
What product goes into glycolysis and what outcomes?
Answer
520.8k+ views
Hint: Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway in which glucose is broken down to produce energy in the form of ATP. It is a multistep process that occurs in the cytoplasm of plants, animals and microorganisms. The breakdown of glucose takes place in the presence of oxygen.
Complete answer:
We as living beings obtain energy through food. Food is the only source of energy which on metabolism liberates ATP. Glycolysis is an important process taking place which liberates ATP and NADH. The glucose is the substrate for the series of enzymatic reactions shown with the help of the diagram below.
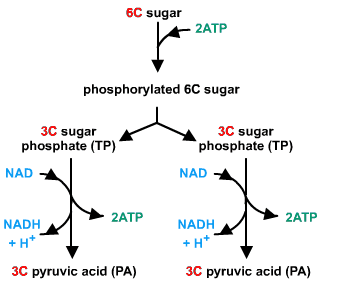
- One glucose molecule (sugar monomer) joins the cell. Enzymes cut glucose in half by converting it from a ringed to a linear structure. The end product is two Pyruvate molecules (pyruvic acid).
- If there is no oxygen available, each Pyruvate molecule is converted to lactic acid (makes your muscles feel sore). This provides a significant amount of energy in a small amount of time. Once oxygen is available again, the reaction can be reversed.
- The entire sequence generates a lot of energy (ATP/NADH/FADH), but it takes a long time.
- Despite the fact that four ATP molecules are generated in the second half of glycolysis, the net gain is only two ATP since two ATP molecules are used in the first half.
- The rate-limiting steps of glycolysis are enzymes that catalyse the reactions that generate ATP, and they must be present in sufficient amounts for glycolysis to complete the synthesis for four ATP, two NADH, and two pyruvate molecules for each glucose molecule that enters the pathway.
One molecule of glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen by the process of glycolysis to produce two pyruvates and yields ATP and NADH as energy.
Note:
- If oxygen is present, 1 glucose molecule is converted to 2 pyruvates, resulting in ATP and NADH energy.
- Since red blood cells lack mitochondria, they must rely on glycolysis as their primary source of ATP to survive.
- Glycolysis is also the primary source of ATP in cancer cells and stem cells (process known as aerobic glycolysis, or Warburg effect).
Complete answer:
We as living beings obtain energy through food. Food is the only source of energy which on metabolism liberates ATP. Glycolysis is an important process taking place which liberates ATP and NADH. The glucose is the substrate for the series of enzymatic reactions shown with the help of the diagram below.

- One glucose molecule (sugar monomer) joins the cell. Enzymes cut glucose in half by converting it from a ringed to a linear structure. The end product is two Pyruvate molecules (pyruvic acid).
- If there is no oxygen available, each Pyruvate molecule is converted to lactic acid (makes your muscles feel sore). This provides a significant amount of energy in a small amount of time. Once oxygen is available again, the reaction can be reversed.
- The entire sequence generates a lot of energy (ATP/NADH/FADH), but it takes a long time.
- Despite the fact that four ATP molecules are generated in the second half of glycolysis, the net gain is only two ATP since two ATP molecules are used in the first half.
- The rate-limiting steps of glycolysis are enzymes that catalyse the reactions that generate ATP, and they must be present in sufficient amounts for glycolysis to complete the synthesis for four ATP, two NADH, and two pyruvate molecules for each glucose molecule that enters the pathway.
One molecule of glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen by the process of glycolysis to produce two pyruvates and yields ATP and NADH as energy.
Note:
- If oxygen is present, 1 glucose molecule is converted to 2 pyruvates, resulting in ATP and NADH energy.
- Since red blood cells lack mitochondria, they must rely on glycolysis as their primary source of ATP to survive.
- Glycolysis is also the primary source of ATP in cancer cells and stem cells (process known as aerobic glycolysis, or Warburg effect).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




