
Major product “A” is
A.
B.
C.

D.





Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: NBS is a very versatile reagent in organic reactions. Its full form is N-Bromosuccinimide which is formed by the reaction of succinimide and bromine in presence of an alkali and at cool conditions.
Complete step by step solution
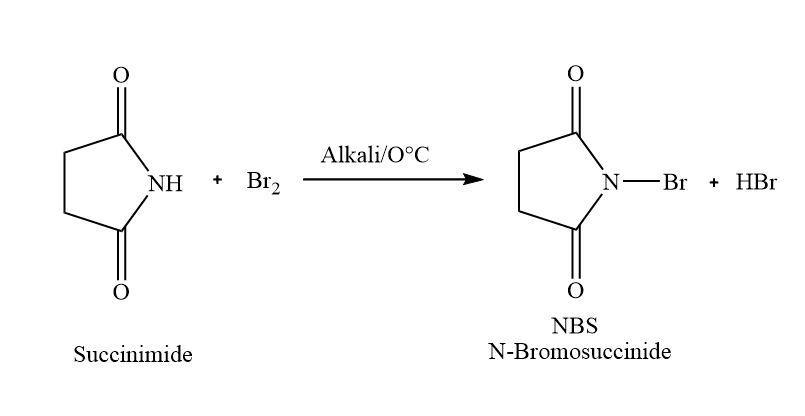
In this sodium hydroxide used as an alkali. In the first step the hydroxide of sodium hydroxide takes away the acidic hydrogen. Then it will react with $B{r_2}$ to form N-Bromosuccinimide and hydrogen bromide as the by-product.
Let us explain the mechanism of allylic bromination using NBS-
Step 1-Initiation;
Step 2-Propagation;
Step 3-Termination;
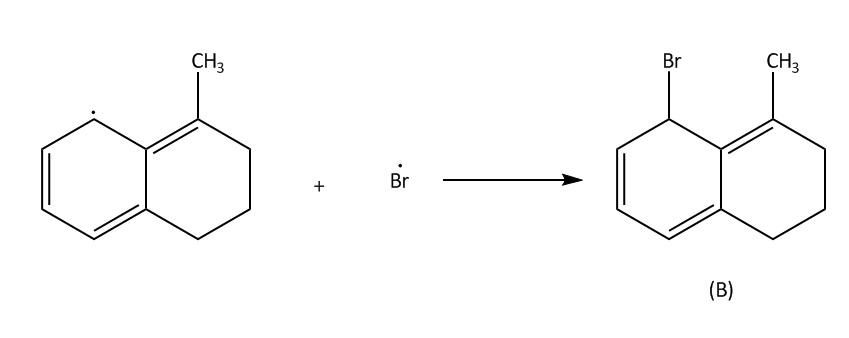
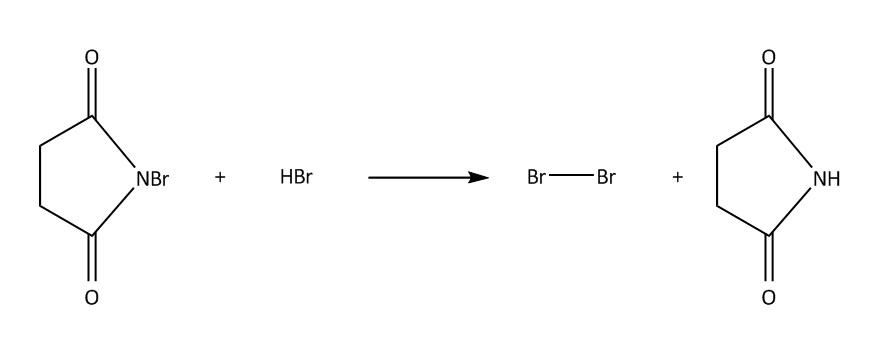
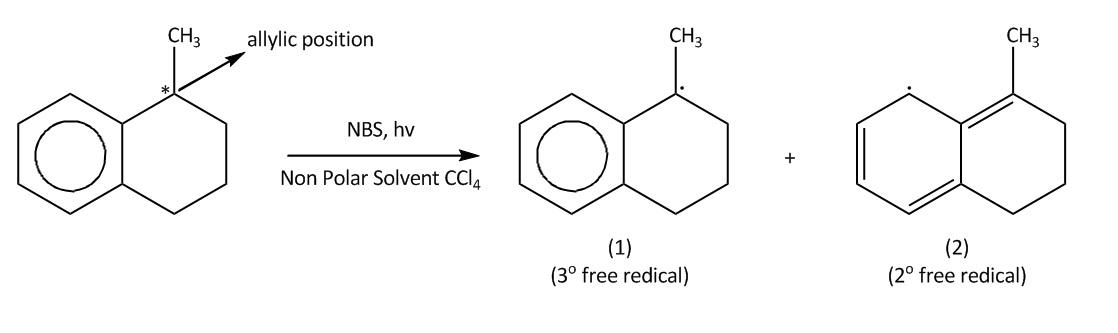
In NBS Hydrogen bromide is available in traces. Then we will get bromine molecules. Then in the next step hv will cleave the bromine molecule homolytically to bromine radical. This process is also known as initiation. Then in second step the bromine radical will attack at allylic position of benzene which is marked in the molecule and there will be the formation of ${3^0}$ free radical $\left( 1 \right)$.This process is known as propagation .This ${3^0}$ free radical can also undergo resonance to form ${2^0}$ free radical $\left( 2 \right)$
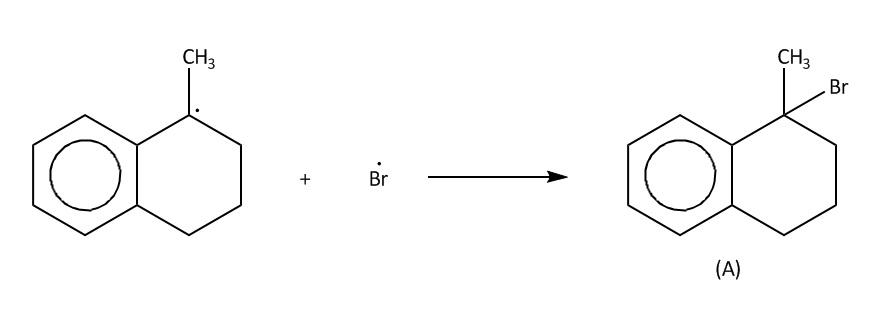
Now in the last step which is also called termination step, these free radicals will react with bromine free radicals to form the desired product. A and B.
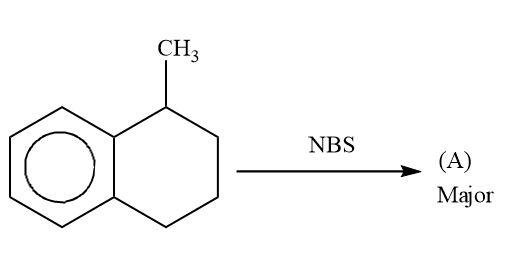
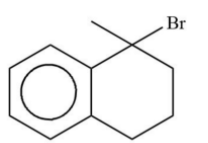
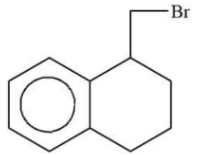
Now lets us emphasise on these two products. In case of product A and B. A product will be formed by reaction of ${3^0}$ free radical while product B is formed by ${2^0}$ free radical. The ${3^0}$ free radical is more stable then ${2^0}$ free radical and in ${2^0}$ free radical the aromatisation of benzene is also lost. So, from all these points we can say that ${3^0}$ free radical is more stable than ${2^0}$ free radical.
Hence, A is a more stable product.
Hence, option (A) is correct.
Note:
NBS has a very different reaction. It can be used as a brominating agent, as an oxidizing agent and also as a dehydrating agent. It can also convert primary alcohol to aldehyde and secondary alcohol converts to ketone. It can react via both Free radical mechanism and electrophilic addition reaction.

Complete step by step solution
In this sodium hydroxide used as an alkali. In the first step the hydroxide of sodium hydroxide takes away the acidic hydrogen. Then it will react with $B{r_2}$ to form N-Bromosuccinimide and hydrogen bromide as the by-product.
Let us explain the mechanism of allylic bromination using NBS-
Step 1-Initiation;

Step 2-Propagation;

Step 3-Termination;


In NBS Hydrogen bromide is available in traces. Then we will get bromine molecules. Then in the next step hv will cleave the bromine molecule homolytically to bromine radical. This process is also known as initiation. Then in second step the bromine radical will attack at allylic position of benzene which is marked in the molecule and there will be the formation of ${3^0}$ free radical $\left( 1 \right)$.This process is known as propagation .This ${3^0}$ free radical can also undergo resonance to form ${2^0}$ free radical $\left( 2 \right)$
Now in the last step which is also called termination step, these free radicals will react with bromine free radicals to form the desired product. A and B.
Now lets us emphasise on these two products. In case of product A and B. A product will be formed by reaction of ${3^0}$ free radical while product B is formed by ${2^0}$ free radical. The ${3^0}$ free radical is more stable then ${2^0}$ free radical and in ${2^0}$ free radical the aromatisation of benzene is also lost. So, from all these points we can say that ${3^0}$ free radical is more stable than ${2^0}$ free radical.
Hence, A is a more stable product.
Hence, option (A) is correct.
Note:
NBS has a very different reaction. It can be used as a brominating agent, as an oxidizing agent and also as a dehydrating agent. It can also convert primary alcohol to aldehyde and secondary alcohol converts to ketone. It can react via both Free radical mechanism and electrophilic addition reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




