
$\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{5}}$ has a shape of trigonal bipyramidal whereas $\text{I}{{\text{F}}_{5}}$ has the shape of a square pyramid. It is due to
A. presence of an unshared electron pair on I which is oriented so as to minimise the repulsion while in P in $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{5}}$ has no unshared pair.
B. octet of P is complete while that of I is incomplete.
C. P and I are of different groups.
D. F and Cl have different degrees of repulsion.
Answer
536.9k+ views
Hint: Phosphorus has five electrons in the outermost shell and it can make five bonds with other molecules whereas iodine has 7 electrons and has a tendency to accept a pair of electrons so it forms mainly a single bond.
Complete answer:
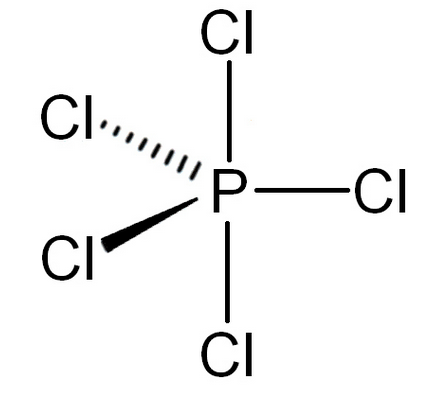
-In $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{5}}$, the electronic configuration of phosphorus is $\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{6}}\text{ 3}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 3}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$ to form five bonds with chlorine electron form s-orbital is excited to the vacant d-orbital due to which phosphorus gains the ability to make 5 bonds.
-Now, it has a total of five unpaired electrons.
-So, the hybridisation of phosphorus is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}\text{d}$ and the geometry will be trigonal bipyramidal.
-Because it has 5 bond pairs and 0 lone pairs.
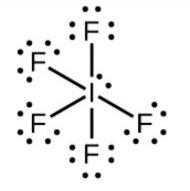
-In $\text{I}{{\text{F}}_{5}}$, according to the electronic configuration of iodine two electrons from 5p-orbital are excited to move to the 5d-orbital.
-So, now iodine tends to make 5 bonds and along with it have one lone pair.
-The lone pair will cause the repulsion towards the bond pair and increases the bond angles that’s why it is oriented in such a way that it causes less repulsion.
-So, the hybridisation will be $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}{{\text{d}}^{2}}$and the geometry will be square pyramidal.
-The structure is:
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The lone pair- lone pair repulsion causes maximum repulsion than lone pair-bond pair and lone pair-bond pair repulsion is more than the bond pair-bond pair repulsion.
Complete answer:
-In $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{5}}$, the electronic configuration of phosphorus is $\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{6}}\text{ 3}{{\text{s}}^{2}}\text{ 3}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$ to form five bonds with chlorine electron form s-orbital is excited to the vacant d-orbital due to which phosphorus gains the ability to make 5 bonds.
-Now, it has a total of five unpaired electrons.
-So, the hybridisation of phosphorus is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}\text{d}$ and the geometry will be trigonal bipyramidal.
-Because it has 5 bond pairs and 0 lone pairs.

-In $\text{I}{{\text{F}}_{5}}$, according to the electronic configuration of iodine two electrons from 5p-orbital are excited to move to the 5d-orbital.
-So, now iodine tends to make 5 bonds and along with it have one lone pair.
-The lone pair will cause the repulsion towards the bond pair and increases the bond angles that’s why it is oriented in such a way that it causes less repulsion.
-So, the hybridisation will be $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}{{\text{d}}^{2}}$and the geometry will be square pyramidal.
-The structure is:

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The lone pair- lone pair repulsion causes maximum repulsion than lone pair-bond pair and lone pair-bond pair repulsion is more than the bond pair-bond pair repulsion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




