
In which option correct rate for step-2 is given for the different R-X
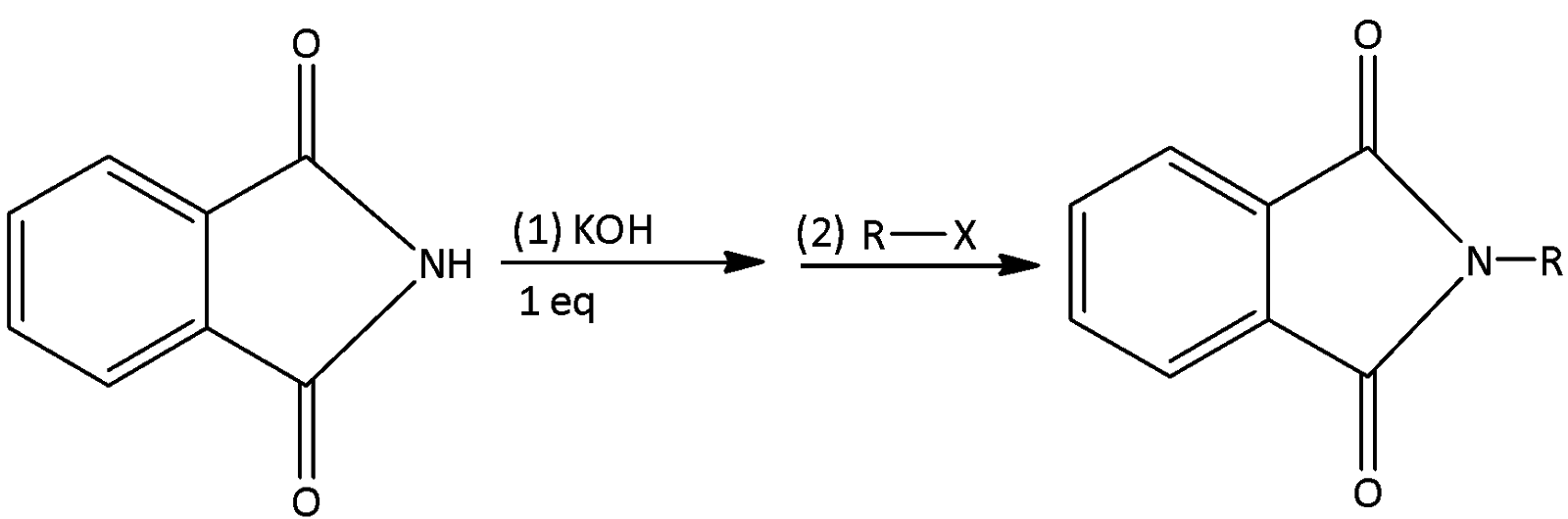
A.
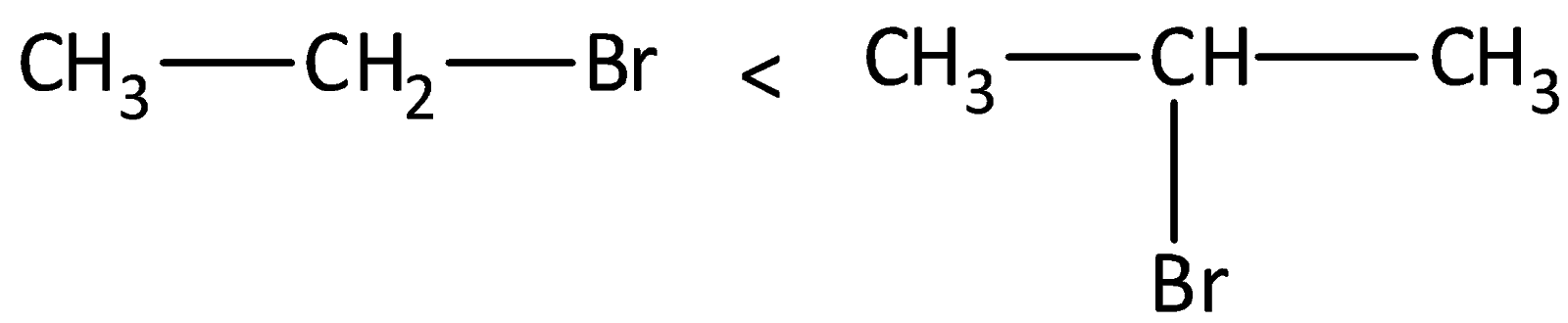
B. $Ph - Cl > C{H_3} - Cl$
C. $Ph - C{H_2} - Br > Ph - CH - C{H_3}$
D. $C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - Cl > C{H_3} - C{H_2}$

Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: We know that a carbocation is an ion that contains a positively charged carbon atom. In many organic reactions, carbocations are intermediates that are reactive. They are planar in structure and the trivalent carbon is$s{p^2}$ hybridized.
