
How Many Nand Gates Are Required For Full Adder?
Answer
502.5k+ views
Hint: A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic (specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, boolean functions, and propositional calculus) that lists the functional values of logical expressions for each of their functional arguments, that is, for each set of values taken by their logical variables.
Complete step by step solution:
A Full Adder is a Combinational Logic Circuit that adds two-digit integers in binary. When compared to half adders, full adders are more complicated and difficult to install. The major difference between a full adder and a half adder is that a full adder calculates the sum of three binary bits. Two of the three bits, A, the augend bit, and B, the addend bit, are the same as previously. The third bit is called Carry–in and is typically denoted as${{C}_{IN}}$. It is the carry bit from the previous step. It adds up three bits, including the carry, to get the total. Carry–out is the name for the output carry, which is denoted as${{C}_{OUT}}$. In digital electronics, a NAND gate (NOT-AND) is a logic gate which produces an output which is false only if all its inputs are true; thus its output is complement to that of an AND gate. A LOW (0) output results only if all the inputs to the gate are HIGH (1); if any input is LOW (0), a HIGH (1) output results. A NAND gate is made using transistors and junction diodes. By De Morgan's laws, a two-input NAND gate's logic may be expressed as AB=A+B, making a NAND gate equivalent to inverters followed by an OR gate.
Truth table of full adder is given as
A Full Adder requires a total of 9 NOR gates to be implemented.
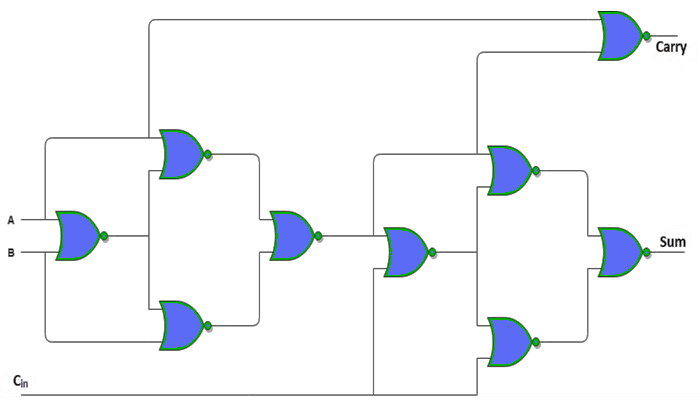
Note: An adder is a digital circuit that adds two integers together. Adders are used in the arithmetic logic units (ALU) of many computers and other types of processors. They're also used to compute addresses, table indices, increment and decrement operators, and other operations in other sections of the CPU.
Complete step by step solution:
A Full Adder is a Combinational Logic Circuit that adds two-digit integers in binary. When compared to half adders, full adders are more complicated and difficult to install. The major difference between a full adder and a half adder is that a full adder calculates the sum of three binary bits. Two of the three bits, A, the augend bit, and B, the addend bit, are the same as previously. The third bit is called Carry–in and is typically denoted as${{C}_{IN}}$. It is the carry bit from the previous step. It adds up three bits, including the carry, to get the total. Carry–out is the name for the output carry, which is denoted as${{C}_{OUT}}$. In digital electronics, a NAND gate (NOT-AND) is a logic gate which produces an output which is false only if all its inputs are true; thus its output is complement to that of an AND gate. A LOW (0) output results only if all the inputs to the gate are HIGH (1); if any input is LOW (0), a HIGH (1) output results. A NAND gate is made using transistors and junction diodes. By De Morgan's laws, a two-input NAND gate's logic may be expressed as AB=A+B, making a NAND gate equivalent to inverters followed by an OR gate.
Truth table of full adder is given as
| input | output | |||
| A | B | Cin | Cout | S |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
A Full Adder requires a total of 9 NOR gates to be implemented.

Note: An adder is a digital circuit that adds two integers together. Adders are used in the arithmetic logic units (ALU) of many computers and other types of processors. They're also used to compute addresses, table indices, increment and decrement operators, and other operations in other sections of the CPU.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




