
Let the equations of two sides of a triangle be \[3x-2y+6=0\] and \[4x+5y-20=0\]. If the
orthocentre of this triangle is at \[(1,1)\], then the equation of its third side is
(a) \[122y-26x-1675=0\]
(b) \[26x+61y+1675=0\]
(c) \[122y+26x+1675=0\]
(d) \[26x-122y-1675=0\]
Answer
625.5k+ views
Hint: Find the slope of the given two lines and use this slope and given orthocentre to find the coordinates of the triangle.
The equations of the sides of a triangle given in the questions are,
\[3x-2y+6=0\] and \[4x+5y-20=0\]
The orthocentre of a triangle is the point where all the altitudes intersect. Its coordinates are given
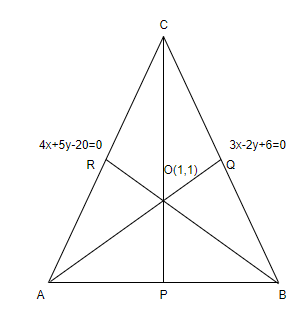
in the question as \[(1,1)\]. Draw a triangle ABC with all the given data as shown below,
Consider the line AC. The slope of the line can be obtained by rearranging the equation as,
\[\begin{align}
& 4x+5y-20=0 \\
& 5y=20-4x \\
& y=-\dfrac{4}{5}x+4 \\
\end{align}\]
Comparing it with the general equation, \[y=mx+c\], we have the slope as \[-\dfrac{4}{5}\]. The slope
of perpendicular lines is related as \[m\times n=-1\]. Now since the line BR is perpendicular to the
line AC, the slope of BR would be \[\dfrac{5}{4}\].
The line BR has slope \[\dfrac{5}{4}\] and passes through the point \[(1,1)\]. The equation of a line
passing through point \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and having slope \[m\] is given by,\[y-{{y}_{1}}=m(x-
{{x}_{1}})\]. The equation of the line BR can hence be obtained as,
\[\begin{align}
& y-1=\dfrac{5}{4}(x-1) \\
& 4(y-1)=5(x-1) \\
& 4y-4=5x-5 \\
& 5x-4y-1=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Next, we have to consider line BC. The slope of the line can be obtained by rearranging the equation
as,
\[\begin{align}
& 3x-2y+6=0 \\
& -2y=-6-3x \\
& y=\dfrac{3}{2}x+3 \\
\end{align}\]
Comparing it with the general equation, \[y=mx+c\], we have the slope as \[\dfrac{3}{2}\]. The slope
of perpendicular lines is related as \[m\times n=-1\]. Now since the line AQ is perpendicular to the
line BC, the slope of AQ would be \[-\dfrac{2}{3}\].
The line AQ has slope \[-\dfrac{2}{3}\] and passes through the point \[(1,1)\]. The equation of a line
passing through point \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and having slope \[m\] is given by,\[y-{{y}_{1}}=m(x-
{{x}_{1}})\]. The equation of the line AQ can hence be obtained as,
\[\begin{align}
& y-1=-\dfrac{2}{3}(x-1) \\
& 3(y-1)=-2(x-1) \\
& 3y-3=-2x+2 \\
& 2x+3y-5=0 \\
\end{align}\]
The vertex A is passing through both lines AC and AQ. So, we can get the coordinates of vertex A by
solving the equations \[4x+5y-20=0\] and \[2x+3y-5=0\]. Multiplying the equation \[2x+3y-5=0\] by 2
and subtracting from the equation \[4x+5y-20=0\], we get,
\[\dfrac{\begin{align}
& 4x+5y-20=0 \\
& -4x-6y+10=0 \\
\end{align}}{\begin{align}
& -y-10=0 \\
& y=-10 \\
\end{align}}\]
Substituting the value of \[y\] in \[2x+3y-5=0\], we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 2x+(3\times -10)-5=0 \\
& 2x-30-5=0 \\
& 2x=35 \\
& x=\dfrac{35}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the coordinates of A are \[\left( \dfrac{35}{2},-10 \right)\].
