
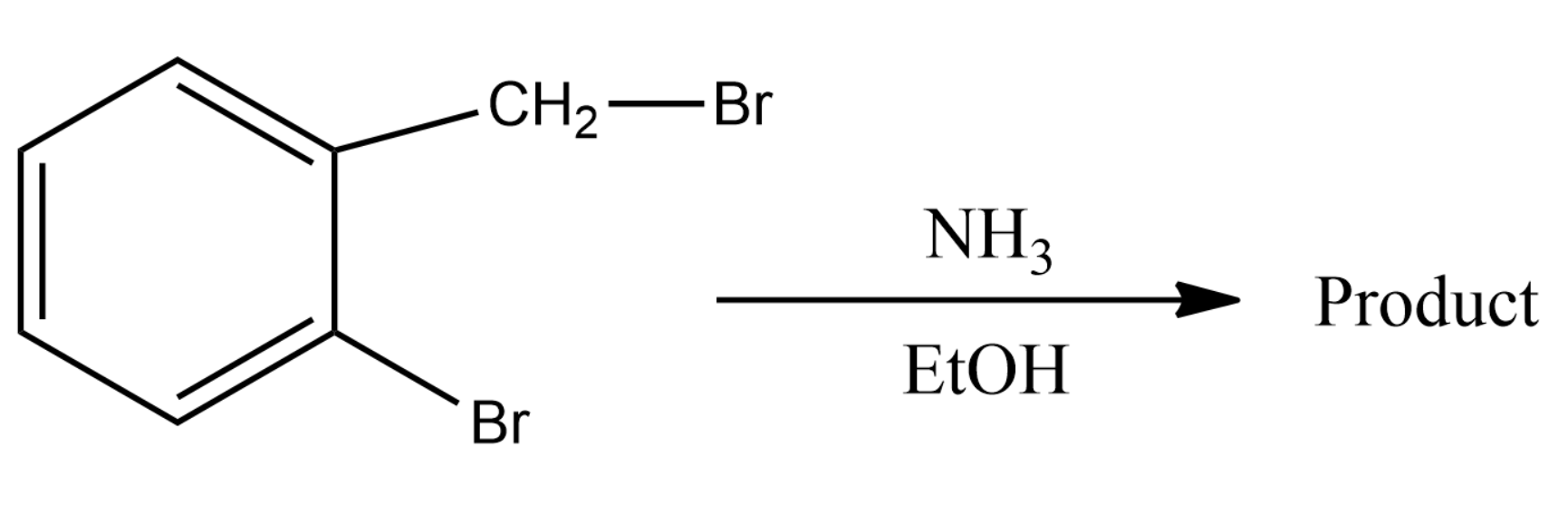
What is the major product obtained in the following reaction?
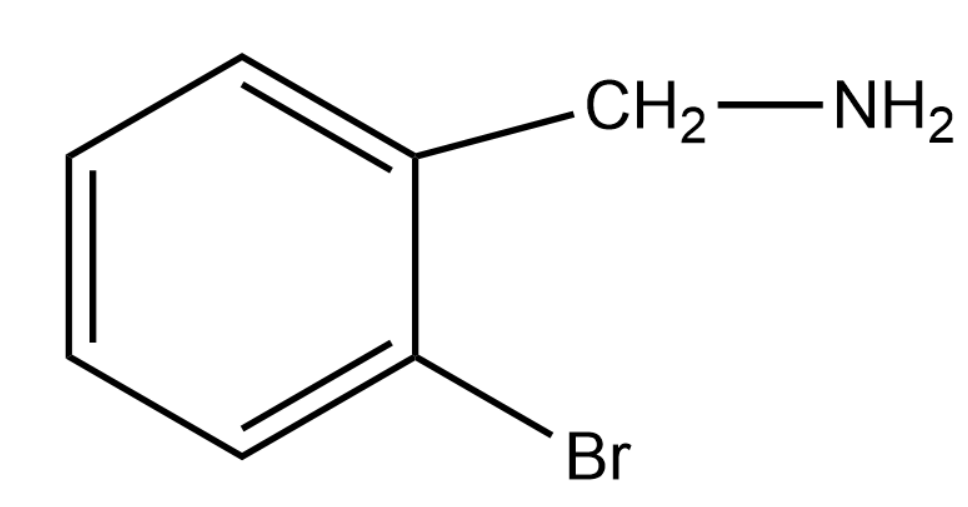
A.
B.
C.
D.
