
Most acidic hydrogen is present in:
A.
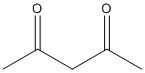
B.
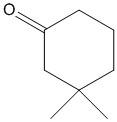
C. ${(C{H_3}CO)_3}CH$
D. ${(C{H_3})_3}COH$


Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: The stability of the corresponding conjugate base produced decides the acidity of the compound. The more the stability of the base, the easier it was for the compound to liberate the hydrogen.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the Brønsted-Lowry concept, an acid is a compound which donates protons during a reaction. The acidic strength of a compound depends on several factors. The polarity of a bond affects the acidity of a molecule.
\[A - H \to {A^ - } + {H^ + }\]
Thus the \[A - H\] acid produces \[{A^ - }\] and \[{H^ + }\]. For the acid \[A - H\] the \[{A^ - }\] produced is the conjugate base. The stability of the conjugate base also decides the acidity of the original compound.
The given sets of compounds are organic compounds. Let us consider each compound one by one.
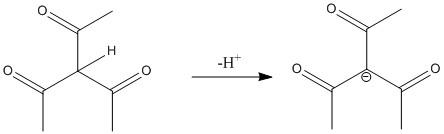
A.
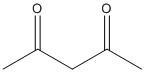
In this compound the methylene hydrogen in the middle is flanked by two electron withdrawing groups. Thus the electron density of the \[C - H\] bonds moves towards the two acetyl groups. So the molecule is acidic and the proton attached to the methylene carbon is easily abstracted with a mild base.
The conjugate base produced by release of a proton is
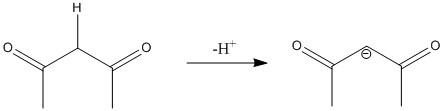
The conjugate base is resonance stabilized with the three resonance structures.
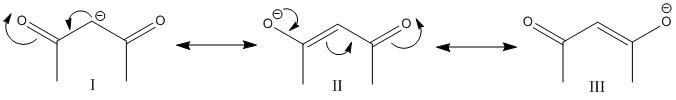
B.
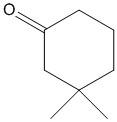
In this compound the methylene hydrogen present adjacent to the carbonyl is acidic due to the electron withdrawing nature of the \[C = O\]. Thus the electron density of \[C - H\] bonds moves towards the \[C = O\] group. Thus the molecule is acidic and the proton attached to the methylene carbon is easily abstracted with a base.
The conjugate base produced by release of a proton is
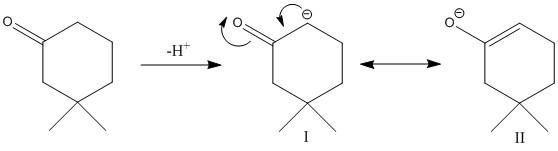
The conjugate base is resonance stabilized and has two resonance structures which make the conjugate base stable.
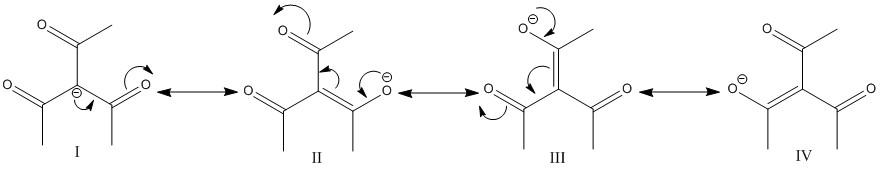
C. ${(C{H_3}CO)_3}CH$.
Like the compound present in option A the methylene hydrogen in the middle is flanked by three electron withdrawing groups. Thus the electron density of \[C - H\] bond moves towards the three acetyl groups. Thus the molecule is acidic and the proton attached to the middle carbon is easily abstracted with a mild base. In fact the acidity of this compound is more than the compound A and C.
The corresponding conjugate base is
The conjugate base is resonance stabilized with the most (four) number of resonance structures.
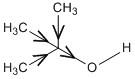
D. ${(C{H_3})_3}COH$
In this compound the conjugate base produced is very unstable as the hydroxyl group is attached to a tertiary butyl group. The three methyl groups have electron donating groups. This destabilizes the oxide anion produced by the release of protons. Thus the compound is not acidic.
Note:
The most acidic hydrogen is determined by the most facile release of proton by a compound. Thus the compound or molecule which liberates protons easily and smoothly contains the most acidic proton.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the Brønsted-Lowry concept, an acid is a compound which donates protons during a reaction. The acidic strength of a compound depends on several factors. The polarity of a bond affects the acidity of a molecule.
\[A - H \to {A^ - } + {H^ + }\]
Thus the \[A - H\] acid produces \[{A^ - }\] and \[{H^ + }\]. For the acid \[A - H\] the \[{A^ - }\] produced is the conjugate base. The stability of the conjugate base also decides the acidity of the original compound.
The given sets of compounds are organic compounds. Let us consider each compound one by one.
A.

In this compound the methylene hydrogen in the middle is flanked by two electron withdrawing groups. Thus the electron density of the \[C - H\] bonds moves towards the two acetyl groups. So the molecule is acidic and the proton attached to the methylene carbon is easily abstracted with a mild base.
The conjugate base produced by release of a proton is

The conjugate base is resonance stabilized with the three resonance structures.

B.

In this compound the methylene hydrogen present adjacent to the carbonyl is acidic due to the electron withdrawing nature of the \[C = O\]. Thus the electron density of \[C - H\] bonds moves towards the \[C = O\] group. Thus the molecule is acidic and the proton attached to the methylene carbon is easily abstracted with a base.
The conjugate base produced by release of a proton is

The conjugate base is resonance stabilized and has two resonance structures which make the conjugate base stable.
C. ${(C{H_3}CO)_3}CH$.
Like the compound present in option A the methylene hydrogen in the middle is flanked by three electron withdrawing groups. Thus the electron density of \[C - H\] bond moves towards the three acetyl groups. Thus the molecule is acidic and the proton attached to the middle carbon is easily abstracted with a mild base. In fact the acidity of this compound is more than the compound A and C.
The corresponding conjugate base is

The conjugate base is resonance stabilized with the most (four) number of resonance structures.

D. ${(C{H_3})_3}COH$
In this compound the conjugate base produced is very unstable as the hydroxyl group is attached to a tertiary butyl group. The three methyl groups have electron donating groups. This destabilizes the oxide anion produced by the release of protons. Thus the compound is not acidic.

Note:
The most acidic hydrogen is determined by the most facile release of proton by a compound. Thus the compound or molecule which liberates protons easily and smoothly contains the most acidic proton.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




