
Starting from the centre of the earth having radius R, the variation of g (acceleration due to gravity) is shown by which of the following options?
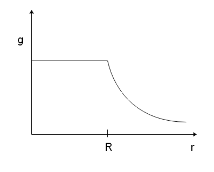
A)
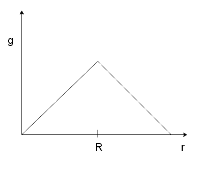
B)
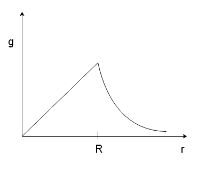
C)
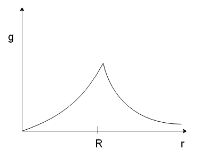
D)




Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint The gravitational acceleration inside the surface of the Earth is linearly proportional to the radius while outside the surface of the Earth it falls off with the inverse square of the distance. Use the formula of gravitational acceleration to determine the graph of gravity inside and outside the surface of the Earth.
Formula used Gravity inside the surface of Earth: $g = \dfrac{{GMr}}{{{R^3}}}$ where $G$ is the gravitational constant, $M$ is the mass of the Earth, $r$ is the distance from the centre of the Earth and $R$ is the radius of Earth.
Gravity outside the surface of Earth: $g = \dfrac{{GM}}{{{R^2}}}$
Complete step by step answer
To determine the graph of the gravitational acceleration below and outside the surface of the Earth, we know the gravity inside the surface of the Earth is calculated A:
$\Rightarrow g = \dfrac{{GMr}}{{{R^3}}}$
This equation is of the form
$\Rightarrow g = Ar$ where $A = GM/{R^3}$ which is the equation of a line. So the gravitational acceleration inside the surface of the Earth increases linearly with $r$ so the possible choices are (B) and (C).
Now outside the surface of the Earth, the gravitational acceleration is calculated as:
$\Rightarrow g = \dfrac{{GM}}{{{R^2}}}$
Since outside the surface of the Earth, the distance from the centre of the Earth is $R$, the gravity falls off with the inverse square of the distance which is shown in option (C) from option (B) and (C).
Note
The trick in this question is to know the gravitational acceleration on Earth as a function of the distance from the centre of the Earth. While option (A) seems tempting, the gravitational acceleration inside the Earth increases with increasing distance since there is more mass as we move towards the surface of the Earth.
Formula used Gravity inside the surface of Earth: $g = \dfrac{{GMr}}{{{R^3}}}$ where $G$ is the gravitational constant, $M$ is the mass of the Earth, $r$ is the distance from the centre of the Earth and $R$ is the radius of Earth.
Gravity outside the surface of Earth: $g = \dfrac{{GM}}{{{R^2}}}$
Complete step by step answer
To determine the graph of the gravitational acceleration below and outside the surface of the Earth, we know the gravity inside the surface of the Earth is calculated A:
$\Rightarrow g = \dfrac{{GMr}}{{{R^3}}}$
This equation is of the form
$\Rightarrow g = Ar$ where $A = GM/{R^3}$ which is the equation of a line. So the gravitational acceleration inside the surface of the Earth increases linearly with $r$ so the possible choices are (B) and (C).
Now outside the surface of the Earth, the gravitational acceleration is calculated as:
$\Rightarrow g = \dfrac{{GM}}{{{R^2}}}$
Since outside the surface of the Earth, the distance from the centre of the Earth is $R$, the gravity falls off with the inverse square of the distance which is shown in option (C) from option (B) and (C).
Note
The trick in this question is to know the gravitational acceleration on Earth as a function of the distance from the centre of the Earth. While option (A) seems tempting, the gravitational acceleration inside the Earth increases with increasing distance since there is more mass as we move towards the surface of the Earth.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




