
Show that the height of the cylinder of maximum volume, that can be inscribed in a sphere of radius R is $\dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}}$. Also, find the maximum volume.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: We solve this question by first finding the volume of the cylinder and then find the radius of cylinder in terms of radius of sphere and height of the cylinder and substitute it in the formula for volume of the cylinder, $Volume\text{ }of\text{ }cylinder=\pi \times {{\left( radius \right)}^{2}}\times \left( height \right)$. Then we differentiate the volume with respect to height and equate it to zero to find the condition for the maximum volume. Then we get the height of the cylinder in terms of the radius of the sphere, substitute it in the formula of volume to get the maximum volume of the cylinder.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We were given that the radius of the sphere is R.
Let the radius of the cylinder be r and the height of the cylinder be h.
Let us consider the formula for the volume of cylinder,
$Volume\text{ }of\text{ }cylinder=\pi \times {{\left( radius \right)}^{2}}\times \left( height \right)$
Using the above formula, we can write the volume of the cylinder as,
$V=\pi {{r}^{2}}h$
Now, as the cylinder is inscribed inside a sphere, the centre of the sphere is the same as the center of the cylinder. So, now let us take a look at the figure below.
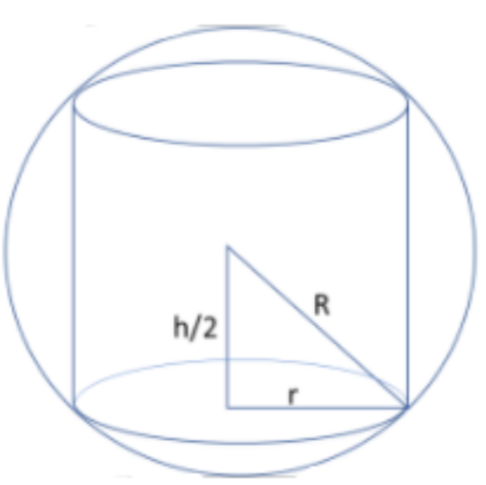
As we see above triangle is right angled. Hence applying the Pythagoras theorem, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{h}{2} \right)}^{2}}={{R}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}+\dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{4}={{R}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}={{R}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Now let us substitute the value of r in the volume. Then, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow V=\pi {{r}^{2}}h \\
& \Rightarrow V=\pi \left( {{R}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{4} \right)h \\
& \Rightarrow V=\pi {{R}^{2}}h-\pi \dfrac{{{h}^{3}}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Now let us discuss the concept of optimization. A function $f\left( x \right)$ is said to achieve extremum that is maximum or minimum if it satisfies the condition,
${f}'\left( x \right)=0$
As we need to find the maximum value of volume, let us differentiate the volume with respective to h.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \pi {{R}^{2}}h-\pi \dfrac{{{h}^{3}}}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \pi {{R}^{2}}h \right)-\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \pi \dfrac{{{h}^{3}}}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
When the volume is maximum, $\dfrac{dV}{dh}=0$. So, equating the value of $\dfrac{dV}{dh}$ to zero.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \pi {{R}^{2}}=\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{R}^{2}}=\dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=\dfrac{4{{R}^{2}}}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}$
So, we get the height of cylinder as $h=\dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}}$.
Now we need to find it is the condition is for maximum or minimum.
The condition for maximum is a double derivative of the function should be negative.
As $\dfrac{dV}{dh}=\pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4}$, let us differentiate it with h to find the double derivative.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}}=\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}}=-\pi \dfrac{3\times 2h}{4}=-\dfrac{3\pi h}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us substitute the values obtained in the double derivative of volume.
\[\Rightarrow {{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}} \right]}_{h=\dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}}}}=-\dfrac{3\pi \dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}}}{2}<0\]
As the double derivative is negative when $h=\dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}}$. It is the value for which the volume is maximum.
Hence proved.
Now let us substitute this value in the formula of volume of cylinder. Then we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow V=\pi {{R}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}} \right)-\pi \dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{3}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{2\pi {{R}^{3}}}{\sqrt{3}}-\pi \dfrac{\dfrac{8{{R}^{3}}}{3\sqrt{3}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{2\pi {{R}^{3}}}{\sqrt{3}}-\dfrac{8\pi {{R}^{3}}}{4\times 3\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{2\pi {{R}^{3}}}{\sqrt{3}}-\dfrac{2\pi {{R}^{3}}}{3\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{4\pi {{R}^{3}}}{3\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}$
So, maximum value of cylinder inscribed in a sphere of radius R is $\dfrac{4\pi {{R}^{3}}}{3\sqrt{3}}$ cubic units.
Note: We can also find the maximum volume by changing the height of the cylinder in terms of the radius of sphere and radius of the cylinder as $h=2\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{r}^{2}}}$ and then substitute it in the volume of the cylinder. Then we can differentiate it with respective to $r$ and find the value of $r$ for maximum volume and substitute in the above formula for $h$. But it a long way to find the answer. As we are asked about the height in the question, it is easier to solve it by starting with eliminating $r$ and writing it in terms of $h$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We were given that the radius of the sphere is R.
Let the radius of the cylinder be r and the height of the cylinder be h.
Let us consider the formula for the volume of cylinder,
$Volume\text{ }of\text{ }cylinder=\pi \times {{\left( radius \right)}^{2}}\times \left( height \right)$
Using the above formula, we can write the volume of the cylinder as,
$V=\pi {{r}^{2}}h$
Now, as the cylinder is inscribed inside a sphere, the centre of the sphere is the same as the center of the cylinder. So, now let us take a look at the figure below.

As we see above triangle is right angled. Hence applying the Pythagoras theorem, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{h}{2} \right)}^{2}}={{R}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}+\dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{4}={{R}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{r}^{2}}={{R}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Now let us substitute the value of r in the volume. Then, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow V=\pi {{r}^{2}}h \\
& \Rightarrow V=\pi \left( {{R}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{4} \right)h \\
& \Rightarrow V=\pi {{R}^{2}}h-\pi \dfrac{{{h}^{3}}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Now let us discuss the concept of optimization. A function $f\left( x \right)$ is said to achieve extremum that is maximum or minimum if it satisfies the condition,
${f}'\left( x \right)=0$
As we need to find the maximum value of volume, let us differentiate the volume with respective to h.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \pi {{R}^{2}}h-\pi \dfrac{{{h}^{3}}}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \pi {{R}^{2}}h \right)-\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \pi \dfrac{{{h}^{3}}}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
When the volume is maximum, $\dfrac{dV}{dh}=0$. So, equating the value of $\dfrac{dV}{dh}$ to zero.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dV}{dh}=\pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \pi {{R}^{2}}=\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{R}^{2}}=\dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}=\dfrac{4{{R}^{2}}}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}$
So, we get the height of cylinder as $h=\dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}}$.
Now we need to find it is the condition is for maximum or minimum.
The condition for maximum is a double derivative of the function should be negative.
As $\dfrac{dV}{dh}=\pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4}$, let us differentiate it with h to find the double derivative.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}}=\dfrac{d}{dh}\left( \pi {{R}^{2}}-\pi \dfrac{3{{h}^{2}}}{4} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}}=-\pi \dfrac{3\times 2h}{4}=-\dfrac{3\pi h}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us substitute the values obtained in the double derivative of volume.
\[\Rightarrow {{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}V}{d{{h}^{2}}} \right]}_{h=\dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}}}}=-\dfrac{3\pi \dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}}}{2}<0\]
As the double derivative is negative when $h=\dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}}$. It is the value for which the volume is maximum.
Hence proved.
Now let us substitute this value in the formula of volume of cylinder. Then we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow V=\pi {{R}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}} \right)-\pi \dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{2R}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{3}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{2\pi {{R}^{3}}}{\sqrt{3}}-\pi \dfrac{\dfrac{8{{R}^{3}}}{3\sqrt{3}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{2\pi {{R}^{3}}}{\sqrt{3}}-\dfrac{8\pi {{R}^{3}}}{4\times 3\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{2\pi {{R}^{3}}}{\sqrt{3}}-\dfrac{2\pi {{R}^{3}}}{3\sqrt{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{4\pi {{R}^{3}}}{3\sqrt{3}} \\
\end{align}$
So, maximum value of cylinder inscribed in a sphere of radius R is $\dfrac{4\pi {{R}^{3}}}{3\sqrt{3}}$ cubic units.
Note: We can also find the maximum volume by changing the height of the cylinder in terms of the radius of sphere and radius of the cylinder as $h=2\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}-{{r}^{2}}}$ and then substitute it in the volume of the cylinder. Then we can differentiate it with respective to $r$ and find the value of $r$ for maximum volume and substitute in the above formula for $h$. But it a long way to find the answer. As we are asked about the height in the question, it is easier to solve it by starting with eliminating $r$ and writing it in terms of $h$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




