
In which compound, benzene acts as a +M group?A
A.
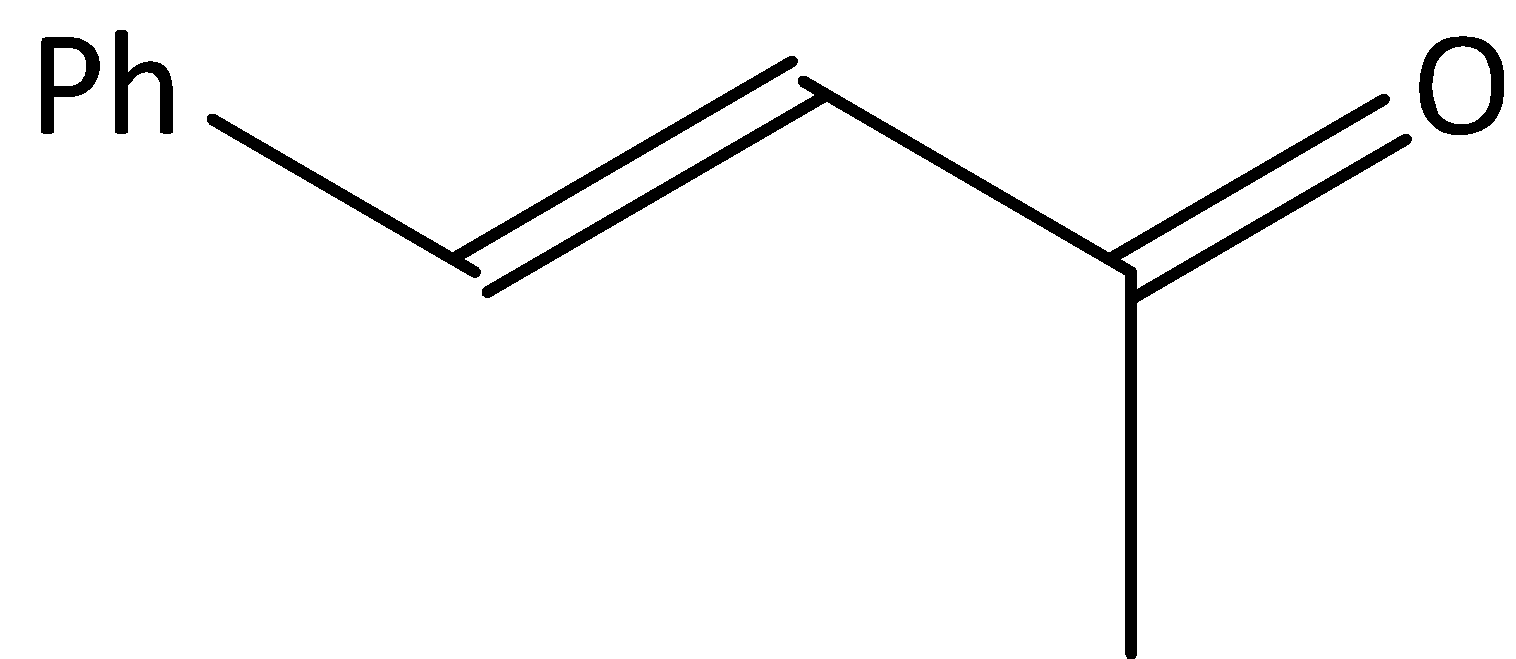
B. $Ph - CH = CH - CN$
C.
D. Both A and C


Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: We have to know that when the electrons or the pi electrons are moved from a particular group in the direction of a conjugate system, thus the electron density of the conjugated system is increased, and the effect is called as positive mesomeric effect (or) +M effect.
Complete step by step answer:
We can say mesomeric effect takes place when pi electrons are moved away from or in the direction of a substituent group present in a conjugated orbital system. Positive mesomeric effect and negative mesomeric effect are the two types of mesomeric effect.
We have to know that when the electrons or the pi electrons are moved from a particular group in the direction of a conjugate system, thus the electron density of the conjugated system is increased, and the effect is called a positive mesomeric effect (or) +M effect.
When the pi-bond electrons are moved from the conjugate system to a particular group thus reducing the electron density of the conjugated system, then the effect is called the negative mesomeric effect (or) –M effect.
For the +M effect, the group should contain either a lone pair of electrons or contain negative charge.
The +M effect provides negative charge to the conjugate system or the electron density rises on the conjugate system because of this.
In both A and C compounds, we know that benzene is in conjugation with double bonds of substituted groups. In both compounds electrons to the substituted groups are provided by the benzene.
Therefore benzene acts +M group is compound A and C.
Therefore, the option (D) is correct.
Note:
One should not confuse between mesomeric effect and inductive effect. The net electron flow from or to the substituent is also obtained by the inductive effect. As a result of overlap of p-orbital, the mesomeric effect shows no effect on this inductive effect, as the inductive effect is related with the electronegativity of the atoms and their molecular topology.
We can give the +M effect order as,
$ - {O^ - } > - N{H_2} > - NHR > - OR > - NHCOR > - OCOR > - Ph > - F > - Cl > - Br > - I$
We can give the -M effect order as,
$ - N{O_2} > - CN > - CHO > - C = O > - COOCOR > - COOR > - COOH > - CON{H_2} > - CO{O^ - }$
Complete step by step answer:
We can say mesomeric effect takes place when pi electrons are moved away from or in the direction of a substituent group present in a conjugated orbital system. Positive mesomeric effect and negative mesomeric effect are the two types of mesomeric effect.
We have to know that when the electrons or the pi electrons are moved from a particular group in the direction of a conjugate system, thus the electron density of the conjugated system is increased, and the effect is called a positive mesomeric effect (or) +M effect.
When the pi-bond electrons are moved from the conjugate system to a particular group thus reducing the electron density of the conjugated system, then the effect is called the negative mesomeric effect (or) –M effect.
For the +M effect, the group should contain either a lone pair of electrons or contain negative charge.
The +M effect provides negative charge to the conjugate system or the electron density rises on the conjugate system because of this.
In both A and C compounds, we know that benzene is in conjugation with double bonds of substituted groups. In both compounds electrons to the substituted groups are provided by the benzene.
Therefore benzene acts +M group is compound A and C.
Therefore, the option (D) is correct.
Note:
One should not confuse between mesomeric effect and inductive effect. The net electron flow from or to the substituent is also obtained by the inductive effect. As a result of overlap of p-orbital, the mesomeric effect shows no effect on this inductive effect, as the inductive effect is related with the electronegativity of the atoms and their molecular topology.
We can give the +M effect order as,
$ - {O^ - } > - N{H_2} > - NHR > - OR > - NHCOR > - OCOR > - Ph > - F > - Cl > - Br > - I$
We can give the -M effect order as,
$ - N{O_2} > - CN > - CHO > - C = O > - COOCOR > - COOR > - COOH > - CON{H_2} > - CO{O^ - }$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




