
Isobutene $+HBr\xrightarrow[Peroxide]{}$. Product is
A. Tertiary butyl bromide
B. Isobutyl bromide
C. Tertiary butyl alcohol
D. Isobutyl alcohol
Answer
355.5k+ views
Hint: Alkenes undergo an addition reaction called hydrohalogenation to form alkyl halide. The major product that is formed upon halohydrogenation reaction is governed by Makovnikov’s rule. But when peroxide is present with hydrogen halide the major product is formed according to anti-Markovnikov's rule.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
To solve this question, first, we have to know about the anti-Markownikoff rule.
Anti-Markovnikov's rule: When a polar reagent such as hydrogen halide reacts with an asymmetrical alkene in presence of peroxide, an addition reaction takes place. The negative part of the polar reagent is added to the carbon bearing a higher number of the hydrogen atom and also the positive part is added to the carbon with less number of the hydrogen atom.
Here we have an alkene isobutene. The structure of isobutene is:
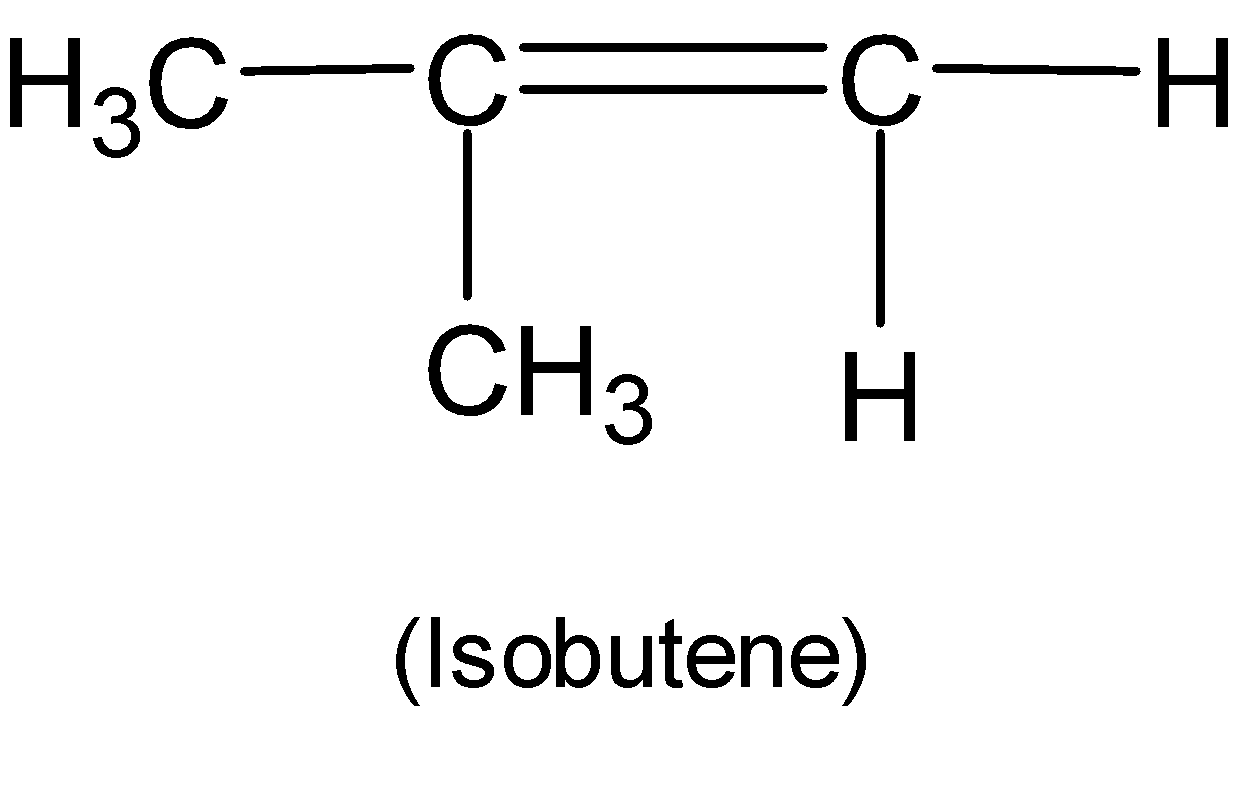
When isobutene reacts with hydrogen halide named hydrogen bromide (HBr) an addition reaction takes place. Therefore in the presence of peroxide anti-Markovnikov rule follows. After halohydrogenation isobutyl bromide $1-bromo-2-methylpropane$ is formed as the major product. Also, another product $2-bromo-2-methylpropane$ is formed with a lower percentage as a minor product. The overall reaction is shown below:
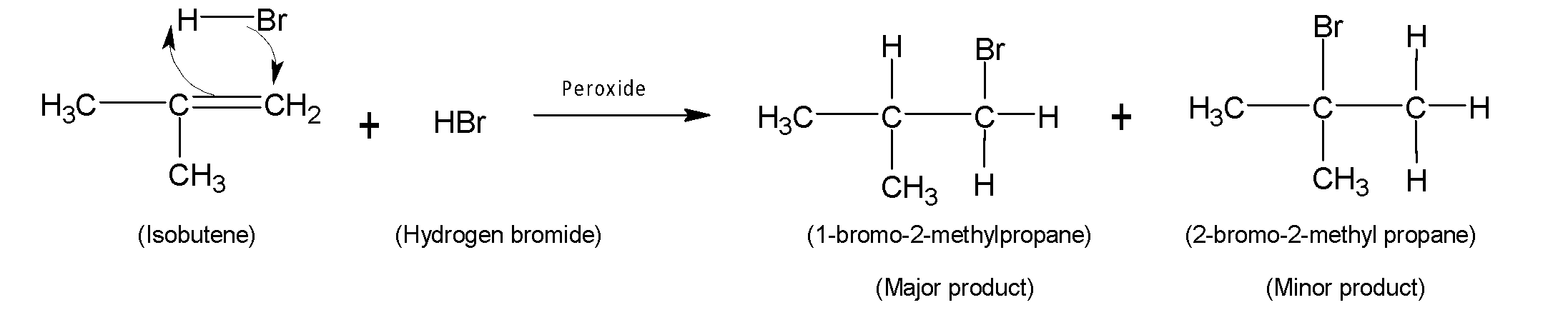
