
Phenol is less acidic than?
A. Ethanol
B. O-nitrophenol
C. O-methyl phenyl
D. O-methoxy phenol
Answer
611.1k+ views
Hint: The acidic character depends on the stability of the ion which is left behind after ${ H }^{ + }$ is released. A negative charge is formed after the ${ H }^{ + }$ ion leaves. An electron-withdrawing group will have greater stability than an electron releasing group.
Complete answer:
Acids are the compounds that release ${ H }^{ + }$ ions. When the ${ H }^{ + }$ ion leaves the compound, it becomes a negatively charged ion. The stability of the negative charge determines the acidic character of the compound. Higher the stability, the higher is the acidic character.
Phenol, O-nitrophenol, O-methyl phenol, and O-methoxy phenol all are aromatic compounds. In aromatic compounds, the negative charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge gives additional stability to the compound. Ethanol is not aromatic and it cannot delocalise the negative charge formed after the ${ H }^{ + }$ ion leaves the compound. So, it is the least acidic among the given options. Thus, we can eliminate it.
There are two types of groups, the electron-withdrawing, and the electron releasing group. The methyl group and the methoxy group are electron releasing groups. They release the electrons inside the aromatic ring. Thus, they increase the electron density inside the aromatic ring. When the ${ H }^{ + }$ ion is released from the O-methyl phenol and the O-methoxy phenol, they acquire a negative charge. Releasing the electrons in the ring will increase the negative charge density and it will decrease the stability of the ion.
On the other hand, a nitro group is an electron-withdrawing group. They withdraw the electrons from the aromatic ring. When ${ H }^{ + }$ ion is released from the O-nitrophenol, it acquires a negative charge. Withdrawing the negative charge from the ring will increase the stability of the compound in this case.
When an ${ H }^{ + }$ ion leaves phenol, it forms a phenoxide ion, and the negative charge in it is delocalised in the ring through resonance. The resonance effect takes place in compounds having a conjugated double bond system. In the conjugated double bond system, there are alternate single and double bonds. The phenoxide ion has an alternate system of single and double bonds. The resonance structures which make the phenoxide ion stable are given below.
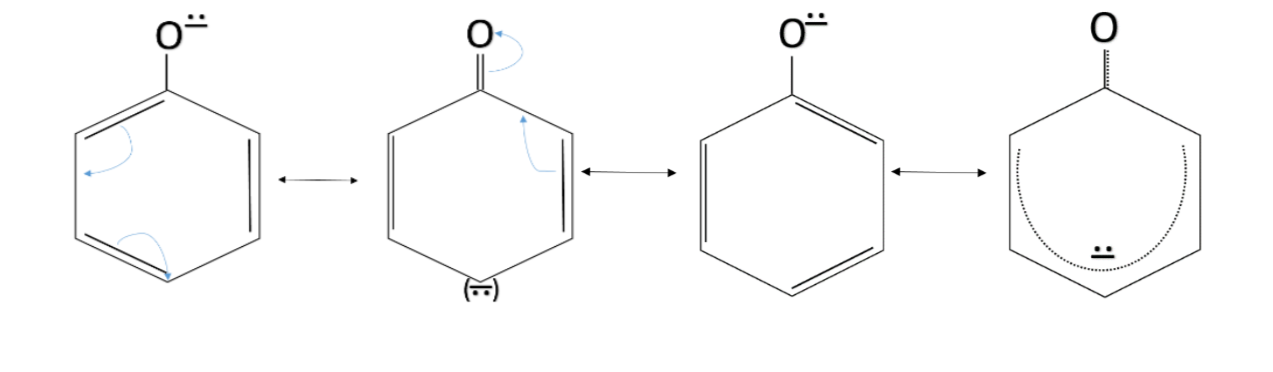
Phenoxide is stabilised by resonance effect only and it does not have any electron releasing group. So, it is more acidic than O-methyl phenol and O-methoxy phenol. But the absence of an electron-withdrawing group makes it less acidic than O-nitrophenol.
Thus option B is the correct one.
Note: All the other aromatic compounds i.e. O-methyl phenol, O-methoxy phenol, and O-nitrophenol have the resonance effect. But the electron-withdrawing and electron releasing effects are the determining factors for their acidic character. Since phenol does not have any of these groups, its acidic character is governed by the resonance effect only.
Complete answer:
Acids are the compounds that release ${ H }^{ + }$ ions. When the ${ H }^{ + }$ ion leaves the compound, it becomes a negatively charged ion. The stability of the negative charge determines the acidic character of the compound. Higher the stability, the higher is the acidic character.
Phenol, O-nitrophenol, O-methyl phenol, and O-methoxy phenol all are aromatic compounds. In aromatic compounds, the negative charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge gives additional stability to the compound. Ethanol is not aromatic and it cannot delocalise the negative charge formed after the ${ H }^{ + }$ ion leaves the compound. So, it is the least acidic among the given options. Thus, we can eliminate it.
There are two types of groups, the electron-withdrawing, and the electron releasing group. The methyl group and the methoxy group are electron releasing groups. They release the electrons inside the aromatic ring. Thus, they increase the electron density inside the aromatic ring. When the ${ H }^{ + }$ ion is released from the O-methyl phenol and the O-methoxy phenol, they acquire a negative charge. Releasing the electrons in the ring will increase the negative charge density and it will decrease the stability of the ion.
On the other hand, a nitro group is an electron-withdrawing group. They withdraw the electrons from the aromatic ring. When ${ H }^{ + }$ ion is released from the O-nitrophenol, it acquires a negative charge. Withdrawing the negative charge from the ring will increase the stability of the compound in this case.
When an ${ H }^{ + }$ ion leaves phenol, it forms a phenoxide ion, and the negative charge in it is delocalised in the ring through resonance. The resonance effect takes place in compounds having a conjugated double bond system. In the conjugated double bond system, there are alternate single and double bonds. The phenoxide ion has an alternate system of single and double bonds. The resonance structures which make the phenoxide ion stable are given below.

Phenoxide is stabilised by resonance effect only and it does not have any electron releasing group. So, it is more acidic than O-methyl phenol and O-methoxy phenol. But the absence of an electron-withdrawing group makes it less acidic than O-nitrophenol.
Thus option B is the correct one.
Note: All the other aromatic compounds i.e. O-methyl phenol, O-methoxy phenol, and O-nitrophenol have the resonance effect. But the electron-withdrawing and electron releasing effects are the determining factors for their acidic character. Since phenol does not have any of these groups, its acidic character is governed by the resonance effect only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




