
$S{F_6}$ is inert towards hydrolysis. Explain the following:
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: In the question we have a compound - $S{F_6}$, called sulfur hexafluoride which is a greenhouse gas which is used as an electrical insulator. It is colorless, odorless, non-flammable and non-toxic. We have to remember that the inert substance means which is chemically unreactive or non-labile. To understand why it acts like an inert gas, we will study its chemical structure.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to remember that the element sulphur lies in period 3 in the modern periodic table. Which implies that it can have an extended valency. It has 6 electrons in the outermost shell. But rather than losing 6 electrons it can gain two more electrons from a withdrawing atom and thus satisfy its valency, so its valency can be 2 as well.
The valency of fluorine is one, and it is an electron withdrawing element.
To satisfy the valency six of the sulphur atom, 6 fluorine atoms will bond with 1 sulphur atom to form the compound sulphur hexafluoride. $S{F_6}$ has octahedral shape and we can draw the structure of this compound as,
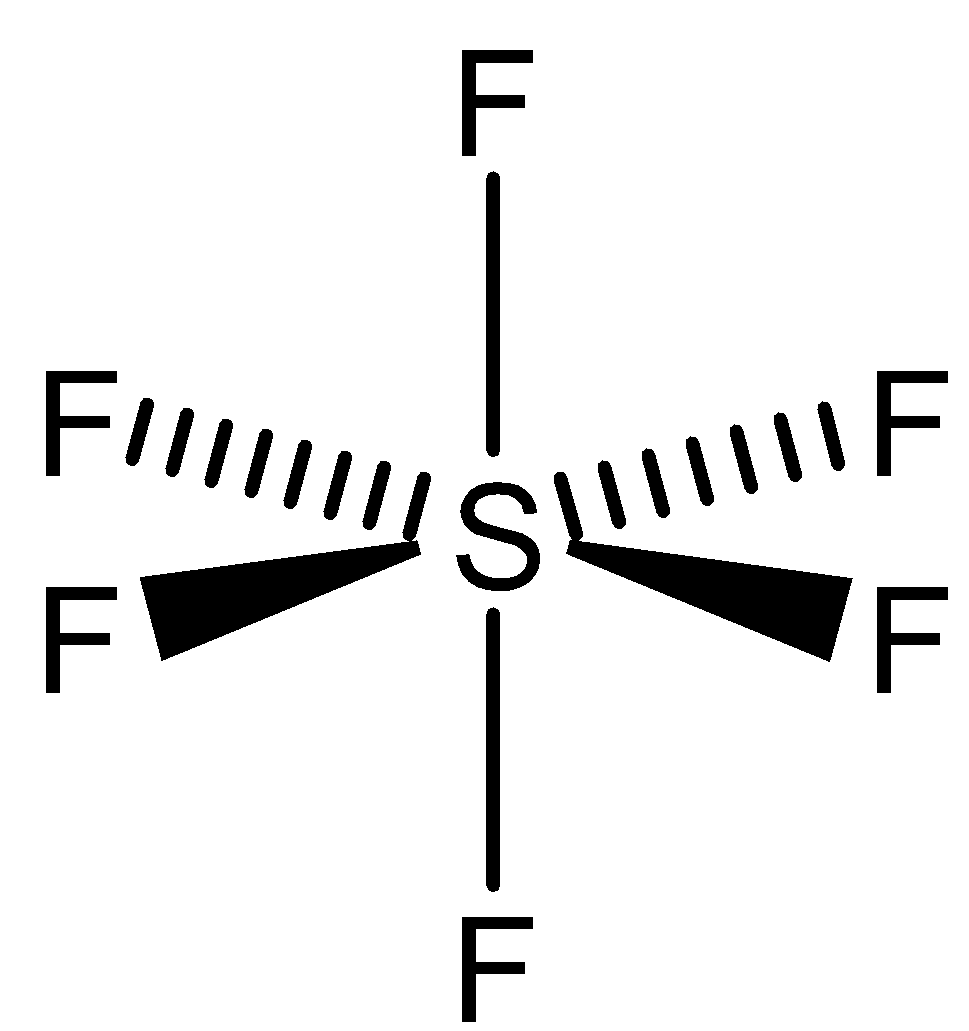
In this there is no lone pair available, all the valency pairs are satisfied. In $S{F_6}$, the sulphur atom is surrounded by six fluorine atoms which does not allow the water molecule to attack sulphur atom. So there is no space for water molecules to attack the sulphur atom. Since the fluorine valence atoms too are satisfied, so the water cannot attack on fluorine as well.
Due to this the hydrolysis cannot take place.
Hence, $S{F_6}$ is inert towards hydrolysis.
Note: We have to know that the sulphur is an element which can have extended valency from -1 to even +12. Due to this property the valency can be satisfied with a number of combinations. And thus having many valencies doesn’t allow it to be paired or attacked by other agents to undergo the process. It only happens when there is a lone pair or a positive anion or cation.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to remember that the element sulphur lies in period 3 in the modern periodic table. Which implies that it can have an extended valency. It has 6 electrons in the outermost shell. But rather than losing 6 electrons it can gain two more electrons from a withdrawing atom and thus satisfy its valency, so its valency can be 2 as well.
The valency of fluorine is one, and it is an electron withdrawing element.
To satisfy the valency six of the sulphur atom, 6 fluorine atoms will bond with 1 sulphur atom to form the compound sulphur hexafluoride. $S{F_6}$ has octahedral shape and we can draw the structure of this compound as,

In this there is no lone pair available, all the valency pairs are satisfied. In $S{F_6}$, the sulphur atom is surrounded by six fluorine atoms which does not allow the water molecule to attack sulphur atom. So there is no space for water molecules to attack the sulphur atom. Since the fluorine valence atoms too are satisfied, so the water cannot attack on fluorine as well.
Due to this the hydrolysis cannot take place.
Hence, $S{F_6}$ is inert towards hydrolysis.
Note: We have to know that the sulphur is an element which can have extended valency from -1 to even +12. Due to this property the valency can be satisfied with a number of combinations. And thus having many valencies doesn’t allow it to be paired or attacked by other agents to undergo the process. It only happens when there is a lone pair or a positive anion or cation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




