
Reserve food material of fungi is
(a) Starch
(b) Protein
(c) Glucose
(d) Glycogen
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Reserve food material is reserve of fats, carbohydrates, or rarely proteins in cells and tissues that function as important stores of energy that can be released and used for ATP production whenever required by the organism. The reserve food material in Fungi is the same as that in the humans.
Complete answer:
Reserve food materials can be fats or complex carbohydrates like Starch. In fungi, the reserve food material is a multibranched polysaccharide called Glycogen.
Additional Information:
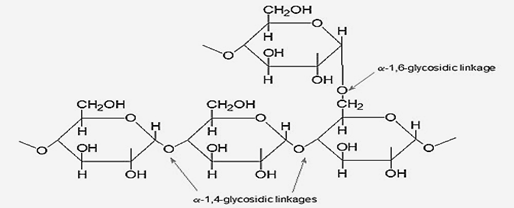
-Glycogen is an insoluble polysaccharide with an empirical formula $({ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 10 }{ O }_{ 5 })_{ n }$.
-Glycogen is a branched polymer formed from linear chains of glucose molecules. They have an average chain length of about 8–12 glucose units.
-Each glucose unit is linked to the other unit linearly by $\alpha ({ 1\rightarrow }{ 4) }$ glycosidic bonds from one molecule to the other. Branches are linked to the linear by $\alpha ({ 1\rightarrow }{ 6) }$ glycosidic bonds between the first glucose of the branch and the glucose molecule on the stem chain.
-Glycogen gives reddish coloration on adding an iodine solution.
-It is present abundantly in the muscles and liver of the animals as reserve food material. It is also called animal starch, due to its function analogous to starch in plants.
-Glycogen is also in some blue-green algae, slime molds, bacteria, and also in fungi and acts as reserve food.
-It is ultimately broken down into glucose by enzymatic action and then assimilated.
-Thus, Glycogen acts as a reserve food storage which can be broken down into glucose and used for energy production and it is the primary storage form in Animals and Fungi.
So, the answer is, “Glycogen.”
Note: In humans this glycogen is stored in the liver and is broken down to glucose whenever energy is required using a process known as Glycogenolysis.
Another polymer of glucose called Starch is the main reserve food material in plants.
It has the same empirical formula $({ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 10 }{ O }_{ 5 })_{ n }$ as Glycogen but it is a linear polysaccharide. It is formed of two different chains, amylose and amylopectin chains.
Complete answer:
Reserve food materials can be fats or complex carbohydrates like Starch. In fungi, the reserve food material is a multibranched polysaccharide called Glycogen.
Additional Information:
-Glycogen is an insoluble polysaccharide with an empirical formula $({ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 10 }{ O }_{ 5 })_{ n }$.
-Glycogen is a branched polymer formed from linear chains of glucose molecules. They have an average chain length of about 8–12 glucose units.
-Each glucose unit is linked to the other unit linearly by $\alpha ({ 1\rightarrow }{ 4) }$ glycosidic bonds from one molecule to the other. Branches are linked to the linear by $\alpha ({ 1\rightarrow }{ 6) }$ glycosidic bonds between the first glucose of the branch and the glucose molecule on the stem chain.
-Glycogen gives reddish coloration on adding an iodine solution.
-It is present abundantly in the muscles and liver of the animals as reserve food material. It is also called animal starch, due to its function analogous to starch in plants.
-Glycogen is also in some blue-green algae, slime molds, bacteria, and also in fungi and acts as reserve food.
-It is ultimately broken down into glucose by enzymatic action and then assimilated.
-Thus, Glycogen acts as a reserve food storage which can be broken down into glucose and used for energy production and it is the primary storage form in Animals and Fungi.

So, the answer is, “Glycogen.”
Note: In humans this glycogen is stored in the liver and is broken down to glucose whenever energy is required using a process known as Glycogenolysis.
Another polymer of glucose called Starch is the main reserve food material in plants.
It has the same empirical formula $({ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 10 }{ O }_{ 5 })_{ n }$ as Glycogen but it is a linear polysaccharide. It is formed of two different chains, amylose and amylopectin chains.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




