
Let the chord of contact is drawn from every point lying on the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=100$ to the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{9}=1$ such that all the lines touches a standard ellipse whose eccentricity is $e$ , then $\dfrac{81{{e}^{{{2}^{{}}}}}}{13}$ is
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Equation of chord of contact of tangent from point $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ where $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ lies outside the ellipse is $\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}^{{}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ . This equation of chord is the tangent to the circle. So if $y=mx+c$ where m is the slope of line and c is the y-intercept, is the tangent to the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}$ with radius $a$ then the radius of circle is given by $a=\dfrac{\left| c \right|}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Standard equation of circle is ${{(x-a)}^{2}}+{{(y-b)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$ where $(a,b)$ is the center of the circle and $r$ is the radius of the given circle.
In the given question we are given a circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=100$ , whose center is (0,0) and radius = 10. And $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{9}=1$ is a given ellipse having major axis in the y-axis direction. Graph of the circle and ellipse is given below.
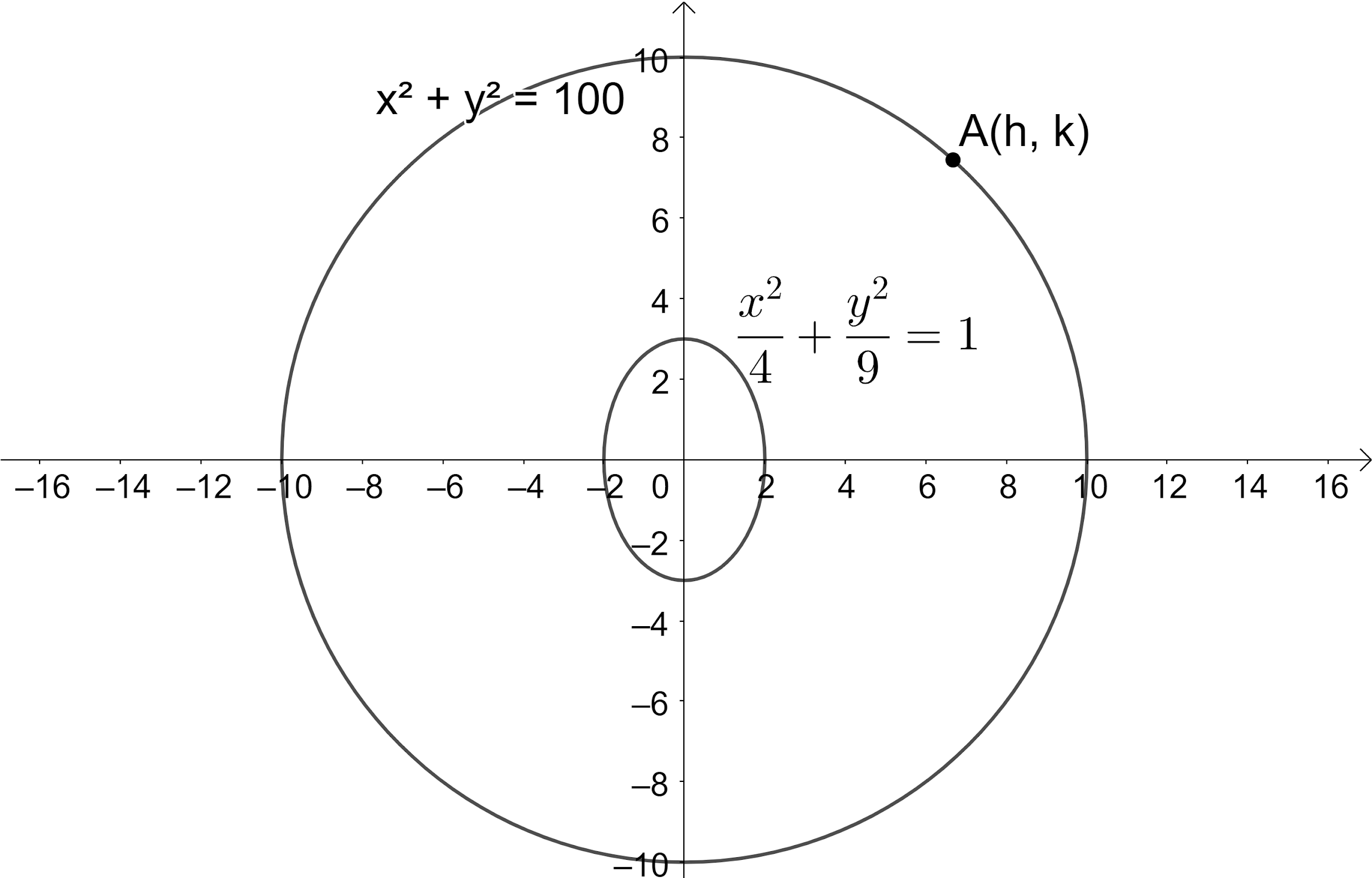
Equation of chord of contact of tangent from point $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ where $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ lies outside the ellipse$\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ is $\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}^{{}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.Let $(h,k)$ be the point outside the ellipse then equation of chord of contact of tangent from point A$(h,k)$ to ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{9}=1$ is $\dfrac{hx}{4}+\dfrac{ky}{9}=1.............(1)$.
