
Radius of curvature of convex mirror is 40cm and the size of the object is twice as that of the image, then the image distance is
A. 60cm
B. 20cm
C. 40cm
D. 30cm
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: From the given radius of curvature, you could find the focal length. Now recall the expressions for magnification and then apply the given condition on height of image and object and thus get the relation between image distance and object distance. Now you could substitute the same along with the focal length in mirror formula and hence get the image distance.
Formula used:
Mirror formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}$
Complete answer:
In the question we are given a convex lens whose radius of curvature is 40cm. We are also told that the size of the object is twice as that of the image and then we are asked to find the image distance using this information.
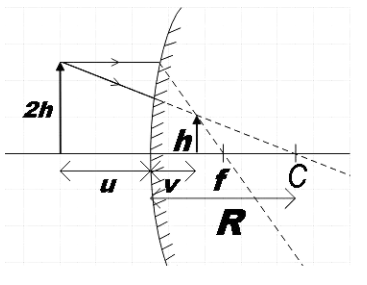
We know that the radius of curvature of a mirror is twice the focal length of the mirror. Therefore,
$R=2f$
Also, as the given mirror is convex, the radius of curvature is positive. So, the focal length given mirror will be,
$f=\dfrac{R}{2}$
$\Rightarrow f=\dfrac{40}{2}$
$\therefore f=20cm$ ……………………………………….. (1)
We know that magnification of a mirror can be given by two expressions: one in terms of height of image $\left( {{h}_{i}} \right)$ and object$\left( {{h}_{o}} \right)$ and the other in terms of object distance (u) and image distance (v).$m=\dfrac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}$
$m=-\dfrac{v}{u}$
Combining the two equations we get,
$\dfrac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}=-\dfrac{v}{u}$ ……………………………….. (2)
But we are given,
${{h}_{o}}=2{{h}_{i}}$
Now (2) becomes,
$\dfrac{{{h}_{i}}}{2{{h}_{i}}}=-\dfrac{v}{u}$
But u is negative for convex mirrors.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}=-\dfrac{v}{-u}$
$\therefore u=2v$ ………………………………………. (3)
Now, recall the mirror formula given by,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}$
But as u is negative for convex mirror,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
$\Rightarrow f=\dfrac{uv}{u-v}$
Substituting (1) and (3),
$20=\dfrac{2{{v}^{2}}}{2v-v}$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{20}{2}$
$\therefore v=10cm$
Therefore, we found the image distance of the given convex mirror to be,
$v=10cm$
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note:
In optics, the most fundamental part of solving numerical problems is getting the sign conventions right while substituting. We normally use the pole of the mirror (the point of the mirror that is on the principal axis) as the reference point while taking measurements. All the measurements made from pole to the left are taken negative and those to the right of pole are taken positive.
Formula used:
Mirror formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}$
Complete answer:
In the question we are given a convex lens whose radius of curvature is 40cm. We are also told that the size of the object is twice as that of the image and then we are asked to find the image distance using this information.

We know that the radius of curvature of a mirror is twice the focal length of the mirror. Therefore,
$R=2f$
Also, as the given mirror is convex, the radius of curvature is positive. So, the focal length given mirror will be,
$f=\dfrac{R}{2}$
$\Rightarrow f=\dfrac{40}{2}$
$\therefore f=20cm$ ……………………………………….. (1)
We know that magnification of a mirror can be given by two expressions: one in terms of height of image $\left( {{h}_{i}} \right)$ and object$\left( {{h}_{o}} \right)$ and the other in terms of object distance (u) and image distance (v).$m=\dfrac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}$
$m=-\dfrac{v}{u}$
Combining the two equations we get,
$\dfrac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}=-\dfrac{v}{u}$ ……………………………….. (2)
But we are given,
${{h}_{o}}=2{{h}_{i}}$
Now (2) becomes,
$\dfrac{{{h}_{i}}}{2{{h}_{i}}}=-\dfrac{v}{u}$
But u is negative for convex mirrors.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}=-\dfrac{v}{-u}$
$\therefore u=2v$ ………………………………………. (3)
Now, recall the mirror formula given by,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}$
But as u is negative for convex mirror,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
$\Rightarrow f=\dfrac{uv}{u-v}$
Substituting (1) and (3),
$20=\dfrac{2{{v}^{2}}}{2v-v}$
$\Rightarrow v=\dfrac{20}{2}$
$\therefore v=10cm$
Therefore, we found the image distance of the given convex mirror to be,
$v=10cm$
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note:
In optics, the most fundamental part of solving numerical problems is getting the sign conventions right while substituting. We normally use the pole of the mirror (the point of the mirror that is on the principal axis) as the reference point while taking measurements. All the measurements made from pole to the left are taken negative and those to the right of pole are taken positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




