
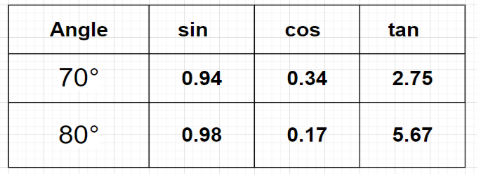
In triangle ABC, AB=5 cm, $\angle {\text{A}} = {80^0}$ and $\angle {\text{B}} = {70^0}$. Calculate the radius of the circumcircle and length of the other two sides. (Necessary values can be taken from the following table)

Answer
618.9k+ views
Hint: Here, we will proceed by using the property of the triangle i.e., the sum of all the interior angles of any triangle is always \[{180^0}\] and then we will use the formula of extended sine rule i.e., \[\dfrac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{\sin {\text{C}}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{\sin {\text{A}}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{\sin {\text{B}}}} = 2{\text{R}}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
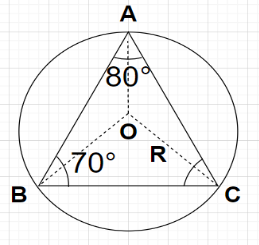
Given, in triangle ABC, AB=5 cm, $\angle {\text{A}} = {80^0}$ and $\angle {\text{B}} = {70^0}$
Let R cm be the radius of the circumcircle of the triangle ABC and O be the centre of this circumcircle.
i.e., OA=OB=OC=R cm
As we know that the sum of all the interior angles of any triangle is always \[{180^0}\]
For triangle ABC,
$
\angle {\text{A}} + \angle {\text{B}} + \angle {\text{C}} = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow {80^0} + {70^0} + \angle {\text{C}} = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow \angle {\text{C}} = {180^0} - \left( {{{80}^0} + {{70}^0}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \angle {\text{C}} = {180^0} - {150^0} \\
\Rightarrow \angle {\text{C}} = {30^0} \\
$
Also we know that according to the extended sine rule
\[\dfrac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{\sin {\text{C}}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{\sin {\text{A}}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{\sin {\text{B}}}} = 2{\text{R }} \to {\text{(1)}}\]
By substituting the known values, equation (1) becomes
\[\dfrac{5}{{\sin {{30}^0}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{\sin {{80}^0}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{\sin {{70}^0}}} = 2{\text{R }} \to {\text{(2)}}\]
According to the given table, \[\sin {80^0} = 0.98\] and \[\sin {70^0} = 0.94\]
According to the general trigonometric table, \[\sin {30^0} = 0.5\]
Now, substitute the above values in equation (2), we get
\[
\dfrac{5}{{0.5}} = \dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{0.98}} = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{0.94}} = 2{\text{R}} \\
\Rightarrow 10 = \dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{0.98}} = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{0.94}} = 2{\text{R }} \to {\text{(3)}} \\
\]
By equation (3), we can write
\[
10 = 2{\text{R}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{R}} = \dfrac{{10}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{R}} = 5{\text{ cm}} \\
\]
So, the radius of the circumcircle of the triangle ABC is equal to 5 cm.
By equation (3), we can write
\[
10 = \dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{0.98}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{BC}} = 0.98 \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{BC}} = 9.8{\text{ cm}} \\
\]
So, the length of side BC of the triangle ABC is equal to 9.8 cm.
By equation (3), we can write
\[
10 = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{0.94}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{AC}} = 10 \times 0.94 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{AC}} = 9.4{\text{ cm}} \\
\]
So, the length of side AC of the triangle ABC is equal to 9.4 cm.
Note: In this particular problem, with the help of the given table we are only using the values of \[\sin {80^0} = 0.98\] and \[\sin {70^0} = 0.94\] whereas the other values are not used for the evaluation of the parameters asked. Here, we have used the extended sine rule because we know the values of all the interior angles and the length of one side.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Given, in triangle ABC, AB=5 cm, $\angle {\text{A}} = {80^0}$ and $\angle {\text{B}} = {70^0}$
Let R cm be the radius of the circumcircle of the triangle ABC and O be the centre of this circumcircle.
i.e., OA=OB=OC=R cm
As we know that the sum of all the interior angles of any triangle is always \[{180^0}\]
For triangle ABC,
$
\angle {\text{A}} + \angle {\text{B}} + \angle {\text{C}} = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow {80^0} + {70^0} + \angle {\text{C}} = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow \angle {\text{C}} = {180^0} - \left( {{{80}^0} + {{70}^0}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \angle {\text{C}} = {180^0} - {150^0} \\
\Rightarrow \angle {\text{C}} = {30^0} \\
$
Also we know that according to the extended sine rule
\[\dfrac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{\sin {\text{C}}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{\sin {\text{A}}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{\sin {\text{B}}}} = 2{\text{R }} \to {\text{(1)}}\]
By substituting the known values, equation (1) becomes
\[\dfrac{5}{{\sin {{30}^0}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{\sin {{80}^0}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{\sin {{70}^0}}} = 2{\text{R }} \to {\text{(2)}}\]
According to the given table, \[\sin {80^0} = 0.98\] and \[\sin {70^0} = 0.94\]
According to the general trigonometric table, \[\sin {30^0} = 0.5\]
Now, substitute the above values in equation (2), we get
\[
\dfrac{5}{{0.5}} = \dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{0.98}} = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{0.94}} = 2{\text{R}} \\
\Rightarrow 10 = \dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{0.98}} = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{0.94}} = 2{\text{R }} \to {\text{(3)}} \\
\]
By equation (3), we can write
\[
10 = 2{\text{R}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{R}} = \dfrac{{10}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{R}} = 5{\text{ cm}} \\
\]
So, the radius of the circumcircle of the triangle ABC is equal to 5 cm.
By equation (3), we can write
\[
10 = \dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{0.98}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{BC}} = 0.98 \times 10 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{BC}} = 9.8{\text{ cm}} \\
\]
So, the length of side BC of the triangle ABC is equal to 9.8 cm.
By equation (3), we can write
\[
10 = \dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{0.94}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{AC}} = 10 \times 0.94 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{AC}} = 9.4{\text{ cm}} \\
\]
So, the length of side AC of the triangle ABC is equal to 9.4 cm.
Note: In this particular problem, with the help of the given table we are only using the values of \[\sin {80^0} = 0.98\] and \[\sin {70^0} = 0.94\] whereas the other values are not used for the evaluation of the parameters asked. Here, we have used the extended sine rule because we know the values of all the interior angles and the length of one side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