Complete step by step answer: We can determine stabilities of carbocations by measuring the amount of energy to form the carbocation by dissociation of the corresponding alkyl halide. The tertiary alkyl halide dissociates to form carbocations more easily than secondary or primary ones. The tri-substituted carbocations are found to be more stable than di-substituted and in turn are more stable than mono-substituted
We can destabilize a carbocation by an electron withdrawing group. Alkyl groups like methyl, ethyl are weak electron donating groups, and thereby stabilize the carbocations that are present nearby.
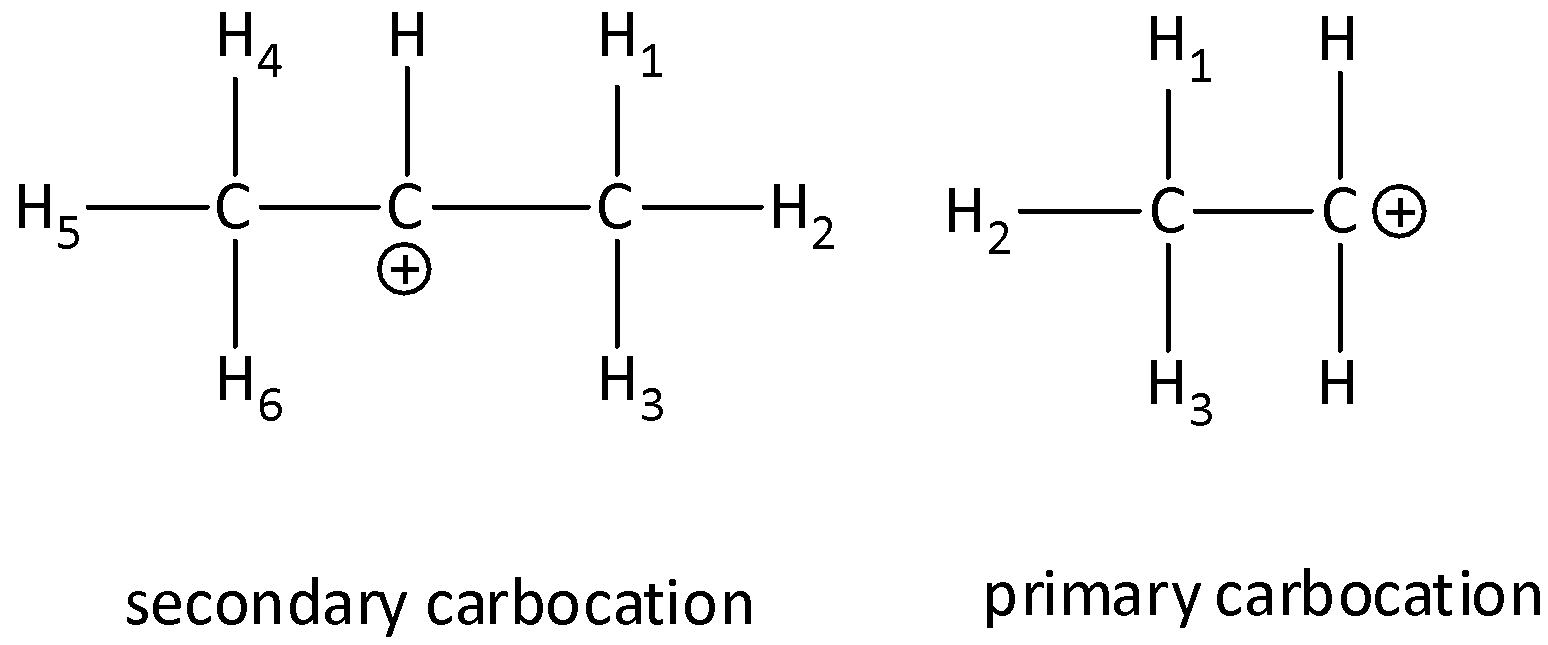
In the second step of the reaction, carbocation is formed as a reaction intermediate and the rate of reaction is dependent on the stability of the carbocation. We know that secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation due to the presence of more hyper conjugable hydrogen atoms present in the secondary carbocation than in primary carbocation. There are six bonds in secondary carbocation and three in primary carbocation.
