
What is the name of the reaction for preparation of methyl isocyanide?
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Methyl isocyanide or iso cyanomethane is a member of the isocyanide family and an organic compound. This colourless liquid is isomeric to methyl cyanide (acetonitrile) but somewhat different in its reactivity. Methyl isocyanide is used primarily to make 5-membered heterocyclic rings. The gap of C-N in methyl isocyanide is very small, 1.158 Å as isocyanide is characteristic.
Complete step by step answer:
Gautier was first to prepare methyl isocyanide by reaction of silver cyanide to methyl iodide. Dehydration of N-methylformamide is the standard method for the preparation of methyl isocyanides. Methyl isocyanide is useful for various heterocyclic preparations. It also forms a ligand in organometallic chemistry. The structure is given below-
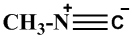
The common method for preparing methyl isocyanides is the dehydration of N-methylformamide.
The classic example of a dehydration reaction is the Fischer esterification which involves the treatment with an alcohol of a carboxylic acid in the presence of a dehydration agent:
$RCOOH+R'OH\xrightarrow{-{{H}_{2}}O}RCOOR$
Using dehydration synthesis, two monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose, can be joined together (to form saccharose). The new molecule, composed of two monosaccharides, is called a disaccharide.
Methyl isocyanide is prepared primarily by small modifications of Gautier 's original method, which is the alkylation of silver cyanide by an alkyl halide.
Note: -A dehydration reaction is a conversion involving water loss from the molecule or ion reacting to it. Dehydration reactions, the opposite of a hydration reaction, are typical processes. Sulfuric acid and alumina are popular dehydrating agents used in organic synthesis.
-Alkylation is the movement of a group of alkyls from one molecule to another. The alkyl group can be moved as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or variants thereof).
Complete step by step answer:
Gautier was first to prepare methyl isocyanide by reaction of silver cyanide to methyl iodide. Dehydration of N-methylformamide is the standard method for the preparation of methyl isocyanides. Methyl isocyanide is useful for various heterocyclic preparations. It also forms a ligand in organometallic chemistry. The structure is given below-
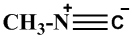
The common method for preparing methyl isocyanides is the dehydration of N-methylformamide.
The classic example of a dehydration reaction is the Fischer esterification which involves the treatment with an alcohol of a carboxylic acid in the presence of a dehydration agent:
$RCOOH+R'OH\xrightarrow{-{{H}_{2}}O}RCOOR$
Using dehydration synthesis, two monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose, can be joined together (to form saccharose). The new molecule, composed of two monosaccharides, is called a disaccharide.
Methyl isocyanide is prepared primarily by small modifications of Gautier 's original method, which is the alkylation of silver cyanide by an alkyl halide.
Note: -A dehydration reaction is a conversion involving water loss from the molecule or ion reacting to it. Dehydration reactions, the opposite of a hydration reaction, are typical processes. Sulfuric acid and alumina are popular dehydrating agents used in organic synthesis.
-Alkylation is the movement of a group of alkyls from one molecule to another. The alkyl group can be moved as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or variants thereof).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




