
${[NiC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$ show the electron filled orbitals of $N{i^{2 + }}$ and $C{l^ - }$ ions, what would be the structural arrangement of the compound, octahedral or tetrahedral?
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint:As we know that according to valence bond theory, the metal atom or ion can use $(n - 1)d$, $ns,np,nd$ orbitals for hybridisation under the influence of ligands to yield a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry like square planar, octahedral, tetrahedral and so on.
Complete step-by-step solution:We know that the Valence Bond Theory (VBT) states that the metal atom or ion use $ns,np,nd$ and $(n - 1)d$ orbitals for the purpose of hybridisation under the influence of a ligand that results in yielding of a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry.
In the given complex compound, we know that one $ns$ orbital and three $np$ orbitals are involved in hybridisation, Nickel has a $ + 2$ oxidation state and has an electronic configuration of $3{d^8}4{s^0}$. Each chlorine ion would donate a pair of electrons to the Nickel.
We also know that the compound contain Chloride ion which are actually weak ligand, so they cannot pair up the unpaired electrons of Nickel in $ + 2$ oxidation state and we can show the hybridisation scheme of this coordination compound as:
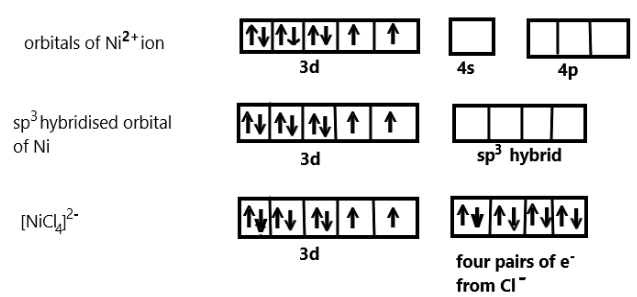
As we can see that ${[NiC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$ undergoes $s{p^3}$ hybridisation to make bonds with the four chloride ion ligands thus we can say that the geometry so formed is tetrahedral. When a strong ligand like carbonyl compound is present with nickel then also the hybridisation is tetrahedral but diamagnetic as nickel contains no unpaired electron in that complex.
Therefore the correct answer is Tetrahedral geometry.
Note:Since this complex coordination compound Nickel tetrachloride possess two unpaired electrons, hence the compound is paramagnetic. Also remember when the weak ligand is present, there is no bonding between the central atom and the side atoms but when a strong ligand is present, bonding in d-orbital will take place and thus no unpaired electrons will be available which makes the compound diamagnetic.
Complete step-by-step solution:We know that the Valence Bond Theory (VBT) states that the metal atom or ion use $ns,np,nd$ and $(n - 1)d$ orbitals for the purpose of hybridisation under the influence of a ligand that results in yielding of a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry.
In the given complex compound, we know that one $ns$ orbital and three $np$ orbitals are involved in hybridisation, Nickel has a $ + 2$ oxidation state and has an electronic configuration of $3{d^8}4{s^0}$. Each chlorine ion would donate a pair of electrons to the Nickel.
We also know that the compound contain Chloride ion which are actually weak ligand, so they cannot pair up the unpaired electrons of Nickel in $ + 2$ oxidation state and we can show the hybridisation scheme of this coordination compound as:

As we can see that ${[NiC{l_4}]^{2 - }}$ undergoes $s{p^3}$ hybridisation to make bonds with the four chloride ion ligands thus we can say that the geometry so formed is tetrahedral. When a strong ligand like carbonyl compound is present with nickel then also the hybridisation is tetrahedral but diamagnetic as nickel contains no unpaired electron in that complex.
Therefore the correct answer is Tetrahedral geometry.
Note:Since this complex coordination compound Nickel tetrachloride possess two unpaired electrons, hence the compound is paramagnetic. Also remember when the weak ligand is present, there is no bonding between the central atom and the side atoms but when a strong ligand is present, bonding in d-orbital will take place and thus no unpaired electrons will be available which makes the compound diamagnetic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




