
What is LED? Show its $V-I$ characteristics drawing circuit diagram.
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: We must know that LED is the abbreviation for light emitting diode. Basically, a LED is a semiconductor device which emits light when current is passed through it. LEDs are always connected as forward biased. The V-I characteristics of a LED is the same as a diode connected in forward biased condition.
Complete step by step answer:
It is an Interesting fact that, from all the different types of semiconductor devices available today, LEDs are the one which is most widely used. They are capable of emitting either visible light or invisible infrared when connected in forward biased condition. So, in short, we can define LEDs as a device which converts electrical energy to light energy.
As diodes, LEDs also have a unique symbol for representation. The symbol for an LED and a p-n junction diode is similar, except that LED contains an arrow pointing away from the diode that indicates the diode is emitting light.
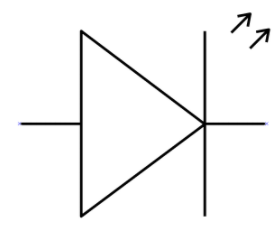
Now, we will discuss the mechanism and connection of an LED in a circuit. We know LED is a forward biased p-n junction diode which emits light when electricity is applied. This light energy is produced due to the recombination of holes and electrons at the junction of a diode. If an LED is connected in reverse biased condition, it will not emit light. Moreover, the LED will be damaged in reverse biased condition.
Mechanism of spontaneous emission explains the mechanism of emission of light energy from an LED. We know that there are two different energy bands present in a semiconductor, conduction band with higher energy and valence band with lower energy. Also, there may be energy bands due to donor impurities $\left( {{E}_{D}} \right)$ near the conduction band and acceptor impurities $\left( {{E}_{A}} \right)$ near the valence band. When an electron transits from a higher to lower energy level, light energy is released.
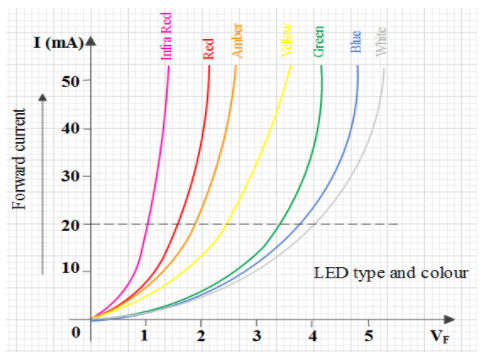
Now, $V-I$ characteristics of LEDs are similar as of a diode connected in forward biased condition. That is,
Note: We must know that the material used for constructing LED depends on the material used for its construction. LEDs need very low current and voltage to function and also, their response time is very low. That means, they will quickly give the output when voltage is applied. But the main disadvantage of LED is considered to be the damage caused to the device when excess current or voltage is applied.
Complete step by step answer:
It is an Interesting fact that, from all the different types of semiconductor devices available today, LEDs are the one which is most widely used. They are capable of emitting either visible light or invisible infrared when connected in forward biased condition. So, in short, we can define LEDs as a device which converts electrical energy to light energy.
As diodes, LEDs also have a unique symbol for representation. The symbol for an LED and a p-n junction diode is similar, except that LED contains an arrow pointing away from the diode that indicates the diode is emitting light.

Now, we will discuss the mechanism and connection of an LED in a circuit. We know LED is a forward biased p-n junction diode which emits light when electricity is applied. This light energy is produced due to the recombination of holes and electrons at the junction of a diode. If an LED is connected in reverse biased condition, it will not emit light. Moreover, the LED will be damaged in reverse biased condition.
Mechanism of spontaneous emission explains the mechanism of emission of light energy from an LED. We know that there are two different energy bands present in a semiconductor, conduction band with higher energy and valence band with lower energy. Also, there may be energy bands due to donor impurities $\left( {{E}_{D}} \right)$ near the conduction band and acceptor impurities $\left( {{E}_{A}} \right)$ near the valence band. When an electron transits from a higher to lower energy level, light energy is released.
Now, $V-I$ characteristics of LEDs are similar as of a diode connected in forward biased condition. That is,

Note: We must know that the material used for constructing LED depends on the material used for its construction. LEDs need very low current and voltage to function and also, their response time is very low. That means, they will quickly give the output when voltage is applied. But the main disadvantage of LED is considered to be the damage caused to the device when excess current or voltage is applied.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




