
Number of $\sigma $ & $\prod $ bonds in benzene are:
${\text{A}}{\text{. 6,3}}$
${\text{B}}{\text{. 3,3}}$
${\text{C}}{\text{. 12,3}}$
${\text{D}}{\text{. 6,6}}$
Answer
606.3k+ views
Hint: We must know the definition and how $\sigma $ & $\prod $ are formed. Also, the molecular formula of Benzene is ${C_6}{H_6}$. These are very important.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Sigma bonds are the most potent covalent chemical bond. They are formed by overlapping of atomic orbitals head on. For diatomic molecules Sigma bonding is most clearly described using the language and resources of symmetry groups.
Pi bonds are covalent chemical bonds in which two orbital lobes on one atom overlap two orbital lobes on another atom and the overlap occurs laterally. The atomic orbitals have zero density of electrons on a common nodal plane going through the two bonded nuclei.
In a sigma bond two atoms that are bound together. It is the most basic of all bonds because it is directly between two atoms. If we draw a straight line between two atoms, we will come across a point where the bond with the sigma is located. Then the big question is where the second or third bond we will put in a double bond or triple bond, because we cannot place two bonds in the same place. Such bonds are formed by the p-orbitals overlap. We must understand the chemistry where the peanut shape of the p orbital is and so we call this a $\prod $ bond.
There is a sigma bond between each atom in benzene and also an additional bond, called a pi bond, whenever a double bond is present. This leads to 12 sigma bonds and 3 pi bonds. We must always remember that the $\prod $ bonds are in a conjugated system and rotate around the ring which gives benzene stability.
Hence our answer is the C option which states that the number of $\sigma $ & $\prod $bonds in benzene are 12 and 3.
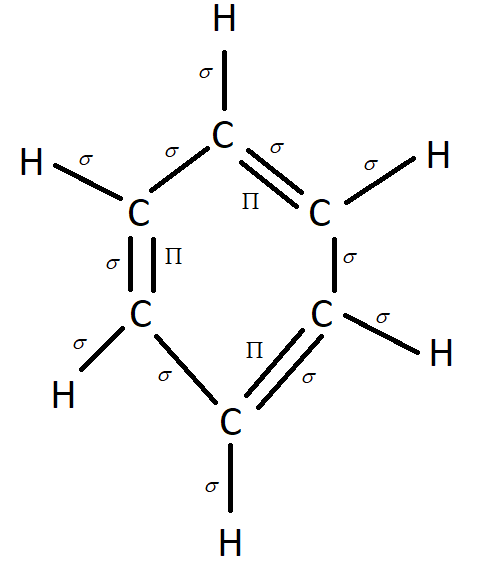 Structure of Benzene.
Structure of Benzene.
Note: For answering these types of questions we must understand how $\sigma $ & $\prod $ are formed. Also, understanding the periodic table is very much needed. The structure of an atom plays a very important role in the formation of these types of bonds and the valence shell electrons are major contributors of bond formation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Sigma bonds are the most potent covalent chemical bond. They are formed by overlapping of atomic orbitals head on. For diatomic molecules Sigma bonding is most clearly described using the language and resources of symmetry groups.
Pi bonds are covalent chemical bonds in which two orbital lobes on one atom overlap two orbital lobes on another atom and the overlap occurs laterally. The atomic orbitals have zero density of electrons on a common nodal plane going through the two bonded nuclei.
In a sigma bond two atoms that are bound together. It is the most basic of all bonds because it is directly between two atoms. If we draw a straight line between two atoms, we will come across a point where the bond with the sigma is located. Then the big question is where the second or third bond we will put in a double bond or triple bond, because we cannot place two bonds in the same place. Such bonds are formed by the p-orbitals overlap. We must understand the chemistry where the peanut shape of the p orbital is and so we call this a $\prod $ bond.
There is a sigma bond between each atom in benzene and also an additional bond, called a pi bond, whenever a double bond is present. This leads to 12 sigma bonds and 3 pi bonds. We must always remember that the $\prod $ bonds are in a conjugated system and rotate around the ring which gives benzene stability.
Hence our answer is the C option which states that the number of $\sigma $ & $\prod $bonds in benzene are 12 and 3.

Note: For answering these types of questions we must understand how $\sigma $ & $\prod $ are formed. Also, understanding the periodic table is very much needed. The structure of an atom plays a very important role in the formation of these types of bonds and the valence shell electrons are major contributors of bond formation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




