
What is the role of graphite in the electrometallurgy of aluminium?
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: We can use the graphite in the electrolysis of alumina. Graphite prevents the evolution of a gas in the electrometallurgy of aluminum.
Complete step by step answer:
The anode used in the electrolysis of alumina is graphite rod and the cathode used is graphite-lined iron.
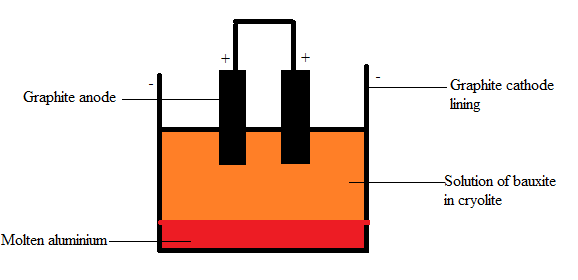
During the electrolysis, aluminum is given at the cathode and oxygen is liberated at the anode. Oxygen further reacts with the anodic graphite to form carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, thereby preventing the evolved oxygen from oxidizing aluminium.
In the cathode,
${\text{A}}{{\text{l}}^{{\text{3 + }}}}{\text{ + 3}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}\xrightarrow{{}}{\text{Al}}$
In the anode,
${\text{C + }}{{\text{O}}^{{\text{2 - }}}}\xrightarrow{{}}{\text{CO + 2}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$
${\text{C + 2}}{{\text{O}}^{{\text{2 - }}}}\xrightarrow{{}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 4}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$
The role of graphite in electrometallurgy of aluminium is to avoid the release of oxygen so that the aluminium is not oxidized by oxygen.
Additional Information:
Electrometallurgy is a process that takes place in the form of an electrolytic cell.
In the electrometallurgy of aluminium, a fused mixture of alumina, cryolite and fluorspar is electrolyzed.
In electrolysis, aluminium is released at the cathode, while carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide are evolved at the anode.
In case any other metal other than graphite is used as anode, oxygen will be evolved.
The metal not only oxidizes the electrode metal, but also converts some of liberated aluminum at the cathode to alumina,
Graphite is cost effective.
Note:
We must know the concept of electrometallurgy deals with the process of electrodeposition of metals. Electrometallurgy is a technique, which uses electrical energy to obtain metals by electrolysis. There are four types of this process. They are electrowinning, electrorefining, electroplating and electroforming. Extraction of aluminum from aluminium oxide is an example of an electroforming process that is processing of thin metal parts through electroplating.
Complete step by step answer:
The anode used in the electrolysis of alumina is graphite rod and the cathode used is graphite-lined iron.

During the electrolysis, aluminum is given at the cathode and oxygen is liberated at the anode. Oxygen further reacts with the anodic graphite to form carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, thereby preventing the evolved oxygen from oxidizing aluminium.
In the cathode,
${\text{A}}{{\text{l}}^{{\text{3 + }}}}{\text{ + 3}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}\xrightarrow{{}}{\text{Al}}$
In the anode,
${\text{C + }}{{\text{O}}^{{\text{2 - }}}}\xrightarrow{{}}{\text{CO + 2}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$
${\text{C + 2}}{{\text{O}}^{{\text{2 - }}}}\xrightarrow{{}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 4}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{ - }}}$
The role of graphite in electrometallurgy of aluminium is to avoid the release of oxygen so that the aluminium is not oxidized by oxygen.
Additional Information:
Electrometallurgy is a process that takes place in the form of an electrolytic cell.
In the electrometallurgy of aluminium, a fused mixture of alumina, cryolite and fluorspar is electrolyzed.
In electrolysis, aluminium is released at the cathode, while carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide are evolved at the anode.
In case any other metal other than graphite is used as anode, oxygen will be evolved.
The metal not only oxidizes the electrode metal, but also converts some of liberated aluminum at the cathode to alumina,
Graphite is cost effective.
Note:
We must know the concept of electrometallurgy deals with the process of electrodeposition of metals. Electrometallurgy is a technique, which uses electrical energy to obtain metals by electrolysis. There are four types of this process. They are electrowinning, electrorefining, electroplating and electroforming. Extraction of aluminum from aluminium oxide is an example of an electroforming process that is processing of thin metal parts through electroplating.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




