
Name the types of roots shown in the figure.

Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: There are two types of root systems. The taproot system is seen in dicots. The fibrous root system is seen in dicots.
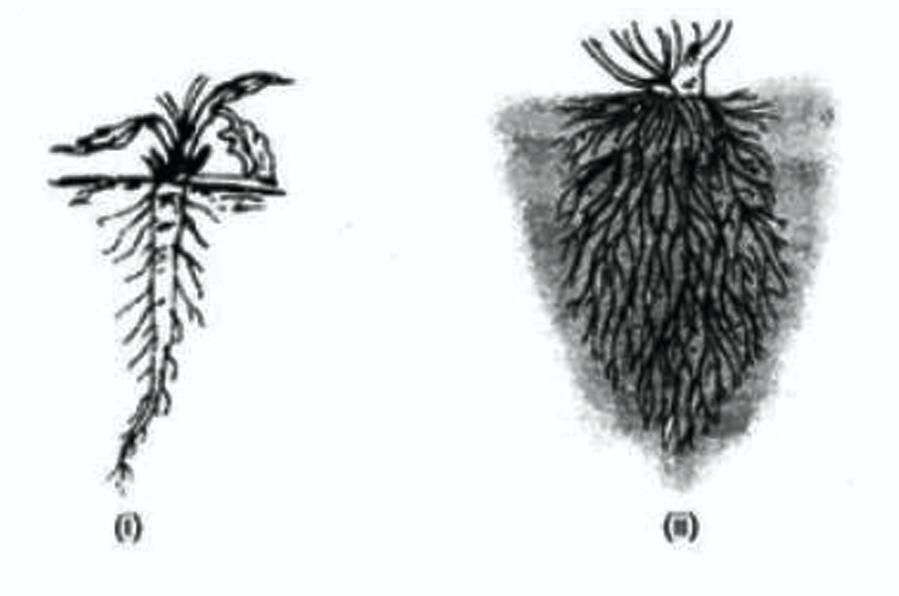
Complete answer: The figure shows two types of root systems. The first figure is the taproot system. It is characterized by the presence of one main root and several branches arising from the main root.
A taproot is a large, central, and dominant root from which other roots arise laterally. Typically, a taproot is somewhat straight and thick, tapering in shape, and grows directly downward. In some plants, such as carrots, the taproot is a storage organ that is so well developed that it is cultivated as a vegetable.
The second figure is that of a fibrous or adventitious root system.
A fibrous root system is usually formed by thin, moderately branching roots growing directly downwards from the stem. The fibrous root system is universal in monocotyledonous plants and ferns, i.e., these plants have only fibrous roots. The fibrous root system looks like a mat made out of roots when the tree has reached full maturity.
Most trees begin life with a taproot, but, after a few years, change to a wide-spreading fibrous root system with mainly horizontal surface roots and only a few vertical, downwards growing, deep anchoring roots. A typical mature tree that is 30 – 50 m tall has a root system that extends horizontally in all directions as far as the tree is tall or even more and over 95% of the roots are in the top 50 cm depth of soil.
Additional information:
Plants which have tap root are –
Carrot
Radish
Turnip
Pea
Gram
Beans
Plants that have a fibrous root system are –
Wheat
Rice
Maize
Corn
Onion
Barley
Note: The root system of plants is mainly responsible for anchorage and for the uptake of water and nutrients from the soil. The deeper the roots, the better is the absorption of nutrients and water from the soil. The plant's growth depends on the root system.
Complete answer: The figure shows two types of root systems. The first figure is the taproot system. It is characterized by the presence of one main root and several branches arising from the main root.
A taproot is a large, central, and dominant root from which other roots arise laterally. Typically, a taproot is somewhat straight and thick, tapering in shape, and grows directly downward. In some plants, such as carrots, the taproot is a storage organ that is so well developed that it is cultivated as a vegetable.
The second figure is that of a fibrous or adventitious root system.
A fibrous root system is usually formed by thin, moderately branching roots growing directly downwards from the stem. The fibrous root system is universal in monocotyledonous plants and ferns, i.e., these plants have only fibrous roots. The fibrous root system looks like a mat made out of roots when the tree has reached full maturity.
Most trees begin life with a taproot, but, after a few years, change to a wide-spreading fibrous root system with mainly horizontal surface roots and only a few vertical, downwards growing, deep anchoring roots. A typical mature tree that is 30 – 50 m tall has a root system that extends horizontally in all directions as far as the tree is tall or even more and over 95% of the roots are in the top 50 cm depth of soil.
Additional information:
Plants which have tap root are –
Carrot
Radish
Turnip
Pea
Gram
Beans
Plants that have a fibrous root system are –
Wheat
Rice
Maize
Corn
Onion
Barley
Note: The root system of plants is mainly responsible for anchorage and for the uptake of water and nutrients from the soil. The deeper the roots, the better is the absorption of nutrients and water from the soil. The plant's growth depends on the root system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




