
What is meant by hydroboration-oxidation reaction? Illustrate it with an example.
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint: Hydroboration oxidation is an anti-markovnikov addition of water across alkene. Also, it is a two-step organic reaction. End product is alcohol.
Complete step by step solution:
- It is known to you that hydroboration oxidation is a two-step organic reaction.
- It is an organic reaction that converts an alkene into an alcohol by the net addition of water across the double bond. THF(Tetrahydrofuran) is used as a solvent.
- The hydrogen (H) and hydroxyl group (OH) are added in a syn (addition of addendum on the same side of the alkene or alkyne) addition leading to cis stereochemistry.
- Hydroboration-oxidation is an anti-Markovnikov’s addition of water across an alkene. The -OH group is added to the less substituted position and the -H is in the more substituted position.
- If there is more than one chiral center in the product, then the product will produce a pair of enantiomers that results from syn addition. A common example of oxidation of 1-Propene is given below.
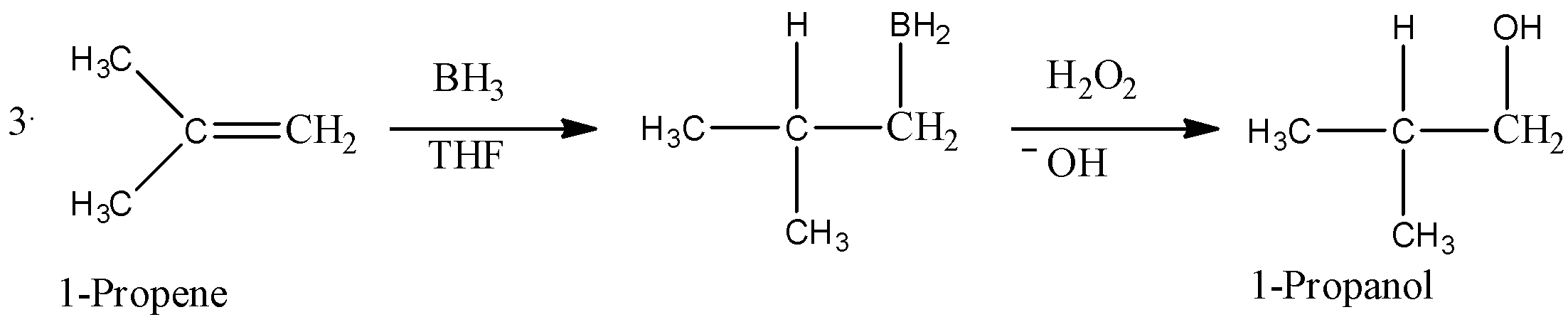
- Here, we can see that first, $B{{H}_{3}}$ is added to the carbon-carbon double bond in a way that H-atom gets bonded to a carbon that has less number of hydrogen atoms(means in anti-markovnikov manner). Then, in presence of hydrogen peroxide-an oxidising agent, the organo-borane compound decomposes and gives an alcohol as shown in the reaction.
- One molecule of $B{{H}_{3}}$ can oxidise three molecules of alkene because one B-H bond is responsible for the oxidation of one molecule of alkene. After oxidising alkene, B-H bond gets converted into B-OH bond. So, $B{{H}_{3}}$ has three B-H bonds, and it will oxidise total of three alkenes and will give ${{H}_{3}}B{{O}_{3}}$ in the end. We can show how one molecule of $B{{H}_{3}}$ oxidises three molecules of alkene as below.