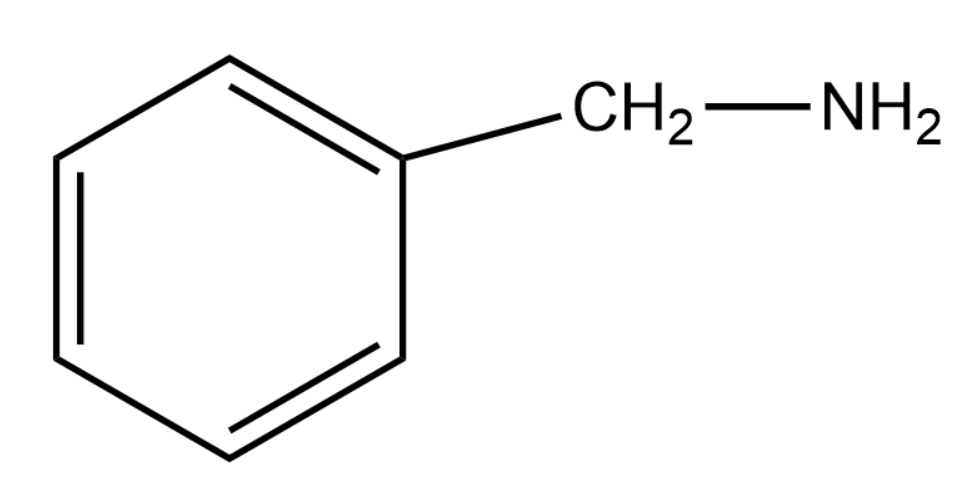





Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: Aromaticity is a property of conjugated cyclic hydrocarbons in which the stabilization of the molecule is enhanced due to the ability of the electrons in the pi orbitals to delocalize. This will always force the molecule to be a planar molecule. If a compound can maintain its aromaticity I will always tend to do so.
Complete answer:
Here we are looking at a substitution reaction. The ammonia molecule will give a \[ - N{H_2}\] group, which can be substituted instead of the Bromines.
The interesting thing to note here is that out of the two bromines only one will provide a stable carbocation. The more stable the carbocation intermediate formed the more probable and thus favourable the reaction becomes. Thus by forming a phenyl carbocation the topmost Bromine will make the major product whereas the Bromine attached to the benzene ring will not take part in any of the reaction because the formed carbocation is not at all stable.
Thus the product formed will be the product given in option (1)
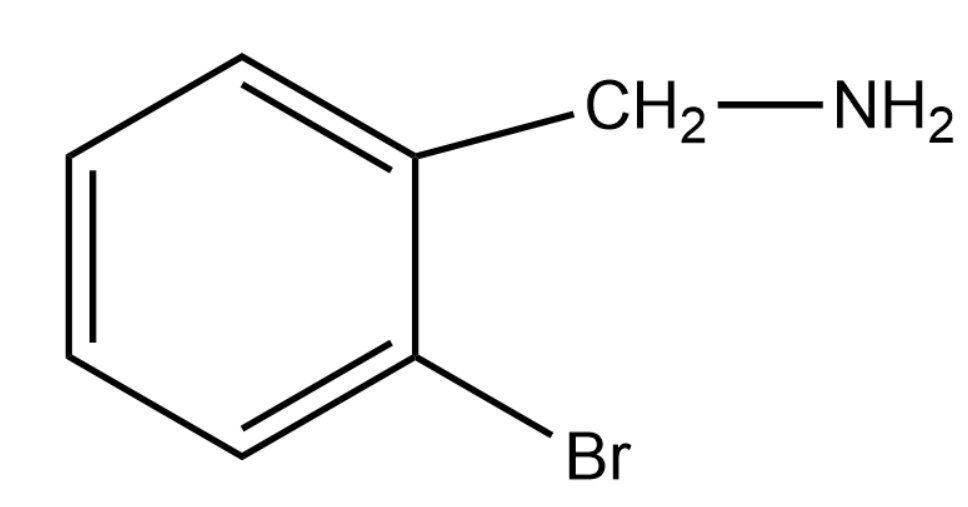
The complete mechanism is that when ammonia comes the bromine will leave that position as \[B{r^ - }\] . This will leave us with phenyl carbocation and thus the \[ - N{H_2}\] is added at that position.
Note:
Another explanation for the bromine attached to the benzene ring not participating in the reaction is that the Bromine-carbon bond will have a partial double bond character due to resonance. Thus it is energetically more expensive to break that bond and form the desired product. Thus that particular bromine does not take part in the reaction.
Complete answer:
Here we are looking at a substitution reaction. The ammonia molecule will give a \[ - N{H_2}\] group, which can be substituted instead of the Bromines.
The interesting thing to note here is that out of the two bromines only one will provide a stable carbocation. The more stable the carbocation intermediate formed the more probable and thus favourable the reaction becomes. Thus by forming a phenyl carbocation the topmost Bromine will make the major product whereas the Bromine attached to the benzene ring will not take part in any of the reaction because the formed carbocation is not at all stable.
Thus the product formed will be the product given in option (1)

The complete mechanism is that when ammonia comes the bromine will leave that position as \[B{r^ - }\] . This will leave us with phenyl carbocation and thus the \[ - N{H_2}\] is added at that position.
Note:
Another explanation for the bromine attached to the benzene ring not participating in the reaction is that the Bromine-carbon bond will have a partial double bond character due to resonance. Thus it is energetically more expensive to break that bond and form the desired product. Thus that particular bromine does not take part in the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




