
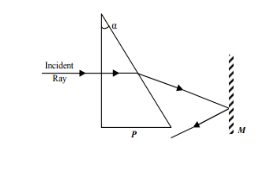
P is a small angled prism of angle ${3^0}$ made of a material of refractive index $1.5$. A ray is incident as shown in figure. M is a plane mirror. The angle of deviation for the ray reflected from the mirror M with respect to the incident ray is,
(A) ${4.5^0}$
(B) ${175^0}$
(C) ${177^0}$
(D) ${178.5^0}$

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint:The angle of deviation of incident ray is determined by calculating the angle of deviation of incident ray from prism and angle of deviation of incident ray (which is refracted from the prism) from the mirror. After getting the angle of deviation, they are added to get the total angle of deviation from the incident ray.
Complete step by step solution:
Deviation produced by the prism is given by the formula
$ \Rightarrow {d_1} = \left( {n - 1} \right)A$
Where ${d_1}$ is the angle of deviation produced by prism, $n$ is the refractive index of the prism and $A$ is the angle of the prism. We have a refractive index $n = 1.5$, angle of prism $A = {3^0}$ ; putting the value of refractive index and angle of prism into the above formula. We get
$ \Rightarrow {d_1} = \left( {1.5 - 1} \right) \times {3^0}$
After simplify we get,
$ \Rightarrow {d_1} = 0.5 \times {3^0}$
$ \Rightarrow {d_1} = {1.5^0}$ in the clockwise direction. $ \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
After refraction from the prism, now ray is incident on mirror and produced deviation. Angle of deviation produced on the mirror by a ray is given by the formula
$ \Rightarrow {d_2} = \left( {180 - 2i} \right)$
Where ${d_2}$ is the angle of deviation produced on the mirror by an incident ray and $i$ is angle of incidence of ray on the mirror. Since, angle of deviation produced by prism and angle of incidence will be alternate angles. So, they will be equal; therefore $i = {1.5^0}$ .
Putting angle of incidence $i = {1.5^0}$ on above formula to get angle of deviation produced on the mirror,
$ \Rightarrow {d_2} = \left( {{{180}^0} - 2 \times {{1.5}^0}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {d_2} = \left( {{{180}^0} - {3^0}} \right)$
After simplify we get,
$ \Rightarrow {d_2} = {177^0}$ in the clockwise direction $ \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
Adding equations $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$, we get the total deviation from the original incident ray,
Total deviation $d = {d_1} + {d_2} = {1.5^0} + {177^0}$
$ \Rightarrow $ $d = {178.5^0}$ in the clockwise direction.
Hence, option (D) is correct
Additional Information: When a ray incident occurs in one medium and goes in another medium, this phenomenon is called refraction. And when a ray incident occurs at one medium and goes in the same medium after touching its surface, this is called reflection.
Note:Angle of deviation is an angle between the original ray and the final ray. In other words, the angle of deviation is the inclination between the original and final ray.
Complete step by step solution:
Deviation produced by the prism is given by the formula
$ \Rightarrow {d_1} = \left( {n - 1} \right)A$
Where ${d_1}$ is the angle of deviation produced by prism, $n$ is the refractive index of the prism and $A$ is the angle of the prism. We have a refractive index $n = 1.5$, angle of prism $A = {3^0}$ ; putting the value of refractive index and angle of prism into the above formula. We get
$ \Rightarrow {d_1} = \left( {1.5 - 1} \right) \times {3^0}$
After simplify we get,
$ \Rightarrow {d_1} = 0.5 \times {3^0}$
$ \Rightarrow {d_1} = {1.5^0}$ in the clockwise direction. $ \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
After refraction from the prism, now ray is incident on mirror and produced deviation. Angle of deviation produced on the mirror by a ray is given by the formula
$ \Rightarrow {d_2} = \left( {180 - 2i} \right)$
Where ${d_2}$ is the angle of deviation produced on the mirror by an incident ray and $i$ is angle of incidence of ray on the mirror. Since, angle of deviation produced by prism and angle of incidence will be alternate angles. So, they will be equal; therefore $i = {1.5^0}$ .
Putting angle of incidence $i = {1.5^0}$ on above formula to get angle of deviation produced on the mirror,
$ \Rightarrow {d_2} = \left( {{{180}^0} - 2 \times {{1.5}^0}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {d_2} = \left( {{{180}^0} - {3^0}} \right)$
After simplify we get,
$ \Rightarrow {d_2} = {177^0}$ in the clockwise direction $ \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
Adding equations $\left( 1 \right)$ and $\left( 2 \right)$, we get the total deviation from the original incident ray,
Total deviation $d = {d_1} + {d_2} = {1.5^0} + {177^0}$
$ \Rightarrow $ $d = {178.5^0}$ in the clockwise direction.
Hence, option (D) is correct
Additional Information: When a ray incident occurs in one medium and goes in another medium, this phenomenon is called refraction. And when a ray incident occurs at one medium and goes in the same medium after touching its surface, this is called reflection.
Note:Angle of deviation is an angle between the original ray and the final ray. In other words, the angle of deviation is the inclination between the original and final ray.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




