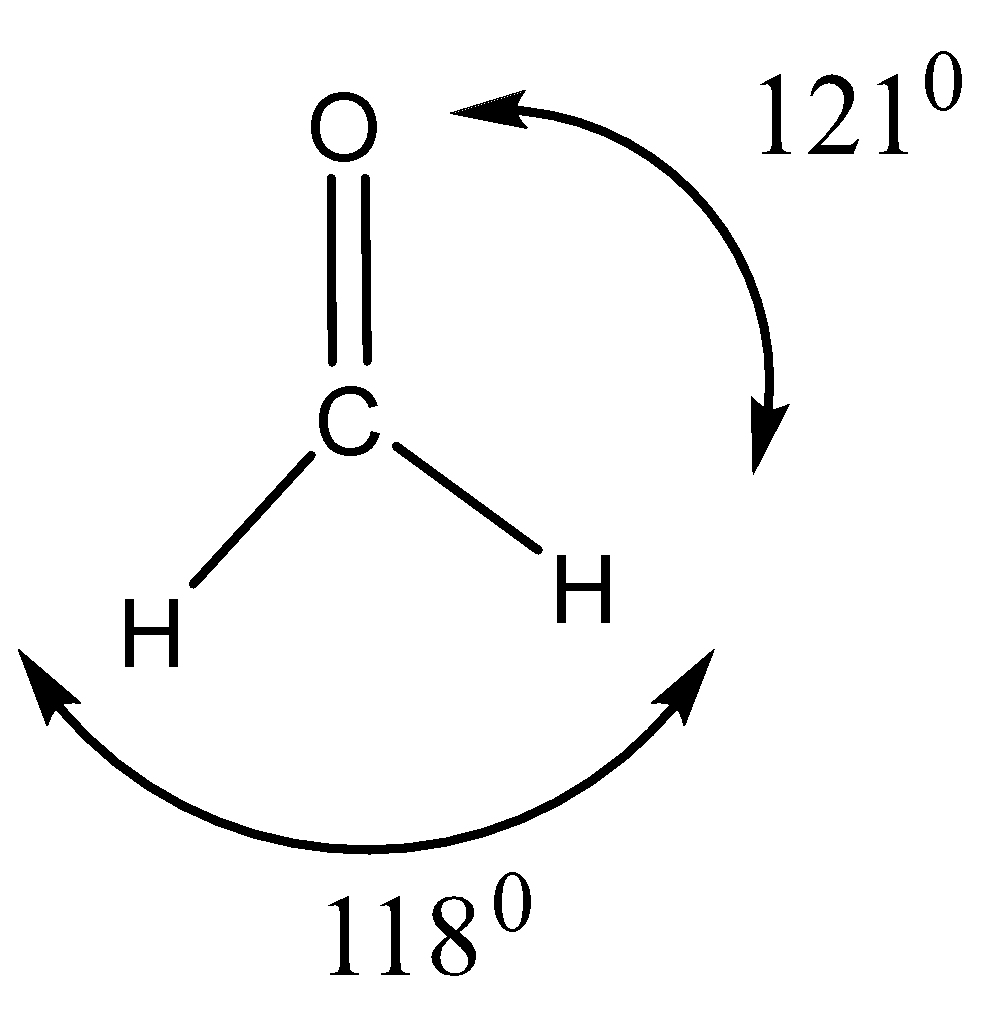
Bond angles in formic acid and formaldehyde
Angles around the carboxyl (COO) group, as illustrated for formic acid are roughly $120^\circ $ around the carbon. This is due to the $s{p^2}$- hybridized carbon of the carboxyl group. All three angles around an $s{p^2}$ - hybridized carbon should be $120^\circ $. But the $H - C - O$ angle is slightly less than $120^\circ $. This is due to the higher steric hindrance at the $O - C - O$ angle, as compared to the $H - C - O$ angle of formic acid.
Carboxylic acids are soluble in water. Carboxylic acid does not dimerize in water but forms hydrogen bonds with water.
Carboxylic acid is polar and due to the presence of the hydroxyl in the carboxyl group, they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Smaller carboxylic acids (C1 to C5) are soluble in water, whereas larger carboxylic acids ( ${C_6}$ and above) are less soluble due to the increasing hydrophobic nature of the hydrocarbon chains.
As the atomic number of the carboxylic acid increases, the boiling point also increases. Carboxylic acids have even higher boiling points than alkenes and alcohols. Carboxylic acids, similar to alcohols, can form hydrogen bonds with each other as well as van der Waals dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions. However, unique to carboxylic acids, hydrogen bonding can occur between molecules to produce a dimer.
Note:
The presence of polar OH groups which can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, lower carboxylic acids are soluble. Even higher organic acids, the COOH group has a polarity, but their R will be a very long chain, preventing them from the formulation of hydrogen bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
In the structure of formic acid and formaldehyde, it is to be found that apart from formic acid’s acidic hydrogen, both have a planar structure that may be accounted for by carbonyl carbon $s{p^2}$ hybridization. The strong carbon-oxygen double bond is shortened. Its length amounts to ${1.23^0}A$


Bond angles in formic acid and formaldehyde
Angles around the carboxyl (COO) group, as illustrated for formic acid are roughly $120^\circ $ around the carbon. This is due to the $s{p^2}$- hybridized carbon of the carboxyl group. All three angles around an $s{p^2}$ - hybridized carbon should be $120^\circ $. But the $H - C - O$ angle is slightly less than $120^\circ $. This is due to the higher steric hindrance at the $O - C - O$ angle, as compared to the $H - C - O$ angle of formic acid.
Carboxylic acids are soluble in water. Carboxylic acid does not dimerize in water but forms hydrogen bonds with water.
Carboxylic acid is polar and due to the presence of the hydroxyl in the carboxyl group, they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. Smaller carboxylic acids (C1 to C5) are soluble in water, whereas larger carboxylic acids ( ${C_6}$ and above) are less soluble due to the increasing hydrophobic nature of the hydrocarbon chains.
As the atomic number of the carboxylic acid increases, the boiling point also increases. Carboxylic acids have even higher boiling points than alkenes and alcohols. Carboxylic acids, similar to alcohols, can form hydrogen bonds with each other as well as van der Waals dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions. However, unique to carboxylic acids, hydrogen bonding can occur between molecules to produce a dimer.
Note:
The presence of polar OH groups which can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, lower carboxylic acids are soluble. Even higher organic acids, the COOH group has a polarity, but their R will be a very long chain, preventing them from the formulation of hydrogen bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