Therefore, the product is isobutyl bromide.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: When hydrogen halide is added to an asymmetric alkene, the negative halide ions get attached to the carbon with the least number of hydrogen atoms. These rules are known as Markovnikov’s rule. The products are produced from Electrophilic addition reactions of alkenes and alkynes following Markovnikov’s rule. These types of electrophilic addition reactions are regioselective in nature.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
To solve this question, first, we have to know about the anti-Markownikoff rule.
Anti-Markovnikov's rule: When a polar reagent such as hydrogen halide reacts with an asymmetrical alkene in presence of peroxide, an addition reaction takes place. The negative part of the polar reagent is added to the carbon bearing a higher number of the hydrogen atom and also the positive part is added to the carbon with less number of the hydrogen atom.
Here we have an alkene isobutene. The structure of isobutene is:

When isobutene reacts with hydrogen halide named hydrogen bromide (HBr) an addition reaction takes place. Therefore in the presence of peroxide anti-Markovnikov rule follows. After halohydrogenation isobutyl bromide $1-bromo-2-methylpropane$ is formed as the major product. Also, another product $2-bromo-2-methylpropane$ is formed with a lower percentage as a minor product. The overall reaction is shown below:

Therefore, the product is isobutyl bromide.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: When hydrogen halide is added to an asymmetric alkene, the negative halide ions get attached to the carbon with the least number of hydrogen atoms. These rules are known as Markovnikov’s rule. The products are produced from Electrophilic addition reactions of alkenes and alkynes following Markovnikov’s rule. These types of electrophilic addition reactions are regioselective in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE