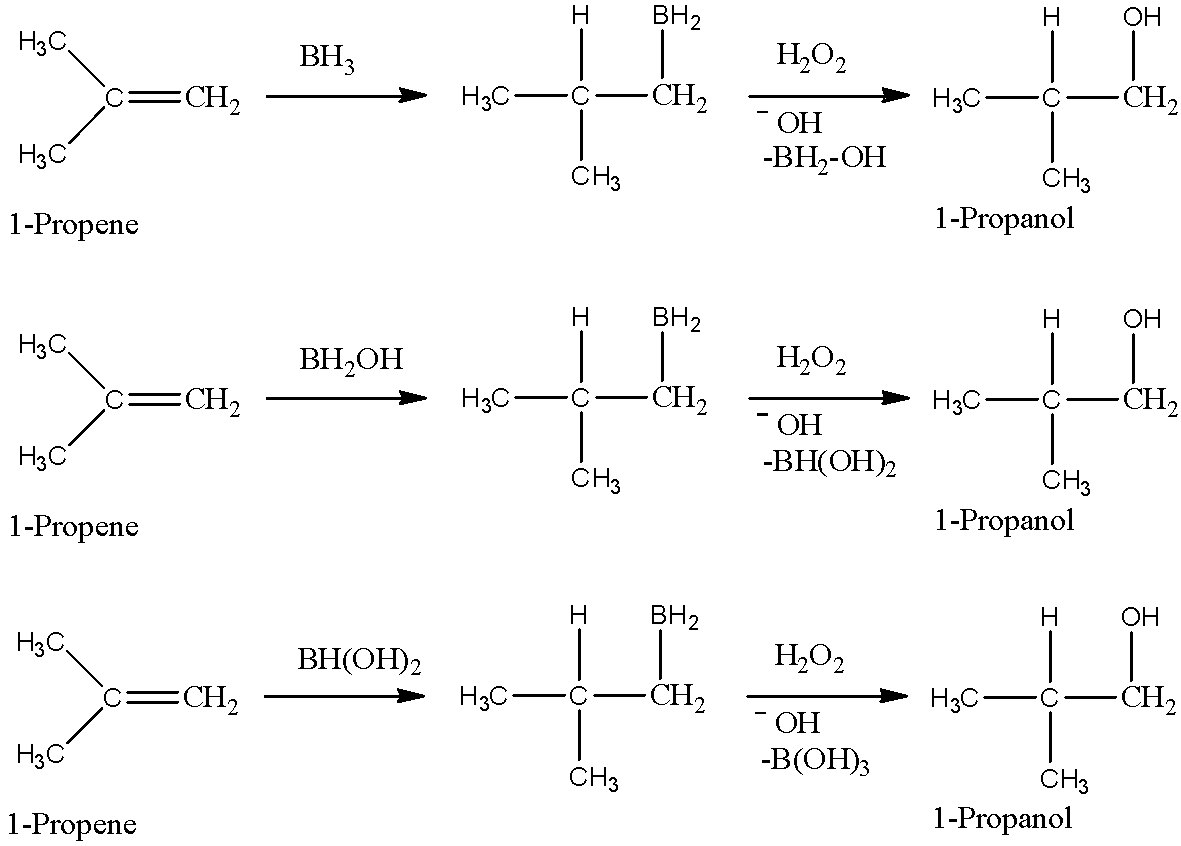
Note: Remember that it will give an anti-markovnikov product after addition to the alkene double bond. We cannot use water as a solvent here because it will immediately react with $B{{H}_{3}}$ as water has an amphoteric nature and $B{{H}_{3}}$ is a lewis acid.
Complete step by step solution:
- It is known to you that hydroboration oxidation is a two-step organic reaction.
- It is an organic reaction that converts an alkene into an alcohol by the net addition of water across the double bond. THF(Tetrahydrofuran) is used as a solvent.
- The hydrogen (H) and hydroxyl group (OH) are added in a syn (addition of addendum on the same side of the alkene or alkyne) addition leading to cis stereochemistry.
- Hydroboration-oxidation is an anti-Markovnikov’s addition of water across an alkene. The -OH group is added to the less substituted position and the -H is in the more substituted position.
- If there is more than one chiral center in the product, then the product will produce a pair of enantiomers that results from syn addition. A common example of oxidation of 1-Propene is given below.

- Here, we can see that first, $B{{H}_{3}}$ is added to the carbon-carbon double bond in a way that H-atom gets bonded to a carbon that has less number of hydrogen atoms(means in anti-markovnikov manner). Then, in presence of hydrogen peroxide-an oxidising agent, the organo-borane compound decomposes and gives an alcohol as shown in the reaction.
- One molecule of $B{{H}_{3}}$ can oxidise three molecules of alkene because one B-H bond is responsible for the oxidation of one molecule of alkene. After oxidising alkene, B-H bond gets converted into B-OH bond. So, $B{{H}_{3}}$ has three B-H bonds, and it will oxidise total of three alkenes and will give ${{H}_{3}}B{{O}_{3}}$ in the end. We can show how one molecule of $B{{H}_{3}}$ oxidises three molecules of alkene as below.

Note: Remember that it will give an anti-markovnikov product after addition to the alkene double bond. We cannot use water as a solvent here because it will immediately react with $B{{H}_{3}}$ as water has an amphoteric nature and $B{{H}_{3}}$ is a lewis acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




