
Select schemes A, B, C out of the given below.
I. Acid catalysed hydration
II. Hydroboration oxidation
III. Oxymercuration-demercuration
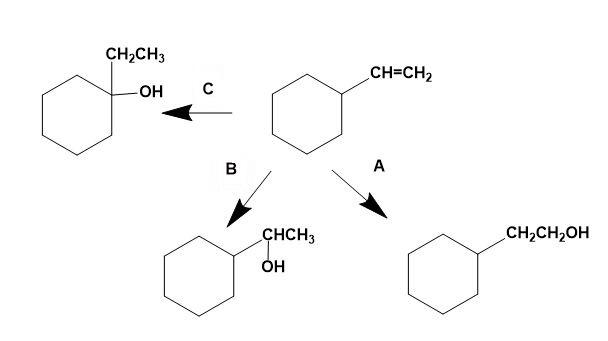
(A) I in all cases
(B) I, II, III
(C) II, III, I
(D) III, I, II

Answer
561k+ views
Hint: The description of all the given reactions can help us link the given illustration with the respective reactions and the products.
The correct sequence and explanation will give us the correct answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us solve this illustration by discussing all the given mechanisms one by one;
Primarily, same alkene produces different types of alcohols or hydration products depending on different hydration pathways; they are
1. Acid catalysed hydration-
This involves replacing the pi bond on the alkene with water molecules. This mechanism follows Markovnikov's rule i.e. alcohol will add to the more substituted carbon atom and hydrogen to the less substituted carbon atom. Notefully, this reaction can undergo carbocation rearrangement due to presence of acid as a catalyst for the same.
- The mechanism is as follows;
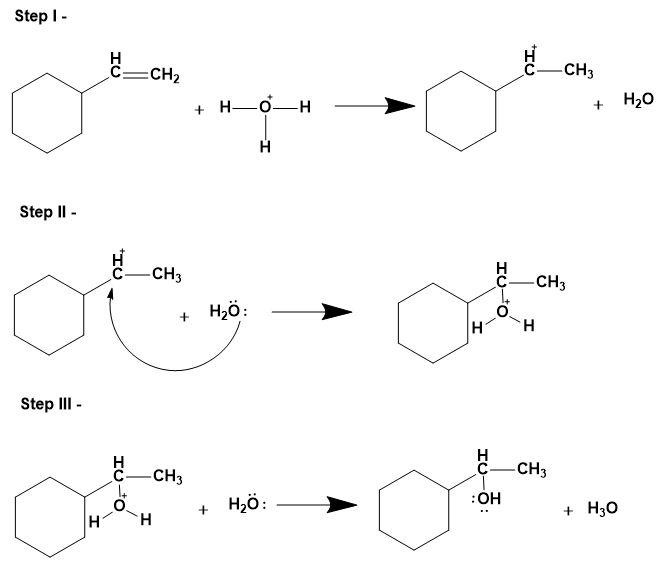
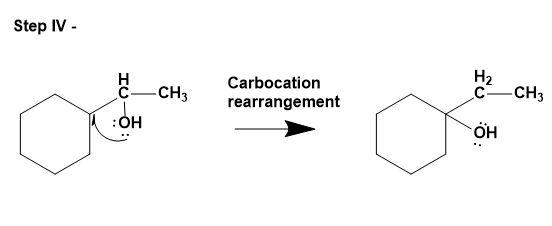
2. Hydroboration oxidation-
This mechanism too involves the replacement of the double bond by single bond and formation of an alcohol molecule. This reaction takes place by Anti-Markovnikov's rule i.e. hydroxyl group attaching to the less substituted carbon atom; for the stability of the substituted carbocation.
The mechanism is as follows:
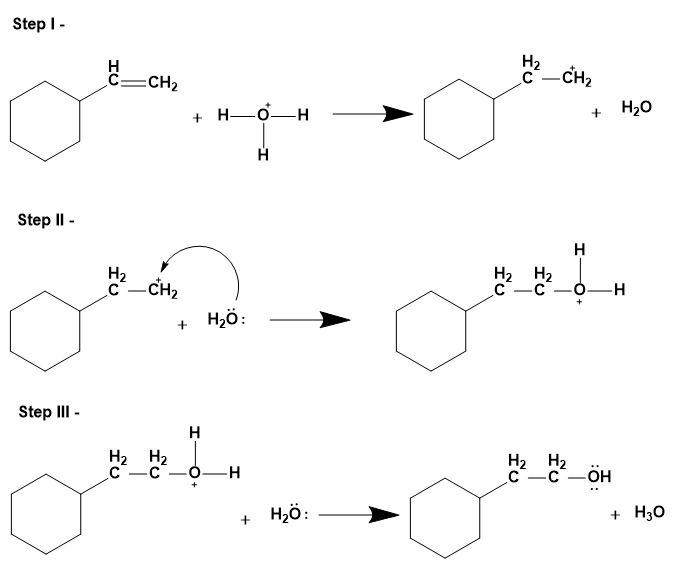
3. Oxymercuration – demercuration-
This is an electrophilic addition of a water molecule across the double bond of alkene compound to give a neutral alcohol. This takes place by Markovnickov’s rule i.e. hydroxyl group attaching to more substituted carbon atom and the hydrogen atom attaching to less substituted carbon atom.
The mechanism is as follows:
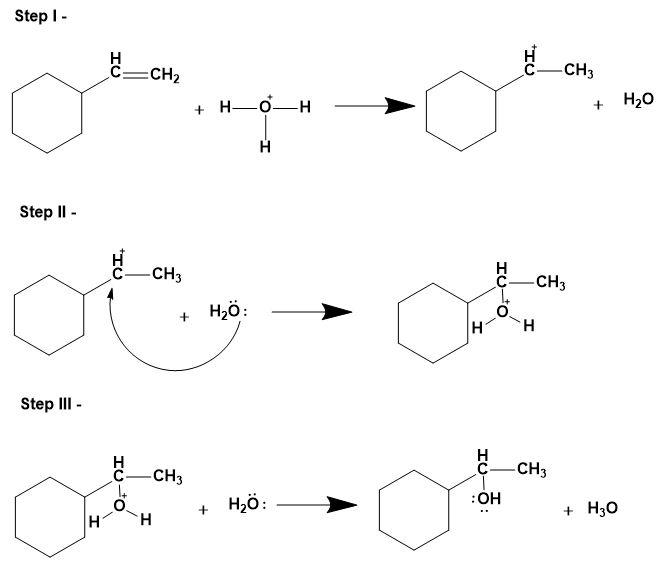
Thus, for the given illustration, we can say that;
A is hydroboration oxidation, B is oxymercuration-demercuration and C is acid catalysed hydration processes to produce different types of alcohols from the same alkene.
The correct answer is option “C” .
