
Photorespiration is favored by
(a)Low light and high ${ O }_{ 2 }$
(b)Low ${ O }_{ 2 }$ and high ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$
(c)Low temperature and high ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$
(d)High ${ O }_{ 2 }$ and low ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: In this process oxidation of RuBisCo enzyme takes place and oxygenates into RuBP, here some of the energy is wasted which was produced during photosynthesis. That is why it is also known as a wasteful pathway. It increases with the increase in temperature and ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ concentration.
Complete answer:
Photorespiration is favored by high ${ O }_{ 2 }$ and low ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ conditions.
During the Calvin cycle, the enzyme RuBisCo attaches to carbon dioxide and starts producing sugar through different stages of the Calvin cycle. But sometimes when the concentration of oxygen is higher than carbon dioxide, then the RuBisCo gets attached to ${ O }_{ 2 }$ instead of ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$. Thus causes the beginning of the photorespiration process. During photorespiration ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ is released and also energy is utilized. So, we can say that photorespiration wastes energy and decreases the synthesis of sugar, as it releases carbon dioxide utilized for the production of sugar.
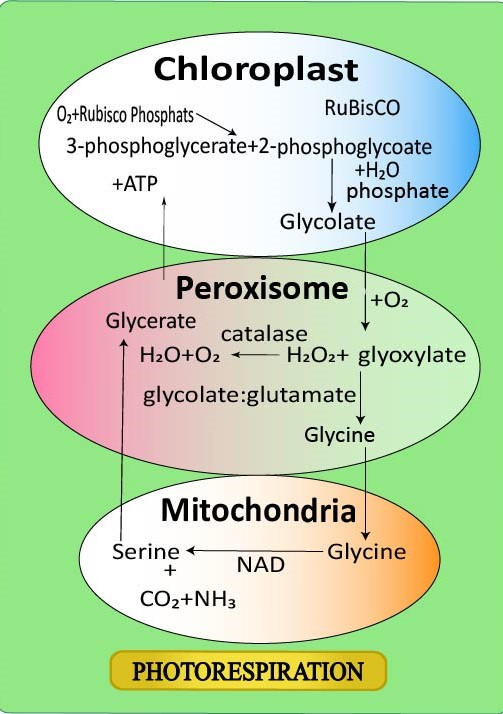
It is also known as the $C_2$ cycle. It is initiated in chloroplasts, but it occurs in peroxisomes.
Rate of photorespiration increased by:
-When stomata are closed to prevent water loss, the amount of ${ O }_{ 2 }$ gas increases, and ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ gas decreases.
-An increase in temperature causes the inability to recognize ${ O }_{ 2 }$ or ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ by RuBisCo and also reduces the solubility of ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ that results in a decrease in ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ concentration.
So, the correct answer is, ‘high ${ O }_{ 2 }$ and low ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$’
Note:
-Rubisco makes up ${ 30 }$%, percent, or more of the soluble protein in a typical plant leaf
ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).
-Photorespiration is also known as the $C_2$ cycle. It begins in chloroplast but occurs in peroxisomes.
-Photorespiration increases with an increase in temperature. Photorespiration does not produce any ATP and leads to a net loss of carbon and nitrogen (as ammonia), as a result, it slowdowns the process of plant growth.
Complete answer:
Photorespiration is favored by high ${ O }_{ 2 }$ and low ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ conditions.
During the Calvin cycle, the enzyme RuBisCo attaches to carbon dioxide and starts producing sugar through different stages of the Calvin cycle. But sometimes when the concentration of oxygen is higher than carbon dioxide, then the RuBisCo gets attached to ${ O }_{ 2 }$ instead of ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$. Thus causes the beginning of the photorespiration process. During photorespiration ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ is released and also energy is utilized. So, we can say that photorespiration wastes energy and decreases the synthesis of sugar, as it releases carbon dioxide utilized for the production of sugar.
It is also known as the $C_2$ cycle. It is initiated in chloroplasts, but it occurs in peroxisomes.

Rate of photorespiration increased by:
-When stomata are closed to prevent water loss, the amount of ${ O }_{ 2 }$ gas increases, and ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ gas decreases.
-An increase in temperature causes the inability to recognize ${ O }_{ 2 }$ or ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ by RuBisCo and also reduces the solubility of ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ that results in a decrease in ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$ concentration.
So, the correct answer is, ‘high ${ O }_{ 2 }$ and low ${ C }_{ O }_{ 2 }$’
Note:
-Rubisco makes up ${ 30 }$%, percent, or more of the soluble protein in a typical plant leaf
ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).
-Photorespiration is also known as the $C_2$ cycle. It begins in chloroplast but occurs in peroxisomes.
-Photorespiration increases with an increase in temperature. Photorespiration does not produce any ATP and leads to a net loss of carbon and nitrogen (as ammonia), as a result, it slowdowns the process of plant growth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




