
What is meant by the chelate effect? Give an example.
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: Chelate is a term related to coordination compounds. When a di- or polydentate ligand uses its two or more donor atoms together to bind a single metal ion then it is said to be a chelate ligand. The number
of such ligating groups is called denticity of the ligand.
Complete answer: When a ligand is bound to a metal ion through one single donor atom then it is called unidetate but when it uses two donor atoms it is said to be a bidentate ligand. $C{l^ - }$ , ${H_2}O$are unidentate ligands and ${C_2}O_4^ - $ , ${H_2}NC{H_2}C{H_2}N{H_2}$are bidentate ligands. Similarly ligands having more than two donor atoms are called polydentate ligands $N{\left( {C{H_2}C{H_2}N{H_2}} \right)_3}$is a polydentate ligand. When a di- or polydentate ligand uses its two or more donor atoms together to bind a single metal ion then it is said to be a chelate ligand. When a ligand uses its two or more donor atoms simultaneously a ring-like structure is formed. The formation of such ring-like structures is called a chelate effect. Compounds having chelate rings are more stable as compared to other compounds. An example of such a complex is ethylenediamine-cadmium. The structure of this complex is:
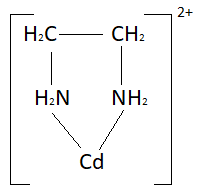
Note:
The coordination number of the metal complex is defined as the number of ligand donor atoms to which metal is directly bonded. The central atom/ion and the ligands attached to it are enclosed in a square bracket and the term collectively used is the coordination sphere.
of such ligating groups is called denticity of the ligand.
Complete answer: When a ligand is bound to a metal ion through one single donor atom then it is called unidetate but when it uses two donor atoms it is said to be a bidentate ligand. $C{l^ - }$ , ${H_2}O$are unidentate ligands and ${C_2}O_4^ - $ , ${H_2}NC{H_2}C{H_2}N{H_2}$are bidentate ligands. Similarly ligands having more than two donor atoms are called polydentate ligands $N{\left( {C{H_2}C{H_2}N{H_2}} \right)_3}$is a polydentate ligand. When a di- or polydentate ligand uses its two or more donor atoms together to bind a single metal ion then it is said to be a chelate ligand. When a ligand uses its two or more donor atoms simultaneously a ring-like structure is formed. The formation of such ring-like structures is called a chelate effect. Compounds having chelate rings are more stable as compared to other compounds. An example of such a complex is ethylenediamine-cadmium. The structure of this complex is:

Note:
The coordination number of the metal complex is defined as the number of ligand donor atoms to which metal is directly bonded. The central atom/ion and the ligands attached to it are enclosed in a square bracket and the term collectively used is the coordination sphere.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Why was the Vernacular Press Act passed by British class 11 social science CBSE

How did silk routes link the world Explain with three class 11 social science CBSE

Graph between Concentration and Time for a first order class 11 chemistry CBSE

The compound used in treatment of lead poisoning is class 11 chemistry CBSE