The structures of secondary carbocation and primary carbocations are,
The completed chemical reaction is written as,
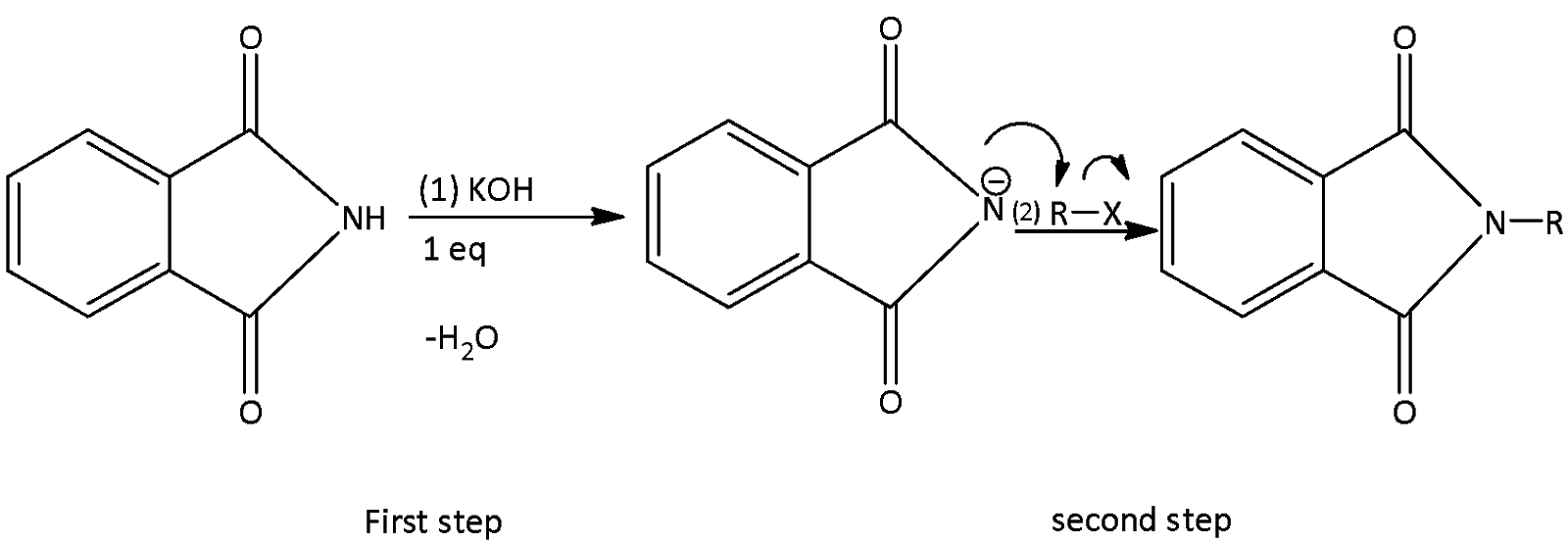
The correct rate for step-2 expressed for different $R - X$ is,
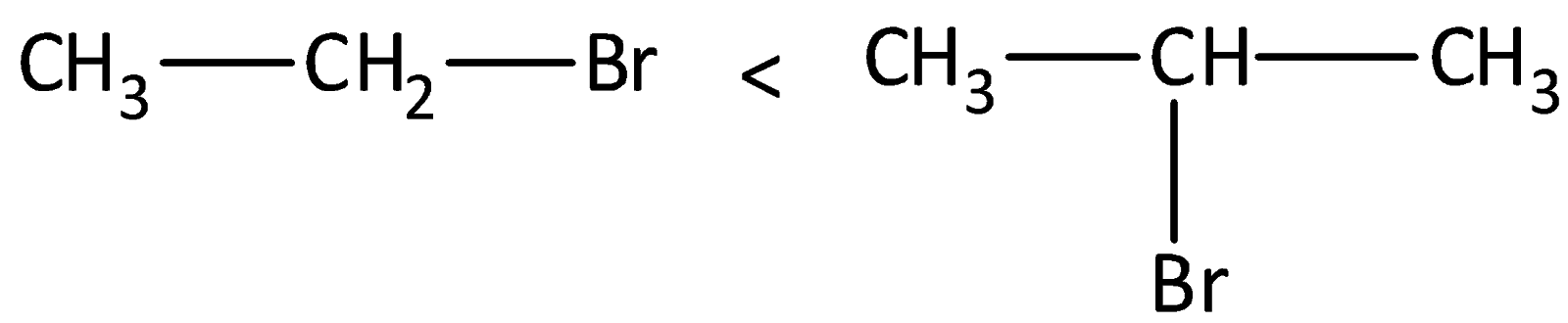
Therefore, option (A) is correct.
