
Sketch the graph \[y = \left| {x - 1} \right|\] . Evaluate \[\int\limits_{ - 2}^4 {\left| {x - 1} \right|} dx\] . What does this value of the integral represent on the graph?
Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: Integration is the process of finding the antiderivative. Finding the integral of a function with respect to x means finding the area to the x axis from the curve. The integral is usually called the antiderivative, because integrating is the reverse process of differentiating. To evaluate \[\int\limits_{ - 2}^4 {\left| {x - 1} \right|} dx\] we need to find the integration of the given function such that the range is from -2 to 4, hence evaluate based on the given interval.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us write the given data,
We need to sketch the graph for: \[y = \left| {x - 1} \right|\] and Evaluate \[\int\limits_{ - 2}^4 {\left| {x - 1} \right|} dx\] .
As the range of the integral given is from -2 to 4, hence we get:
\[\int\limits_{ - 2}^4 {\left| {x - 1} \right|} dx\] = \[\int\limits_{ - 2}^1 {\left| {x - 1} \right|} + \int\limits_1^4 {\left| {x - 1} \right|} \]
\[\left| {x - 1} \right|\] for \[x < 1\] , \[1 - x\]
\[\left| {x - 1} \right|\] for \[x > 1\] , \[x - 1\]
Hence, we get the equation as:
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\int\limits_{ - 2}^1 {\left( {1 - x} \right)dx} + \int\limits_1^4 {\left( {x - 1} \right)dx} \]
Apply the integrals, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\left[ {x - \dfrac{x{^2}}{2}} \right] _{ - 2}^1 + \left[ {\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2} - x} \right] _1^4\]
Now, find the integration of the terms as:
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\left[ {\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) - \left( { - 2 - \dfrac{4}{2}} \right)} \right] + \left[ {\left( {\dfrac{{{4^2}}}{2}} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) - 1} \right] \]
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} + 4} \right] + \left[ {4 + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right] \]
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[8 + 1 = 9\] sq. units.
Hence, the graph of \[y = \left| {x - 1} \right|\] is represented as:
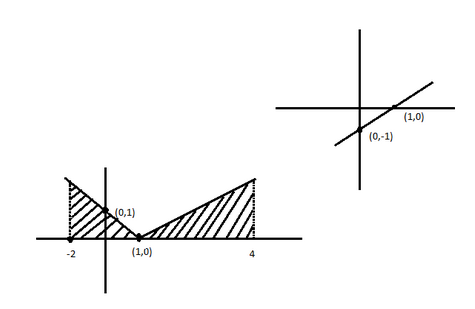
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The different methods of integration include:
Integration by Substitution: To find the integration of a function, thus we can find the integration by introducing a new independent variable. This method is called Integration by Substitution.
A.Integration by Parts: Integration by parts requires a special technique for integration of a function, where the integrand function is the multiple of two or more functions.
B.Integration Using Trigonometric Identities: In the integration of a function, if the integrand involves any kind of trigonometric function, then we use trigonometric identities to simplify the function that can be easily integrated.
C.Integration by Partial Fraction: a rational function is defined as the ratio of two polynomials which can be expressed in the form of partial fractions.
D.Integration of Some particular function: Integration of some particular function involves some important formulae of integration that can be applied to make other integration into the standard form of the integrand.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us write the given data,
We need to sketch the graph for: \[y = \left| {x - 1} \right|\] and Evaluate \[\int\limits_{ - 2}^4 {\left| {x - 1} \right|} dx\] .
As the range of the integral given is from -2 to 4, hence we get:
\[\int\limits_{ - 2}^4 {\left| {x - 1} \right|} dx\] = \[\int\limits_{ - 2}^1 {\left| {x - 1} \right|} + \int\limits_1^4 {\left| {x - 1} \right|} \]
\[\left| {x - 1} \right|\] for \[x < 1\] , \[1 - x\]
\[\left| {x - 1} \right|\] for \[x > 1\] , \[x - 1\]
Hence, we get the equation as:
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\int\limits_{ - 2}^1 {\left( {1 - x} \right)dx} + \int\limits_1^4 {\left( {x - 1} \right)dx} \]
Apply the integrals, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\left[ {x - \dfrac{x{^2}}{2}} \right] _{ - 2}^1 + \left[ {\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2} - x} \right] _1^4\]
Now, find the integration of the terms as:
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\left[ {\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) - \left( { - 2 - \dfrac{4}{2}} \right)} \right] + \left[ {\left( {\dfrac{{{4^2}}}{2}} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right) - 1} \right] \]
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} + 4} \right] + \left[ {4 + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right] \]
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[8 + 1 = 9\] sq. units.
Hence, the graph of \[y = \left| {x - 1} \right|\] is represented as:

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The different methods of integration include:
Integration by Substitution: To find the integration of a function, thus we can find the integration by introducing a new independent variable. This method is called Integration by Substitution.
A.Integration by Parts: Integration by parts requires a special technique for integration of a function, where the integrand function is the multiple of two or more functions.
B.Integration Using Trigonometric Identities: In the integration of a function, if the integrand involves any kind of trigonometric function, then we use trigonometric identities to simplify the function that can be easily integrated.
C.Integration by Partial Fraction: a rational function is defined as the ratio of two polynomials which can be expressed in the form of partial fractions.
D.Integration of Some particular function: Integration of some particular function involves some important formulae of integration that can be applied to make other integration into the standard form of the integrand.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