The vertex B is passing through both lines BC and BR. So, we can get the coordinates of vertex B by
solving the equations \[3x-2y+6=0\] and \[5x-4y-1=0\] . Multiplying the equation \[3x-2y+6=0\] by 2
and subtracting the equation \[5x-4y-1=0\] from it, we get,
\[\dfrac{\begin{align}
& 6x-4y+12=0 \\
& -5x+4y+1=0 \\
\end{align}}{\begin{align}
& x+13=0 \\
& x=-13 \\
\end{align}}\]
Substituting the value of \[x\] in \[3x-2y+6=0\], we get,
\[\begin{align}
& (3\times -13)-2y+6=0 \\
& -39-2y+6=0 \\
& -2y=33 \\
& y=-\dfrac{33}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the coordinates of B are \[\left( -13,-\dfrac{33}{2} \right)\].
The equation of a line passing through two points \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] is
given by,
\[\begin{align}
& y-{{y}_{1}}=m(x-{{x}_{1}}) \\
& \Rightarrow y-{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\times (x-{{x}_{1}}) \\
\end{align}\]
The equation of line AB passing through points \[\left( \dfrac{35}{2},-10 \right)\] and \[\left( -13,-
\dfrac{33}{2} \right)\] can hence be found as,
\[\left( y+10 \right)=\dfrac{\left( -\dfrac{33}{2}+10 \right)}{\left( -13-\dfrac{35}{2} \right)}\times
\left( x-\dfrac{35}{2} \right)\]
Taking the LCM of the terms in the numerator and denominator,
\[\begin{align}
& y+10=\dfrac{-\dfrac{13}{2}}{-\dfrac{61}{2}}\times \left( x-\dfrac{35}{2} \right) \\
& y+10=\dfrac{13}{61}\times \left( x-\dfrac{35}{2} \right) \\
& 61(y+10)=13\left( x-\dfrac{35}{2} \right) \\
& 61y+610=13x-\dfrac{455}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Multiplying both sides by 2,
\[\begin{align}
& 122y+1220=26x-455 \\
& 26x-122y-1675=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the required equation of the straight line is \[26x-122y-1675=0\].
We get option (d) as the correct answer.
Note: There is one more way to approach this problem. The coordinates of the vertices A and B can
be taken as \[\left( p,\dfrac{20-4p}{5} \right)\] and \[\left( q,\dfrac{3+6q}{2} \right)\] by assuming
\[x\] as \[p\] and \[q\] respectively in the equations \[4x+5y-20=0\]and \[3x-2y+6=0\]. Then we can
formulate the equations using the slope of the lines and solve for \[p\] and \[q\]. The equation of AB
can then be obtained.
The equations of the sides of a triangle given in the questions are,
\[3x-2y+6=0\] and \[4x+5y-20=0\]
The orthocentre of a triangle is the point where all the altitudes intersect. Its coordinates are given
in the question as \[(1,1)\]. Draw a triangle ABC with all the given data as shown below,
Consider the line AC. The slope of the line can be obtained by rearranging the equation as,
\[\begin{align}
& 4x+5y-20=0 \\
& 5y=20-4x \\
& y=-\dfrac{4}{5}x+4 \\
\end{align}\]
Comparing it with the general equation, \[y=mx+c\], we have the slope as \[-\dfrac{4}{5}\]. The slope
of perpendicular lines is related as \[m\times n=-1\]. Now since the line BR is perpendicular to the
line AC, the slope of BR would be \[\dfrac{5}{4}\].
The line BR has slope \[\dfrac{5}{4}\] and passes through the point \[(1,1)\]. The equation of a line
passing through point \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and having slope \[m\] is given by,\[y-{{y}_{1}}=m(x-
{{x}_{1}})\]. The equation of the line BR can hence be obtained as,
\[\begin{align}
& y-1=\dfrac{5}{4}(x-1) \\
& 4(y-1)=5(x-1) \\
& 4y-4=5x-5 \\
& 5x-4y-1=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Next, we have to consider line BC. The slope of the line can be obtained by rearranging the equation
as,
\[\begin{align}
& 3x-2y+6=0 \\
& -2y=-6-3x \\
& y=\dfrac{3}{2}x+3 \\
\end{align}\]
Comparing it with the general equation, \[y=mx+c\], we have the slope as \[\dfrac{3}{2}\]. The slope
of perpendicular lines is related as \[m\times n=-1\]. Now since the line AQ is perpendicular to the
line BC, the slope of AQ would be \[-\dfrac{2}{3}\].