This chord is the tangent to the circle. If $y=mx+c...........(2)$ where m is the slope of line and c is the y-intercept, is the tangent to the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}$ with radius $a$ then the radius of circle is given by $a=\dfrac{\left| c \right|}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}............(3)$.
Let $p=\dfrac{h}{4}$ ,$q=\dfrac{k}{9}$ and $r=1$ then equation (1) can be written as
\[\Rightarrow px+qy=r\].
$\Rightarrow qy=r-px$.
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{r}{q}-\dfrac{px}{q}$.
Comparing equation (2) and (4) we get $m=\dfrac{-p}{q}$ and $c=\dfrac{r}{q}$. Putting these value in equation (3) we get $\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{\left| \left( \dfrac{r}{q} \right) \right|}{\sqrt{1+{{\left( \dfrac{-p}{q} \right)}^{2}}}} \\
& \\
\end{align}$.
Squaring on both sides we get,
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{\left| \left( \dfrac{r}{q} \right) \right|}{\sqrt{1+{{\left( \dfrac{-p}{q} \right)}^{2}}}} \right)}^{2}}$.
\[\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=\dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{r}{q} \right)}^{2}}}{1+{{\left( \dfrac{-p}{q} \right)}^{2}}}\].
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{\left( \dfrac{1+{{\left( \dfrac{-p}{q} \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{r}{q} \right)}^{2}}} \right)}$.
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{{{\left( \dfrac{q}{r} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{p}{r} \right)}^{2}}}...............(5)$.
Here $r=1$ so equation (5) becomes ${{a}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{{{q}^{2}}+{{p}^{2}}}...........(6)$.
We know that the radius of circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=100$ is 10 so here $a$ is 10. Putting the values of $a=10$, $p=\dfrac{h}{4}$ and$q=\dfrac{k}{9}$ in equation (6) we get
$\Rightarrow 100=\left( \dfrac{1}{\dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{16}+\dfrac{{{k}^{2}}}{81}} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{16}+\dfrac{{{k}^{2}}}{81}=\dfrac{1}{100}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{100{{h}^{2}}}{16}+\dfrac{100{{k}^{2}}}{81}=1$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{\left( \dfrac{16}{100} \right)}+\dfrac{{{k}^{2}}}{\left( \dfrac{81}{100} \right)}=1.............(7)$.
Standard equation of ellipse is given as $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ here we got $b < a$, comparing this equation with (7) we get ${{b}^{2}}=\dfrac{81}{100}$ and ${{a}^{2}}=\dfrac{16}{100}$.
Eccentricity is given by formula, $e=\dfrac{c}{b}..........(8)$, where $c=\sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}$.
$\Rightarrow c=\sqrt{\dfrac{81}{100}-\dfrac{16}{100}}$.
$\Rightarrow c=\sqrt{\dfrac{81-16}{100}}$.
$\Rightarrow c=\dfrac{\sqrt{65}}{10}$.
Putting the value of c and a in equation (8) we get,
$\Rightarrow e=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{65}}{10} \right)}{\left( \dfrac{9}{10} \right)}$.
$\Rightarrow e=\dfrac{\sqrt{65}}{9}$.
Therefore,
$\dfrac{81{{e}^{2}}}{13}=\dfrac{81}{13}\times \dfrac{65}{81}$.
$\dfrac{81{{e}^{2}}}{13}=\dfrac{65}{13}$.
$\dfrac{81{{e}^{2}}}{13}=5$.
Hence the value of $\dfrac{81{{e}^{2}}}{13}$ is 5.
Note:
We need not always get the equation of ellipse as $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ where $a>b$. We should know that the equation of the ellipse depends on the condition given in the problem. We should not confuse it with eccentricity while solving this problem. We can also solve this problem by taking the equation of common chords at the points $\left( 0,10 \right)$ and $\left( 10,0 \right)$ of the points which gives us the values of a and b directly.
Complete step by step answer:
Standard equation of circle is ${{(x-a)}^{2}}+{{(y-b)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$ where $(a,b)$ is the center of the circle and $r$ is the radius of the given circle.
In the given question we are given a circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=100$ , whose center is (0,0) and radius = 10. And $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{9}=1$ is a given ellipse having major axis in the y-axis direction. Graph of the circle and ellipse is given below.

Equation of chord of contact of tangent from point $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ where $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ lies outside the ellipse$\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ is $\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}^{{}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$.Let $(h,k)$ be the point outside the ellipse then equation of chord of contact of tangent from point A$(h,k)$ to ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{9}=1$ is $\dfrac{hx}{4}+\dfrac{ky}{9}=1.............(1)$.
This chord is the tangent to the circle. If $y=mx+c...........(2)$ where m is the slope of line and c is the y-intercept, is the tangent to the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}$ with radius $a$ then the radius of circle is given by $a=\dfrac{\left| c \right|}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}............(3)$.
Let $p=\dfrac{h}{4}$ ,$q=\dfrac{k}{9}$ and $r=1$ then equation (1) can be written as
\[\Rightarrow px+qy=r\].
$\Rightarrow qy=r-px$.
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{r}{q}-\dfrac{px}{q}$.
Comparing equation (2) and (4) we get $m=\dfrac{-p}{q}$ and $c=\dfrac{r}{q}$. Putting these value in equation (3) we get $\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{\left| \left( \dfrac{r}{q} \right) \right|}{\sqrt{1+{{\left( \dfrac{-p}{q} \right)}^{2}}}} \\
& \\
\end{align}$.
Squaring on both sides we get,
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{\left| \left( \dfrac{r}{q} \right) \right|}{\sqrt{1+{{\left( \dfrac{-p}{q} \right)}^{2}}}} \right)}^{2}}$.
\[\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=\dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{r}{q} \right)}^{2}}}{1+{{\left( \dfrac{-p}{q} \right)}^{2}}}\].
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{\left( \dfrac{1+{{\left( \dfrac{-p}{q} \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{r}{q} \right)}^{2}}} \right)}$.
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{{{\left( \dfrac{q}{r} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{p}{r} \right)}^{2}}}...............(5)$.
Here $r=1$ so equation (5) becomes ${{a}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{{{q}^{2}}+{{p}^{2}}}...........(6)$.
We know that the radius of circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=100$ is 10 so here $a$ is 10. Putting the values of $a=10$, $p=\dfrac{h}{4}$ and$q=\dfrac{k}{9}$ in equation (6) we get
$\Rightarrow 100=\left( \dfrac{1}{\dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{16}+\dfrac{{{k}^{2}}}{81}} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{16}+\dfrac{{{k}^{2}}}{81}=\dfrac{1}{100}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{100{{h}^{2}}}{16}+\dfrac{100{{k}^{2}}}{81}=1$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{h}^{2}}}{\left( \dfrac{16}{100} \right)}+\dfrac{{{k}^{2}}}{\left( \dfrac{81}{100} \right)}=1.............(7)$.
Standard equation of ellipse is given as $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ here we got $b < a$, comparing this equation with (7) we get ${{b}^{2}}=\dfrac{81}{100}$ and ${{a}^{2}}=\dfrac{16}{100}$.
Eccentricity is given by formula, $e=\dfrac{c}{b}..........(8)$, where $c=\sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}$.
$\Rightarrow c=\sqrt{\dfrac{81}{100}-\dfrac{16}{100}}$.
$\Rightarrow c=\sqrt{\dfrac{81-16}{100}}$.
$\Rightarrow c=\dfrac{\sqrt{65}}{10}$.
Putting the value of c and a in equation (8) we get,
$\Rightarrow e=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{65}}{10} \right)}{\left( \dfrac{9}{10} \right)}$.
$\Rightarrow e=\dfrac{\sqrt{65}}{9}$.
Therefore,
$\dfrac{81{{e}^{2}}}{13}=\dfrac{81}{13}\times \dfrac{65}{81}$.
$\dfrac{81{{e}^{2}}}{13}=\dfrac{65}{13}$.
$\dfrac{81{{e}^{2}}}{13}=5$.
Hence the value of $\dfrac{81{{e}^{2}}}{13}$ is 5.
Note:
We need not always get the equation of ellipse as $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ where $a>b$. We should know that the equation of the ellipse depends on the condition given in the problem. We should not confuse it with eccentricity while solving this problem. We can also solve this problem by taking the equation of common chords at the points $\left( 0,10 \right)$ and $\left( 10,0 \right)$ of the points which gives us the values of a and b directly.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




