
What is the minimum number of rays required for locating the image formed by a concave mirror for an object. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: For the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror, the object is to be placed between the mirror and the focal point.
Complete step by step solution:
When an object is placed in between the focus and pole of concave mirror, then a virtual image is formed as shown in figure below:
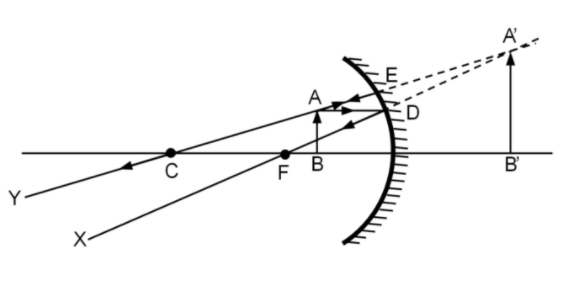
The incident ray parallel to the principal axis is refracted passing through the focus and the incident ray passing through the optical center retraces its path after refraction. The two rays appear to converge behind the mirror forming a virtual, erect image.
From the above figure, we can understand that the minimum number of rays required for locating the image formed by a concave mirror for an object is two.
Additional information:
A concave mirror converges the beam of light. The focal length of a concave mirror is taken to be positive.
A convex mirror diverges the beam of light. The focal length of a convex mirror is taken to be negative.
Note: The focus of a concave mirror lies on the same side from where the incident light rays are incident on the mirror surface. The virtual image is formed behind the mirror, and is erect and magnified.
Complete step by step solution:
When an object is placed in between the focus and pole of concave mirror, then a virtual image is formed as shown in figure below:

The incident ray parallel to the principal axis is refracted passing through the focus and the incident ray passing through the optical center retraces its path after refraction. The two rays appear to converge behind the mirror forming a virtual, erect image.
From the above figure, we can understand that the minimum number of rays required for locating the image formed by a concave mirror for an object is two.
Additional information:
A concave mirror converges the beam of light. The focal length of a concave mirror is taken to be positive.
A convex mirror diverges the beam of light. The focal length of a convex mirror is taken to be negative.
Note: The focus of a concave mirror lies on the same side from where the incident light rays are incident on the mirror surface. The virtual image is formed behind the mirror, and is erect and magnified.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




