
How is phenol prepared from chlorobenzene by Dow’s process?
Answer
520.2k+ views
Hint: Chlorobenzene is reacted with sodium hydroxide to form a phenoxide ion. This is treated with dilute HCl. There is the formation of two intermediates during the mechanism. One of which is highly reactive and unstable and this soon gets attacked by OH- to form the send intermediate which finally gives phenol.
Complete answer: Dow’s process is a process of preparation of phenol from chlorobenzene. During the process, the chlorobenzene reacts with an aqueous solution of NaOH at a temperature of \[{350^0}C\] and a pressure of \[150\] atmospheres. This produces sodium phenoxide ions. After this, the sodium phenoxide ion is treated with dilute HCl which finally gives phenol. The reaction gives rise to a formation of benzyne intermediate.
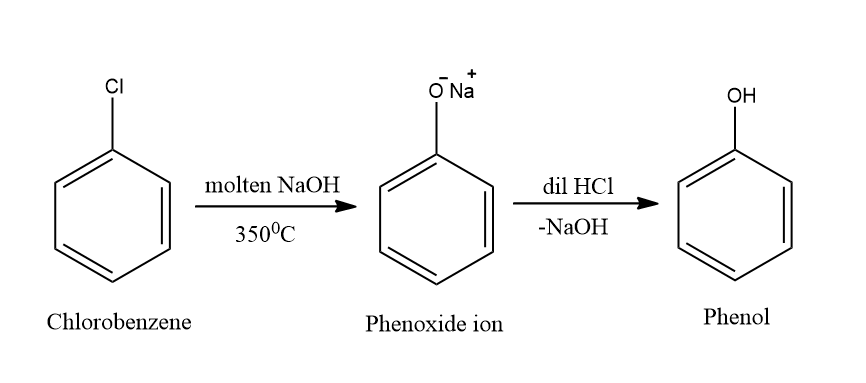
The above reaction can also be referred to as hydrolysis of chlorobenzene. The reaction taking place here is electrophilic-aromatic substitution. The preparation of phenol from chlorobenzene takes place through the following mechanism:
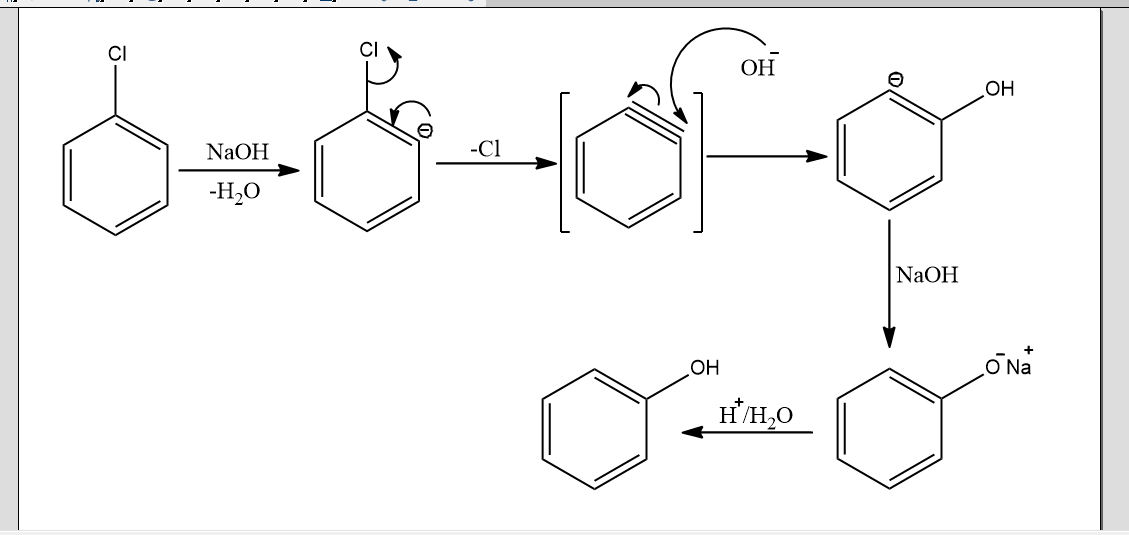
In the above mechanism, there is the removal of a proton from carbon adjacent to the carbon bonded to chlorine by the base in the first step. This leads to the formation of carbanion. Then, chlorine ions will leave the benzene ring to form a triple bond in the benzene ring. This is the intermediate form called benzyne intermediate. This intermediate is short-lived. It is very unstable and highly reactive. So in the second step, this is attacked by nucleophile OH- to form another intermediate phenoxide ion. Now in the final step, this phenoxide ion undergoes acidification and finally gives phenol.
Therefore in the following way phenol is prepared from chlorobenzene by Dow’s process.
Note:
It is important to note that there is no direct substitution happening in chlorine. First, the chlorine gets removed then intermediate forms, and then finally phenol is produced. The reaction occurring above is via the elimination-addition mechanism which involves a benzyne intermediate. Dow’s process is also an electrolytic method for the extraction of bromine from brine.
Complete answer: Dow’s process is a process of preparation of phenol from chlorobenzene. During the process, the chlorobenzene reacts with an aqueous solution of NaOH at a temperature of \[{350^0}C\] and a pressure of \[150\] atmospheres. This produces sodium phenoxide ions. After this, the sodium phenoxide ion is treated with dilute HCl which finally gives phenol. The reaction gives rise to a formation of benzyne intermediate.

The above reaction can also be referred to as hydrolysis of chlorobenzene. The reaction taking place here is electrophilic-aromatic substitution. The preparation of phenol from chlorobenzene takes place through the following mechanism:

In the above mechanism, there is the removal of a proton from carbon adjacent to the carbon bonded to chlorine by the base in the first step. This leads to the formation of carbanion. Then, chlorine ions will leave the benzene ring to form a triple bond in the benzene ring. This is the intermediate form called benzyne intermediate. This intermediate is short-lived. It is very unstable and highly reactive. So in the second step, this is attacked by nucleophile OH- to form another intermediate phenoxide ion. Now in the final step, this phenoxide ion undergoes acidification and finally gives phenol.
Therefore in the following way phenol is prepared from chlorobenzene by Dow’s process.
Note:
It is important to note that there is no direct substitution happening in chlorine. First, the chlorine gets removed then intermediate forms, and then finally phenol is produced. The reaction occurring above is via the elimination-addition mechanism which involves a benzyne intermediate. Dow’s process is also an electrolytic method for the extraction of bromine from brine.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE




