
Sketch the diagrammatic representation of replication of retrovirus inside an animal cell.
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Viruses are unique creations of nature that are alive inside the host but exist as non-living particles outside the host. They are used to study various phenomena of molecular biology. A typical virus contains an outer protein coat and a nucleic acid component inside it. The nucleic acid may either be DNA or RNA. Viruses proliferate inside a host cell, which can be prokaryotic or eukaryotic, by replicating its genetic component (either DNA or RNA) using host cell machinery.
Complete answer:
The virion first attaches to the surface of the bacterial membrane and inserts its genetic material, RNA molecules inside the host cell. The RNA, using the enzymes of the host cell, first produces reverse transcriptase enzymes to direct the phenomena of Reverse transcription. In this procedure, the reverse transcriptase enzyme synthesizes DNA from the viral RNA molecules. The DNA thus produced enters the nucleus and integrates with the host’s chromosome. The viral DNA now replicates as well as transcripts along with the host DNA using the host's replication and transcription machinery and thus produces viral RNA and proteins (via translation) forming multiple copies of virus within the host. The mechanism of viral RNA infection and the method of replication and synthesis of new viruses are described in the diagram below.
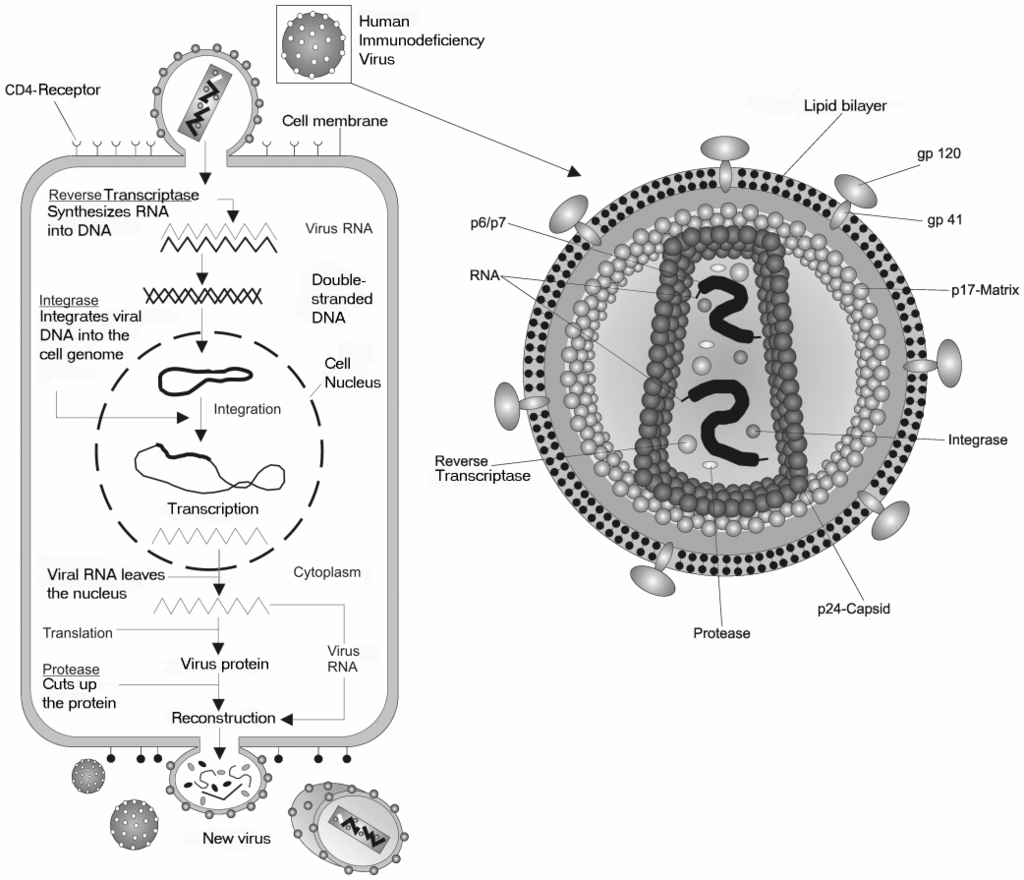
Figure: Diagrammatic representation of replication of retrovirus inside an animal cell
Note:
Retroviruses contain two identical single-stranded RNA molecules. During their growth cycle, these viruses reverse their flow of genetic information, that is, DNA from RNA. This phenomena is accomplished by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This is a very unique feature exhibited in retroviruses. An example of Retrovirus is Rous sarcoma virus (RSV).
Complete answer:
The virion first attaches to the surface of the bacterial membrane and inserts its genetic material, RNA molecules inside the host cell. The RNA, using the enzymes of the host cell, first produces reverse transcriptase enzymes to direct the phenomena of Reverse transcription. In this procedure, the reverse transcriptase enzyme synthesizes DNA from the viral RNA molecules. The DNA thus produced enters the nucleus and integrates with the host’s chromosome. The viral DNA now replicates as well as transcripts along with the host DNA using the host's replication and transcription machinery and thus produces viral RNA and proteins (via translation) forming multiple copies of virus within the host. The mechanism of viral RNA infection and the method of replication and synthesis of new viruses are described in the diagram below.

Figure: Diagrammatic representation of replication of retrovirus inside an animal cell
Note:
Retroviruses contain two identical single-stranded RNA molecules. During their growth cycle, these viruses reverse their flow of genetic information, that is, DNA from RNA. This phenomena is accomplished by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This is a very unique feature exhibited in retroviruses. An example of Retrovirus is Rous sarcoma virus (RSV).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




