
Schottky defect in crystals is observed when:
A ) An unequal number of cations and anions are missing from the lattice.
B ) equal number of cations and anions are missing from the lattice.
C ) an ion leaves its normal site and occupies an interstitial site.
D ) density of the crystal is increased.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Different types of defects present in the crystal are stoichiometric and non stoichiometric defects. Schottky defect and frenkel defect are stoichiometric defects. Non stoichiometric effects include metal excess defects and metal deficiency defects.
Complete answer:
The diagrammatic representation for schottky defect and frenkel defect is as shown below:
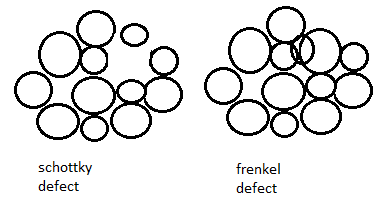
Schottky defect in crystals is observed when equal numbers of cations and anions are missing from the lattice. It is important that an equal number of cations and anions are missing, otherwise the electrical neutrality of the crystal will get affected.
A crystal is electrically neutral when the total of positive charges is equal to the total of negative charges. When an unequal number of cations and anions are missing, the crystal will have a net charge and will not be electrically neutral. Hence, option A ) is the incorrect answer.
Due to the Schottky defect, the density of the crystal is decreased. This is because ions (both cations and anions) are missing from the crystal. In the position, from which ions are present, only empty space (or void) is present.
Due to the presence of a large number of empty spaces, the density of the crystal decreases. This is because the total volume of the crystal remains the same as the dimensions of the unit cells are the same, but the total mass of the crystal decreases as some ions are missing. Density is the ratio of mass to volume. When volume remains the same, and if mass decreases, the density decreases. Hence, the option D ) is an incorrect option.
Schottky defect in crystals is observed when equal numbers of cations and anions are missing from the lattice.
Hence, the option B ) is the correct answer.
Additional Information In Frenkel defect, a cation is missing from its original position and is present in interstitial position.
Note: In the schottky defect, atoms or ions are permanently missing from the crystal. In the Frenkel defect, atoms or ions are present in the interstitial sites of the crystal, they do not permanently leave the crystal. In schottky defect, both cation and anion are missing from the crystal. In the Frenkel defect, only cations leave their original position as cations are smaller than anion and can easily fit into interstitial positions.
Complete answer:
The diagrammatic representation for schottky defect and frenkel defect is as shown below:

Schottky defect in crystals is observed when equal numbers of cations and anions are missing from the lattice. It is important that an equal number of cations and anions are missing, otherwise the electrical neutrality of the crystal will get affected.
A crystal is electrically neutral when the total of positive charges is equal to the total of negative charges. When an unequal number of cations and anions are missing, the crystal will have a net charge and will not be electrically neutral. Hence, option A ) is the incorrect answer.
Due to the Schottky defect, the density of the crystal is decreased. This is because ions (both cations and anions) are missing from the crystal. In the position, from which ions are present, only empty space (or void) is present.
Due to the presence of a large number of empty spaces, the density of the crystal decreases. This is because the total volume of the crystal remains the same as the dimensions of the unit cells are the same, but the total mass of the crystal decreases as some ions are missing. Density is the ratio of mass to volume. When volume remains the same, and if mass decreases, the density decreases. Hence, the option D ) is an incorrect option.
Schottky defect in crystals is observed when equal numbers of cations and anions are missing from the lattice.
Hence, the option B ) is the correct answer.
Additional Information In Frenkel defect, a cation is missing from its original position and is present in interstitial position.
Note: In the schottky defect, atoms or ions are permanently missing from the crystal. In the Frenkel defect, atoms or ions are present in the interstitial sites of the crystal, they do not permanently leave the crystal. In schottky defect, both cation and anion are missing from the crystal. In the Frenkel defect, only cations leave their original position as cations are smaller than anion and can easily fit into interstitial positions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




