
Match list-I (complexes) with list-II (Hybridization of central atom) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I List-II A. $Ni{{\left( CO \right)}_{4}}$ 1. $s{{p}^{3}}$ B. $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$ 2. $ds{{p}^{2}}$ C. $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$ 3. $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ D. $MnF_{6}^{4-}$ 4. ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ 5. $s{{p}^{2}}d$...
A. A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
B. A-5, B-2, C-4, D-3
C. A-5, B-3, C-2, D-4
D. A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
| List-I | List-II |
| A. $Ni{{\left( CO \right)}_{4}}$ | 1. $s{{p}^{3}}$ |
| B. $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$ | 2. $ds{{p}^{2}}$ |
| C. $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$ | 3. $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ |
| D. $MnF_{6}^{4-}$ | 4. ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ |
| 5. $s{{p}^{2}}d$... |
Answer
573k+ views
Hint As we know that hybridization is the process of producing a degenerated type of orbital by mixing two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels. During hybridization, atomic orbitals are mixed and a new hybrid orbital is formed.
Complete Step by step solution:
- In $Ni{{\left( CO \right)}_{4}}$, Ni atom is $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to a tetrahedral geometry. We can see the structure:
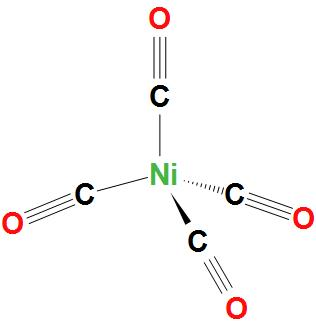
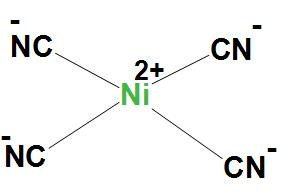
- In $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$, Ni atom is $ds{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to a square planar geometry.
Here, $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$ is showing $ds{{p}^{2}}$ hybridisation, because here CN group is a strong field ligand and it forms inner complexes. We can see the structure:
- In $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$, Ni atom is ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to an octahedral geometry. Here, $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$ is showing ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridisation, because here cyanide group is present. And as we know that cyanide group is a strong field ligand and it forms inner complexes. We can see the structure:
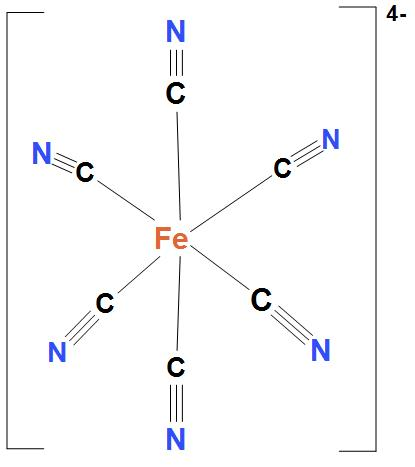
- In $MnF_{6}^{4-}$, Ni atom is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to an octahedral geometry. We can see the structure:
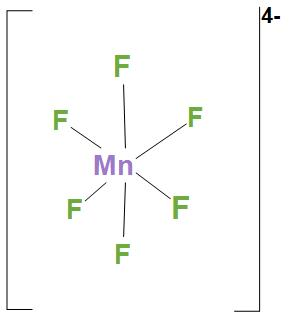
Hence, we can say that correct option is (d), that is A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
Note:
- We must note the key features of hybridization: the atomic orbitals that have equal energies undergo hybridization. Shape of any molecule can be predicted from hybridization.
- The number of hybrid orbitals that are formed during hybridization will be equal to the number of atomic orbitals mixed.
Complete Step by step solution:
- In $Ni{{\left( CO \right)}_{4}}$, Ni atom is $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to a tetrahedral geometry. We can see the structure:

- In $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$, Ni atom is $ds{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to a square planar geometry.
Here, $Ni\left( CN \right)_{4}^{2-}$ is showing $ds{{p}^{2}}$ hybridisation, because here CN group is a strong field ligand and it forms inner complexes. We can see the structure:

- In $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$, Ni atom is ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to an octahedral geometry. Here, $Fe\left( CN \right)_{6}^{4-}$ is showing ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridisation, because here cyanide group is present. And as we know that cyanide group is a strong field ligand and it forms inner complexes. We can see the structure:

- In $MnF_{6}^{4-}$, Ni atom is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridised. And this will lead to an octahedral geometry. We can see the structure:

Hence, we can say that correct option is (d), that is A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
Note:
- We must note the key features of hybridization: the atomic orbitals that have equal energies undergo hybridization. Shape of any molecule can be predicted from hybridization.
- The number of hybrid orbitals that are formed during hybridization will be equal to the number of atomic orbitals mixed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




