
Jone’s reagent is:
A.Acidified ${K_2}C{r_2}{O_7}$ solution
B. Alkaline ${K_2}C{r_2}{O_7}$ solution
C.$Cr{O_3}$ in aqueous acetone
D. A solution of ${K_2}C{r_2}{O_7}$/ ${H_2}S{O_4}$ in aqueous ethanol
Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint:Jone’s reagent is a strong oxidising agent which oxidises primary and secondary alcohols to carboxylic acids and aldehydes respectively. This reagent is acidic in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
-Jone’s reagent is basically a solution of chromium trioxide ($Cr{O_3}$) in dilute sulphuric acid (dil. ${H_2}S{O_4}$). Alternatively sodium dichromate ($N{a_2}C{r_2}{O_7}$) or potassium dichromate (${K_2}C{r_2}{O_7}$) can also be used in place of chromium trioxide. This acidic mixture is added to the acetone solution of the substrate to move forward with the reaction.
So, we can say that Jone’s reagent is a mixture of chromic trioxide and dilute sulphuric acid ($Cr{O_3} + {H_2}S{O_4} + {H_2}O$).
It is an oxidising reagent and the reaction it is involved in is known as Jone’s oxidation reaction.
-It causes the oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids and that of secondary alcohols to ketones respectively.
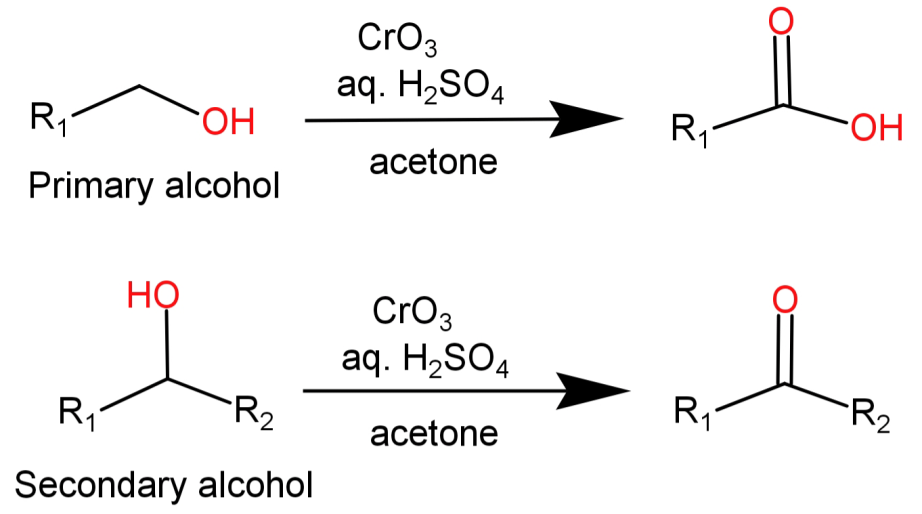
-Since this reagent is acidic in nature the substrate present in acetone is essentially titrated by this oxidant solution.
This oxidation reaction begins with the reaction of $Cr{O_3}$ with the acid ${H_2}S{O_4}$ which forms chromic acid or dichromic acid (in solutions which are more concentrated). Then the primary or secondary alcohol reacts with chromic acid and gets oxidised while chromic acid gets reduced in the process.
-This type of oxidation is very rapid and exothermic. Since it is a very strong oxidising agent it can also reduce aldehydes to carboxylic acids.
So, the correct option is: (C) $Cr{O_3}$ in aqueous acetone.
Note:
The presence of sulphuric acid may result in some side reactions as well so to minimise them its amount can be minimised. But remember that with decrease in its concentration the oxidising power of Jone’s reagent also decreases.
Complete step by step answer:
-Jone’s reagent is basically a solution of chromium trioxide ($Cr{O_3}$) in dilute sulphuric acid (dil. ${H_2}S{O_4}$). Alternatively sodium dichromate ($N{a_2}C{r_2}{O_7}$) or potassium dichromate (${K_2}C{r_2}{O_7}$) can also be used in place of chromium trioxide. This acidic mixture is added to the acetone solution of the substrate to move forward with the reaction.
So, we can say that Jone’s reagent is a mixture of chromic trioxide and dilute sulphuric acid ($Cr{O_3} + {H_2}S{O_4} + {H_2}O$).
It is an oxidising reagent and the reaction it is involved in is known as Jone’s oxidation reaction.
-It causes the oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids and that of secondary alcohols to ketones respectively.

-Since this reagent is acidic in nature the substrate present in acetone is essentially titrated by this oxidant solution.
This oxidation reaction begins with the reaction of $Cr{O_3}$ with the acid ${H_2}S{O_4}$ which forms chromic acid or dichromic acid (in solutions which are more concentrated). Then the primary or secondary alcohol reacts with chromic acid and gets oxidised while chromic acid gets reduced in the process.
-This type of oxidation is very rapid and exothermic. Since it is a very strong oxidising agent it can also reduce aldehydes to carboxylic acids.
So, the correct option is: (C) $Cr{O_3}$ in aqueous acetone.
Note:
The presence of sulphuric acid may result in some side reactions as well so to minimise them its amount can be minimised. But remember that with decrease in its concentration the oxidising power of Jone’s reagent also decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