Note: Do note that students may get confused between the mechanisms of acid catalysed hydration and oxymercuration-demercuration reactions. As they are same but the prior one can go carbocation rearrangement for the stabilisation whereas, the later won’t and that’s why the products will differ.
The correct sequence and explanation will give us the correct answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us solve this illustration by discussing all the given mechanisms one by one;
Primarily, same alkene produces different types of alcohols or hydration products depending on different hydration pathways; they are
1. Acid catalysed hydration-
This involves replacing the pi bond on the alkene with water molecules. This mechanism follows Markovnikov's rule i.e. alcohol will add to the more substituted carbon atom and hydrogen to the less substituted carbon atom. Notefully, this reaction can undergo carbocation rearrangement due to presence of acid as a catalyst for the same.
- The mechanism is as follows;


2. Hydroboration oxidation-
This mechanism too involves the replacement of the double bond by single bond and formation of an alcohol molecule. This reaction takes place by Anti-Markovnikov's rule i.e. hydroxyl group attaching to the less substituted carbon atom; for the stability of the substituted carbocation.
The mechanism is as follows:

3. Oxymercuration – demercuration-
This is an electrophilic addition of a water molecule across the double bond of alkene compound to give a neutral alcohol. This takes place by Markovnickov’s rule i.e. hydroxyl group attaching to more substituted carbon atom and the hydrogen atom attaching to less substituted carbon atom.
The mechanism is as follows:

Thus, for the given illustration, we can say that;
A is hydroboration oxidation, B is oxymercuration-demercuration and C is acid catalysed hydration processes to produce different types of alcohols from the same alkene.
The correct answer is option “C” .
Note: Do note that students may get confused between the mechanisms of acid catalysed hydration and oxymercuration-demercuration reactions. As they are same but the prior one can go carbocation rearrangement for the stabilisation whereas, the later won’t and that’s why the products will differ.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