Note: Based on the coordination number of the charged carbon, carbocations is classified into two categories,
-Three in the carbenium ions
-Five in the carbonium ions.
We can give the simplest examples of carbocations are methenium, methanium and vinyl cations. Allylic carbocations similar to allylic radicals contain a double bond next to the electron-deficient carbon. The allyl cation is the simplest allylic carbocation. There is a huge difference in stability between carbocations and free radicals.
Complete step by step answer: We can determine stabilities of carbocations by measuring the amount of energy to form the carbocation by dissociation of the corresponding alkyl halide. The tertiary alkyl halide dissociates to form carbocations more easily than secondary or primary ones. The tri-substituted carbocations are found to be more stable than di-substituted and in turn are more stable than mono-substituted
We can destabilize a carbocation by an electron withdrawing group. Alkyl groups like methyl, ethyl are weak electron donating groups, and thereby stabilize the carbocations that are present nearby.
In the second step of the reaction, carbocation is formed as a reaction intermediate and the rate of reaction is dependent on the stability of the carbocation. We know that secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation due to the presence of more hyper conjugable hydrogen atoms present in the secondary carbocation than in primary carbocation. There are six bonds in secondary carbocation and three in primary carbocation.
The structures of secondary carbocation and primary carbocations are,

The completed chemical reaction is written as,

The correct rate for step-2 expressed for different $R - X$ is,
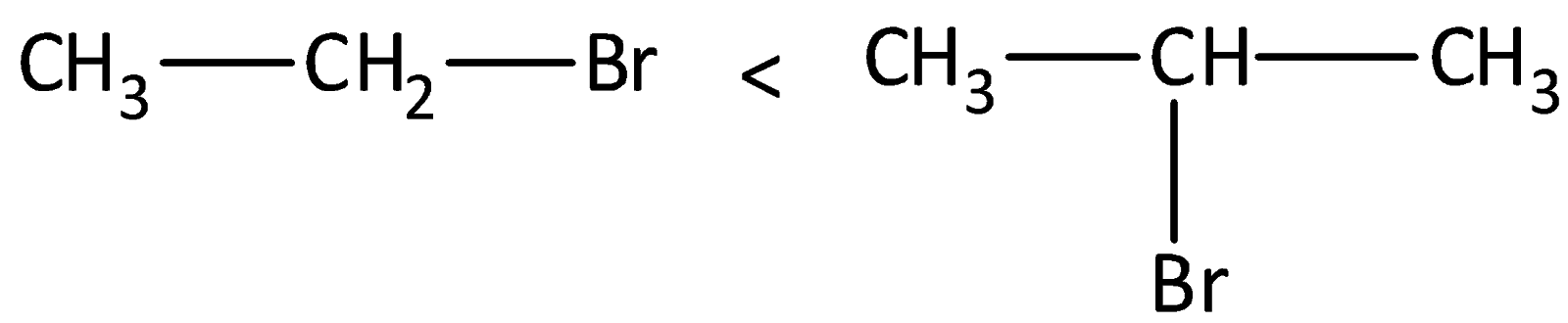
Therefore, option (A) is correct.
Note: Based on the coordination number of the charged carbon, carbocations is classified into two categories,
-Three in the carbenium ions
-Five in the carbonium ions.
We can give the simplest examples of carbocations are methenium, methanium and vinyl cations. Allylic carbocations similar to allylic radicals contain a double bond next to the electron-deficient carbon. The allyl cation is the simplest allylic carbocation. There is a huge difference in stability between carbocations and free radicals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