The line AQ has slope \[-\dfrac{2}{3}\] and passes through the point \[(1,1)\]. The equation of a line
passing through point \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and having slope \[m\] is given by,\[y-{{y}_{1}}=m(x-
{{x}_{1}})\]. The equation of the line AQ can hence be obtained as,
\[\begin{align}
& y-1=-\dfrac{2}{3}(x-1) \\
& 3(y-1)=-2(x-1) \\
& 3y-3=-2x+2 \\
& 2x+3y-5=0 \\
\end{align}\]
The vertex A is passing through both lines AC and AQ. So, we can get the coordinates of vertex A by
solving the equations \[4x+5y-20=0\] and \[2x+3y-5=0\]. Multiplying the equation \[2x+3y-5=0\] by 2
and subtracting from the equation \[4x+5y-20=0\], we get,
\[\dfrac{\begin{align}
& 4x+5y-20=0 \\
& -4x-6y+10=0 \\
\end{align}}{\begin{align}
& -y-10=0 \\
& y=-10 \\
\end{align}}\]
Substituting the value of \[y\] in \[2x+3y-5=0\], we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 2x+(3\times -10)-5=0 \\
& 2x-30-5=0 \\
& 2x=35 \\
& x=\dfrac{35}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the coordinates of A are \[\left( \dfrac{35}{2},-10 \right)\].
The vertex B is passing through both lines BC and BR. So, we can get the coordinates of vertex B by
solving the equations \[3x-2y+6=0\] and \[5x-4y-1=0\] . Multiplying the equation \[3x-2y+6=0\] by 2
and subtracting the equation \[5x-4y-1=0\] from it, we get,
\[\dfrac{\begin{align}
& 6x-4y+12=0 \\
& -5x+4y+1=0 \\
\end{align}}{\begin{align}
& x+13=0 \\
& x=-13 \\
\end{align}}\]
Substituting the value of \[x\] in \[3x-2y+6=0\], we get,
\[\begin{align}
& (3\times -13)-2y+6=0 \\
& -39-2y+6=0 \\
& -2y=33 \\
& y=-\dfrac{33}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the coordinates of B are \[\left( -13,-\dfrac{33}{2} \right)\].
The equation of a line passing through two points \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] is
given by,
\[\begin{align}
& y-{{y}_{1}}=m(x-{{x}_{1}}) \\
& \Rightarrow y-{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\times (x-{{x}_{1}}) \\
\end{align}\]
The equation of line AB passing through points \[\left( \dfrac{35}{2},-10 \right)\] and \[\left( -13,-
\dfrac{33}{2} \right)\] can hence be found as,
\[\left( y+10 \right)=\dfrac{\left( -\dfrac{33}{2}+10 \right)}{\left( -13-\dfrac{35}{2} \right)}\times
\left( x-\dfrac{35}{2} \right)\]
Taking the LCM of the terms in the numerator and denominator,
\[\begin{align}
& y+10=\dfrac{-\dfrac{13}{2}}{-\dfrac{61}{2}}\times \left( x-\dfrac{35}{2} \right) \\
& y+10=\dfrac{13}{61}\times \left( x-\dfrac{35}{2} \right) \\
& 61(y+10)=13\left( x-\dfrac{35}{2} \right) \\
& 61y+610=13x-\dfrac{455}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Multiplying both sides by 2,
\[\begin{align}
& 122y+1220=26x-455 \\
& 26x-122y-1675=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the required equation of the straight line is \[26x-122y-1675=0\].
We get option (d) as the correct answer.
Note: There is one more way to approach this problem. The coordinates of the vertices A and B can
be taken as \[\left( p,\dfrac{20-4p}{5} \right)\] and \[\left( q,\dfrac{3+6q}{2} \right)\] by assuming
\[x\] as \[p\] and \[q\] respectively in the equations \[4x+5y-20=0\]and \[3x-2y+6=0\]. Then we can
formulate the equations using the slope of the lines and solve for \[p\] and \[q\]. The equation of AB
can then be obtained.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




