
How many peroxy linkages are present in $ Cr{O_5} $ ?
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint :Peroxide refers to any chemical compound in which two oxygen atoms are joined by a single covalent bond. Several organic and inorganic peroxides, as well as other oxygen molecules, are also used as bleaching agents. Peroxide linking is essentially an O - O bond.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Peroxides are a class of compounds with the formula ROOR, where R stands for any element. The peroxide group, also known as the peroxo group, is the OO group of a peroxide. The nomenclature is a little erratic.
Hydrogen peroxide (), also known as "peroxide," is the most common peroxide. It's sold as water-based solutions in varying concentrations. Chemical peroxides are also well-known.
The addition of acidified hydrogen peroxide solutions to metal chromates or dichromates, such as sodium chromate or potassium dichromate, produces chromium(VI) peroxide. As chromium(VI) peroxide forms, the normally yellow chromates or orange dichromates turn dark blue. Chromium peroxide and water are formed when chromate or dichromate reacts with hydrogen peroxide and an acid.
$ {\text{CrO}}_4^{2 - } + 2{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} + 2{{\text{H}}^ + } \to {\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_5} + 3{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} $
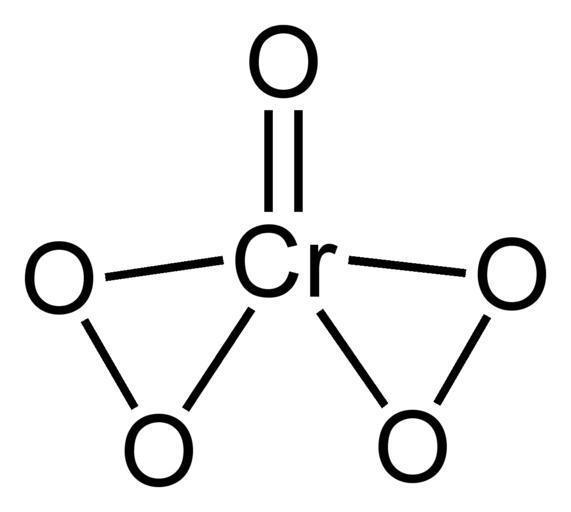
The unstable compound chromium (VI) peroxide, also known as chromium oxide peroxide, has the formula $ Cr{O_5} $ . There are five oxygen atoms per chromium atom in this compound, due to one oxo ligand and two peroxo ligands.
Peroxide linking is essentially an O - O bond
Hence the number of peroxo linkage in $ Cr{O_5} $ is 2.
Note :
To prevent decomposition, chromium(VI) oxide peroxide can be stabilised in water-insoluble organic solvents like diethyl ether, butan-1-ol, or amyl acetate by layering the organic solvent over the chromate/dichromate solution and shaking before applying hydrogen peroxide. The chromium(VI) peroxide (unstable in its newly formed aqueous phase) is dissolved in the immiscible organic solvent in this manner. It can be seen over a much longer period of time in this state.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Peroxides are a class of compounds with the formula ROOR, where R stands for any element. The peroxide group, also known as the peroxo group, is the OO group of a peroxide. The nomenclature is a little erratic.
Hydrogen peroxide (), also known as "peroxide," is the most common peroxide. It's sold as water-based solutions in varying concentrations. Chemical peroxides are also well-known.
The addition of acidified hydrogen peroxide solutions to metal chromates or dichromates, such as sodium chromate or potassium dichromate, produces chromium(VI) peroxide. As chromium(VI) peroxide forms, the normally yellow chromates or orange dichromates turn dark blue. Chromium peroxide and water are formed when chromate or dichromate reacts with hydrogen peroxide and an acid.
$ {\text{CrO}}_4^{2 - } + 2{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{O}}_2} + 2{{\text{H}}^ + } \to {\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_5} + 3{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} $

The unstable compound chromium (VI) peroxide, also known as chromium oxide peroxide, has the formula $ Cr{O_5} $ . There are five oxygen atoms per chromium atom in this compound, due to one oxo ligand and two peroxo ligands.
Peroxide linking is essentially an O - O bond
Hence the number of peroxo linkage in $ Cr{O_5} $ is 2.
Note :
To prevent decomposition, chromium(VI) oxide peroxide can be stabilised in water-insoluble organic solvents like diethyl ether, butan-1-ol, or amyl acetate by layering the organic solvent over the chromate/dichromate solution and shaking before applying hydrogen peroxide. The chromium(VI) peroxide (unstable in its newly formed aqueous phase) is dissolved in the immiscible organic solvent in this manner. It can be seen over a much longer period of time in this state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




